Guinea, West Africa: A Geographic Overview
Related Articles: Guinea, West Africa: A Geographic Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Guinea, West Africa: A Geographic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Guinea, West Africa: A Geographic Overview
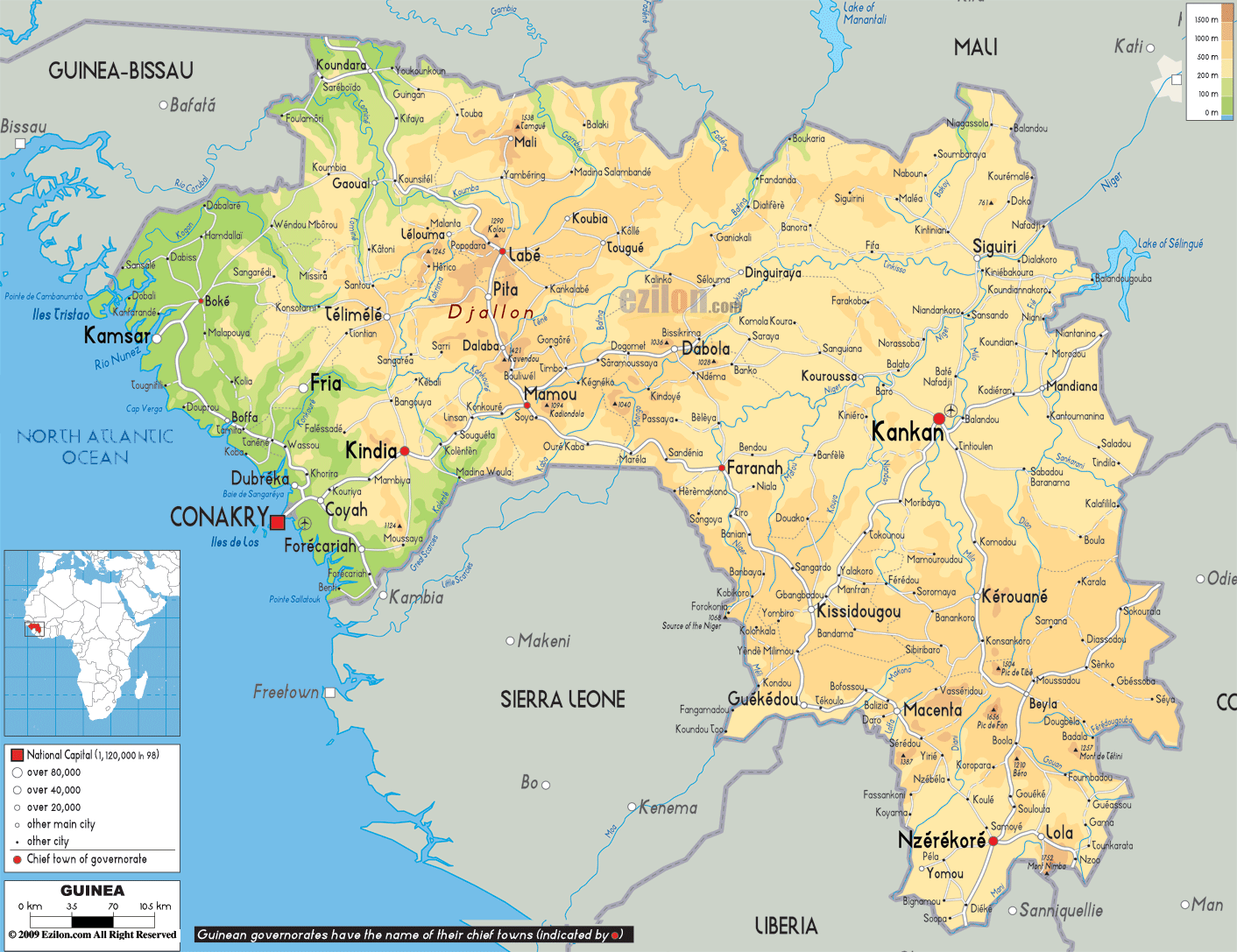
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a West African nation nestled along the Atlantic coast. Its diverse topography, rich history, and vibrant culture make it a captivating destination for exploration and study. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Guinea’s geography, highlighting its unique features and the significance of its location in the broader context of West Africa.
A Land of Contrasts: The Geography of Guinea
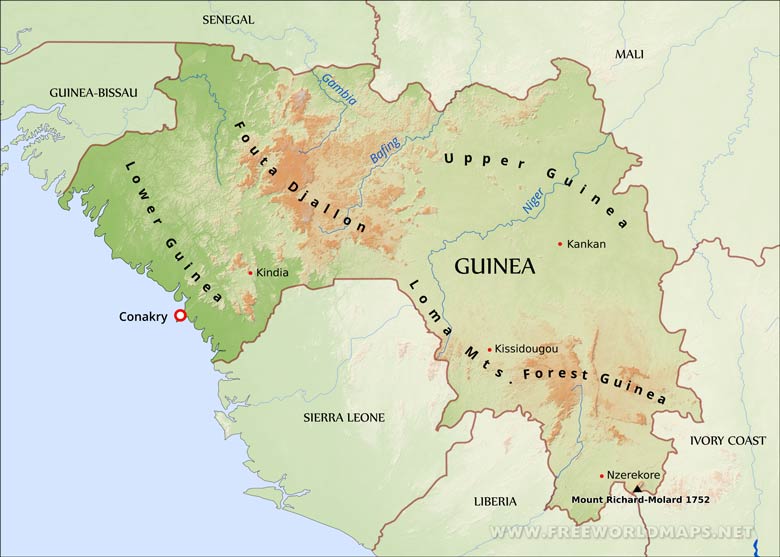
Guinea’s geography is characterized by striking contrasts. The country is divided into four distinct physiographic regions:
-
The Coastal Lowlands: This narrow strip along the Atlantic coast is home to the country’s major cities and harbors, including Conakry, the capital. The lowlands are characterized by fertile soils and mangrove swamps, providing a vital source of sustenance for the local population.
-
The Fouta Djallon Highlands: This mountainous region, also known as the Guinean Highlands, forms the heart of the country. The Fouta Djallon, with its rolling hills and plateaus, is a crucial watershed, supplying water to the major rivers of Guinea and neighboring countries. Its rugged terrain and high elevation create a distinct microclimate, contributing to the region’s unique biodiversity.
-
The Guinean Savanna: This vast expanse of grasslands and woodlands stretches inland from the highlands. The savanna is characterized by a distinct dry season and a wet season, making it suitable for agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice, millet, and sorghum.
-
The Upper Niger Basin: This region lies in the southeast of the country, bordering Mali and Côte d’Ivoire. The Niger River, a lifeline for the region, flows through the basin, providing vital irrigation for agriculture and serving as a vital transportation route.
The Significance of Guinea’s Geography
Guinea’s geographic location and diverse landscape play a crucial role in shaping its economic, social, and political landscape.
-
Resource Rich: Guinea is endowed with abundant natural resources, including bauxite, iron ore, gold, diamonds, and hydropower potential. These resources offer significant economic opportunities, but their exploitation also poses environmental challenges.
-
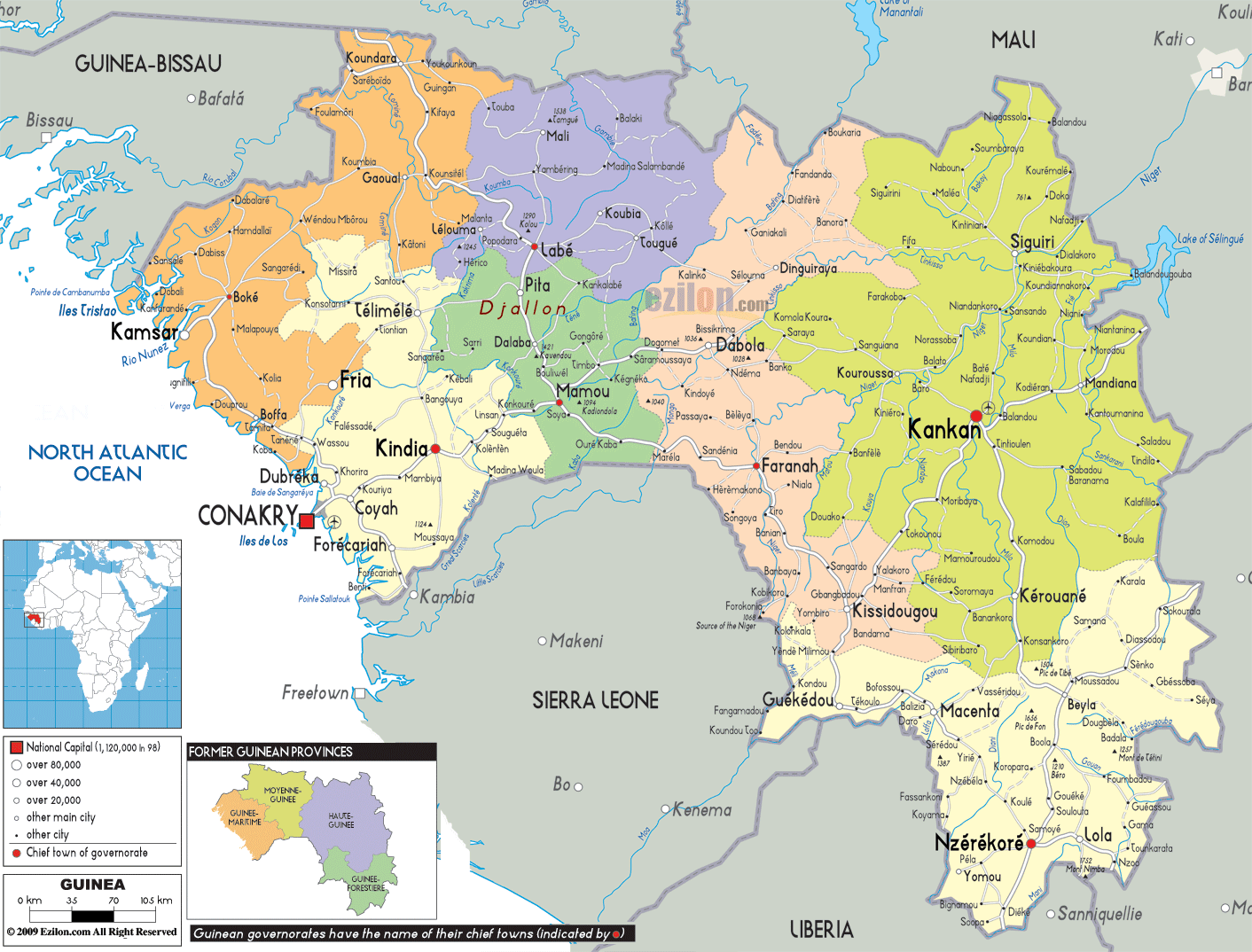
Strategic Location: Guinea’s position on the Atlantic coast and its proximity to other West African countries make it a key transportation hub. Its ports and waterways facilitate trade and connectivity within the region, contributing to economic development and regional integration.
-
Biodiversity Hotspot: Guinea’s diverse ecosystems support a rich array of flora and fauna, making it a biodiversity hotspot. The country is home to numerous national parks and protected areas, safeguarding its unique natural heritage.
-
Challenges of Terrain: Guinea’s rugged terrain, particularly in the Fouta Djallon, presents significant challenges for infrastructure development and transportation. The mountainous landscape also contributes to the country’s vulnerability to natural disasters such as landslides and floods.
Guinea’s Place in West Africa
Guinea is a vital member of the West African community, contributing to regional cooperation and integration. Its involvement in regional organizations such as ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States) and the Mano River Union promotes economic growth, security, and stability in the region.
FAQs about Guinea
1. What is the population of Guinea?
Guinea’s population is estimated to be around 13.5 million people, making it one of the most populous countries in West Africa.
2. What is the capital of Guinea?
The capital of Guinea is Conakry, located on the Atlantic coast.
3. What are the major languages spoken in Guinea?
The official language of Guinea is French. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken, including Malinke, Fulani, and Susu.
4. What are the main religions practiced in Guinea?
The majority of Guinea’s population is Muslim, with a significant minority adhering to traditional African religions and Christianity.
5. What are the major industries in Guinea?
Guinea’s economy is largely dependent on mining, particularly bauxite extraction. Other key industries include agriculture, fishing, and forestry.
Tips for Visiting Guinea
- Visa requirements: Ensure you have the necessary visa documentation before traveling to Guinea.
- Health precautions: Consult a healthcare professional about recommended vaccinations and health precautions.
- Cultural sensitivity: Be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Language barriers: Learning a few basic phrases in French or an indigenous language can be helpful.
- Safety and security: Stay aware of your surroundings and exercise caution in unfamiliar areas.
Conclusion
Guinea, with its diverse geography, rich resources, and vibrant culture, is a country of immense potential. Its strategic location and its role in regional cooperation make it a vital player in the development of West Africa. Understanding Guinea’s geography and its unique features provides valuable insights into the country’s history, society, and its place in the broader context of West Africa.

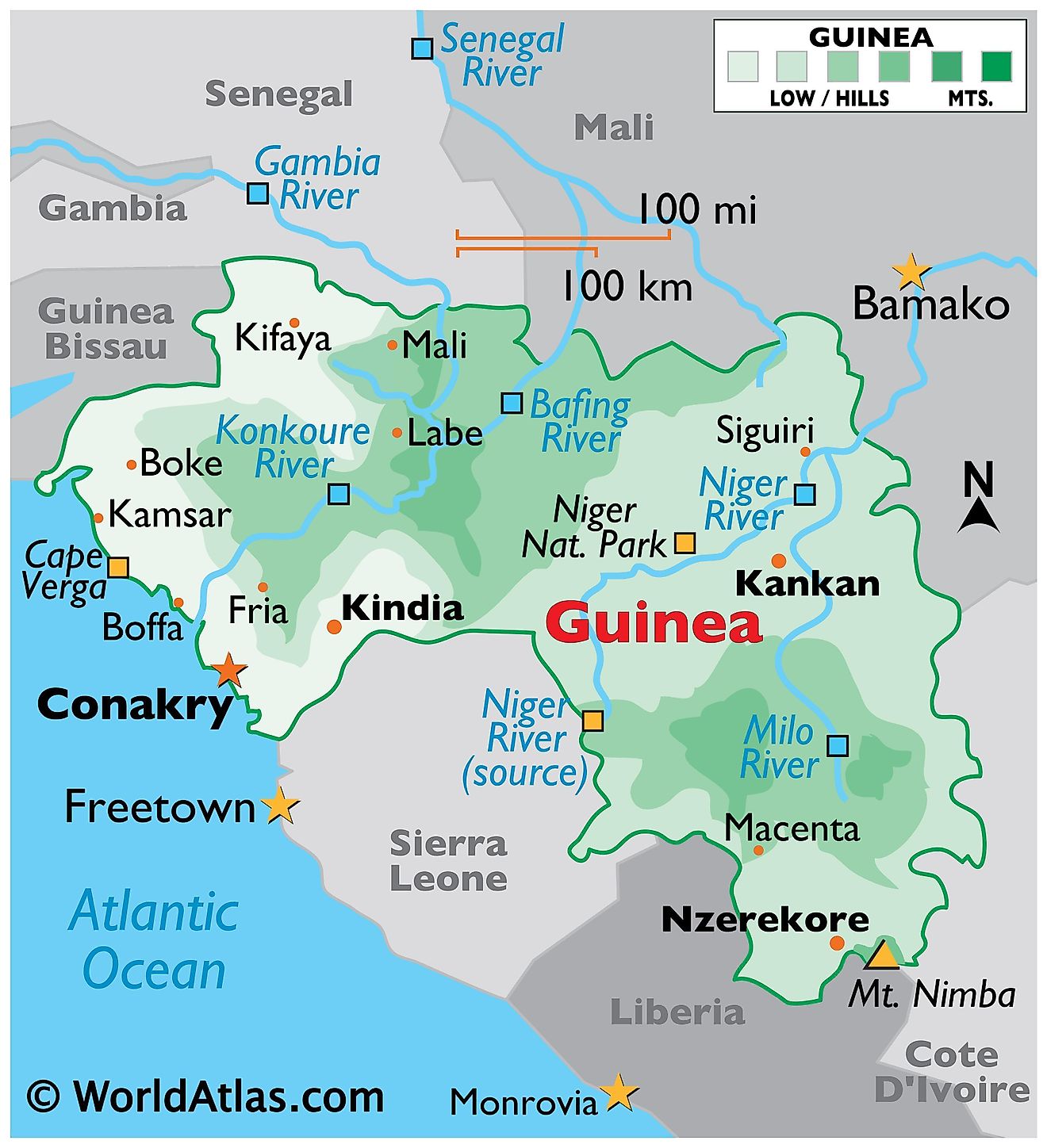


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Guinea, West Africa: A Geographic Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!