A Journey Through Nevada’s Landscape: Unveiling the Secrets of Topographic Maps
Related Articles: A Journey Through Nevada’s Landscape: Unveiling the Secrets of Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Nevada’s Landscape: Unveiling the Secrets of Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Nevada’s Landscape: Unveiling the Secrets of Topographic Maps
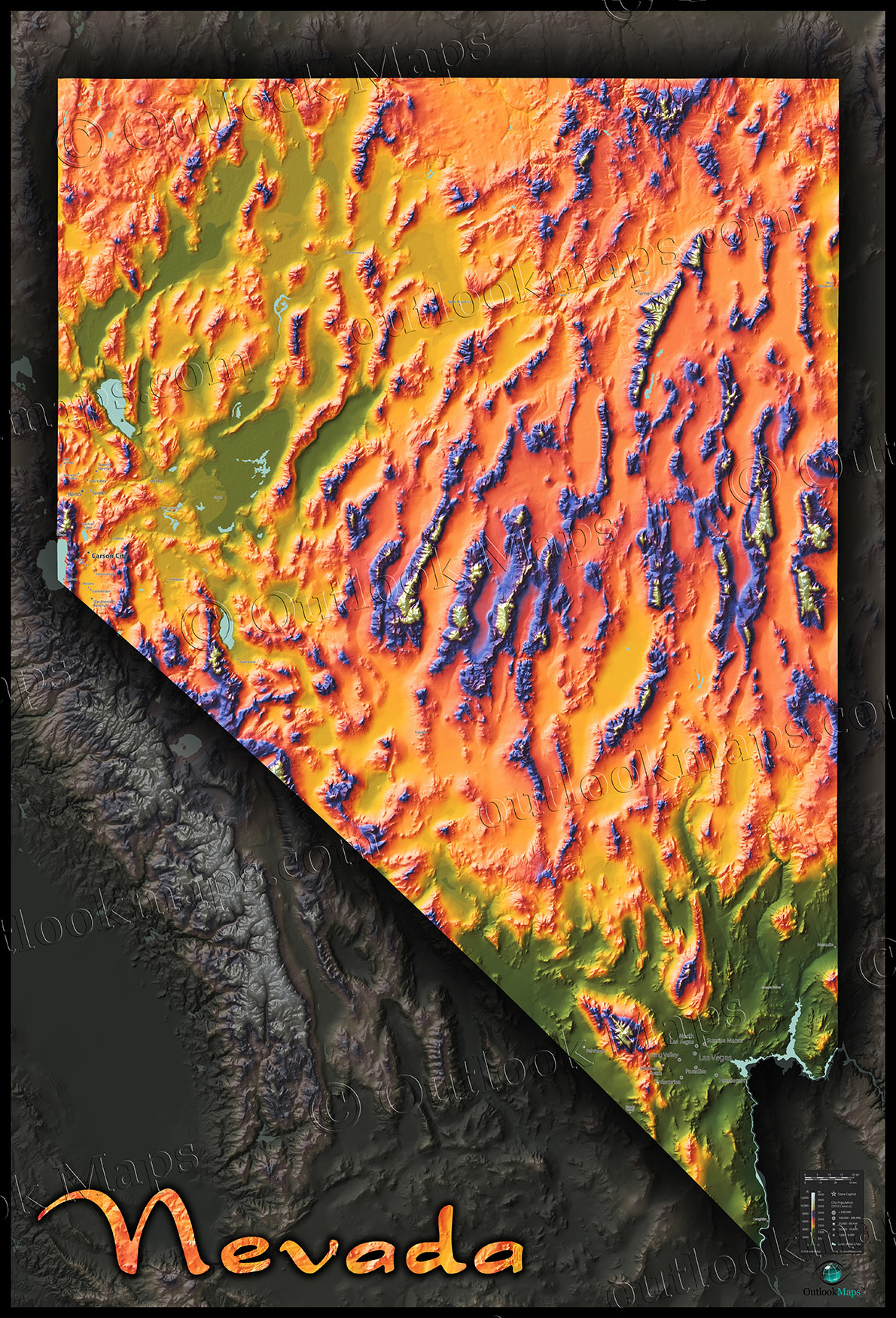
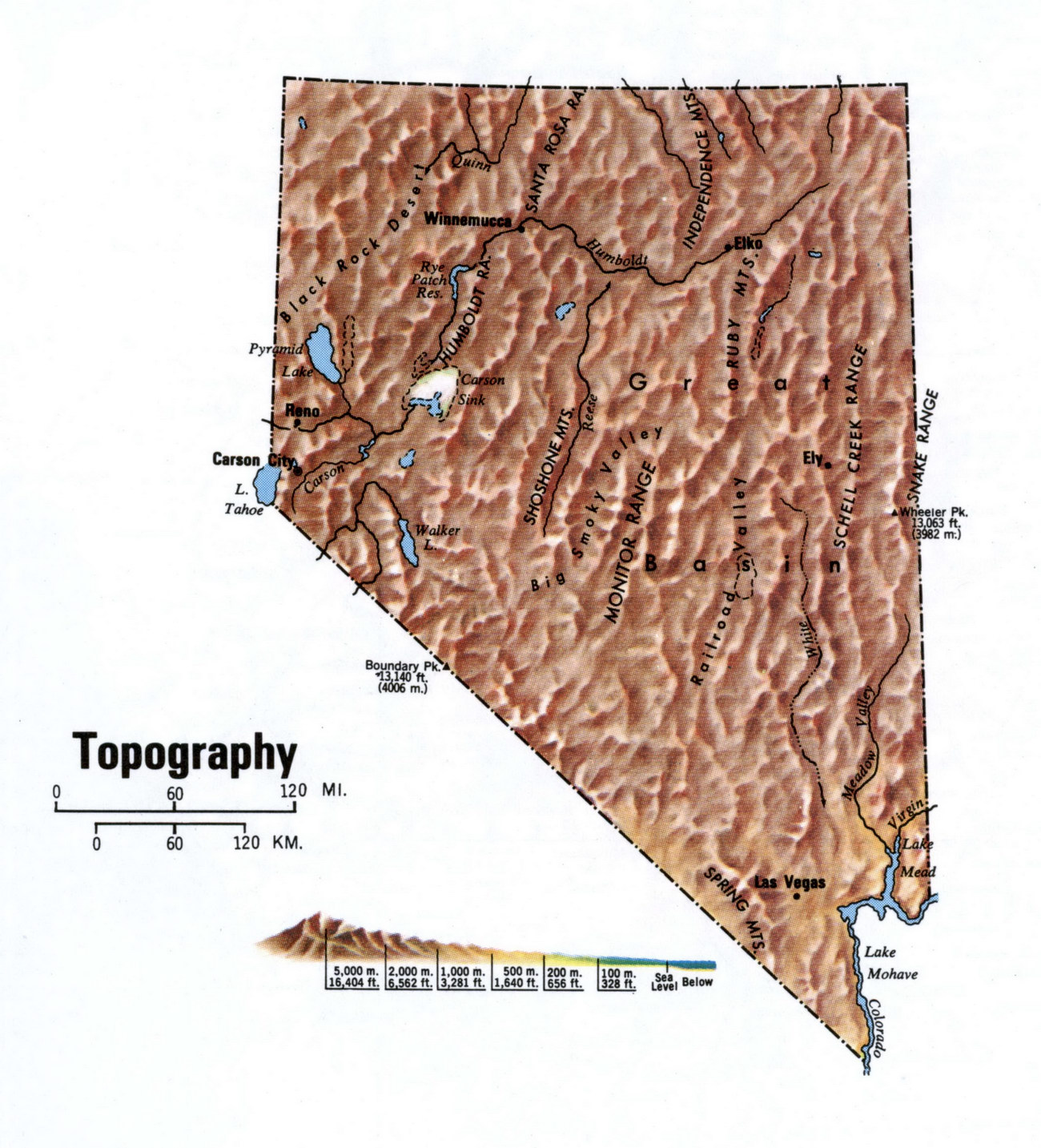
Nevada, the Silver State, is a landscape of stark contrasts. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Nevada to the vast, arid expanse of the Mojave Desert, the state’s topography is a captivating tapestry of elevation, relief, and geological history. Understanding this intricate web of landforms is crucial for various endeavors, from scientific research and resource management to recreational pursuits and urban planning. Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, offer a powerful tool for unlocking the secrets of Nevada’s landscape.
Understanding the Language of Topographic Maps
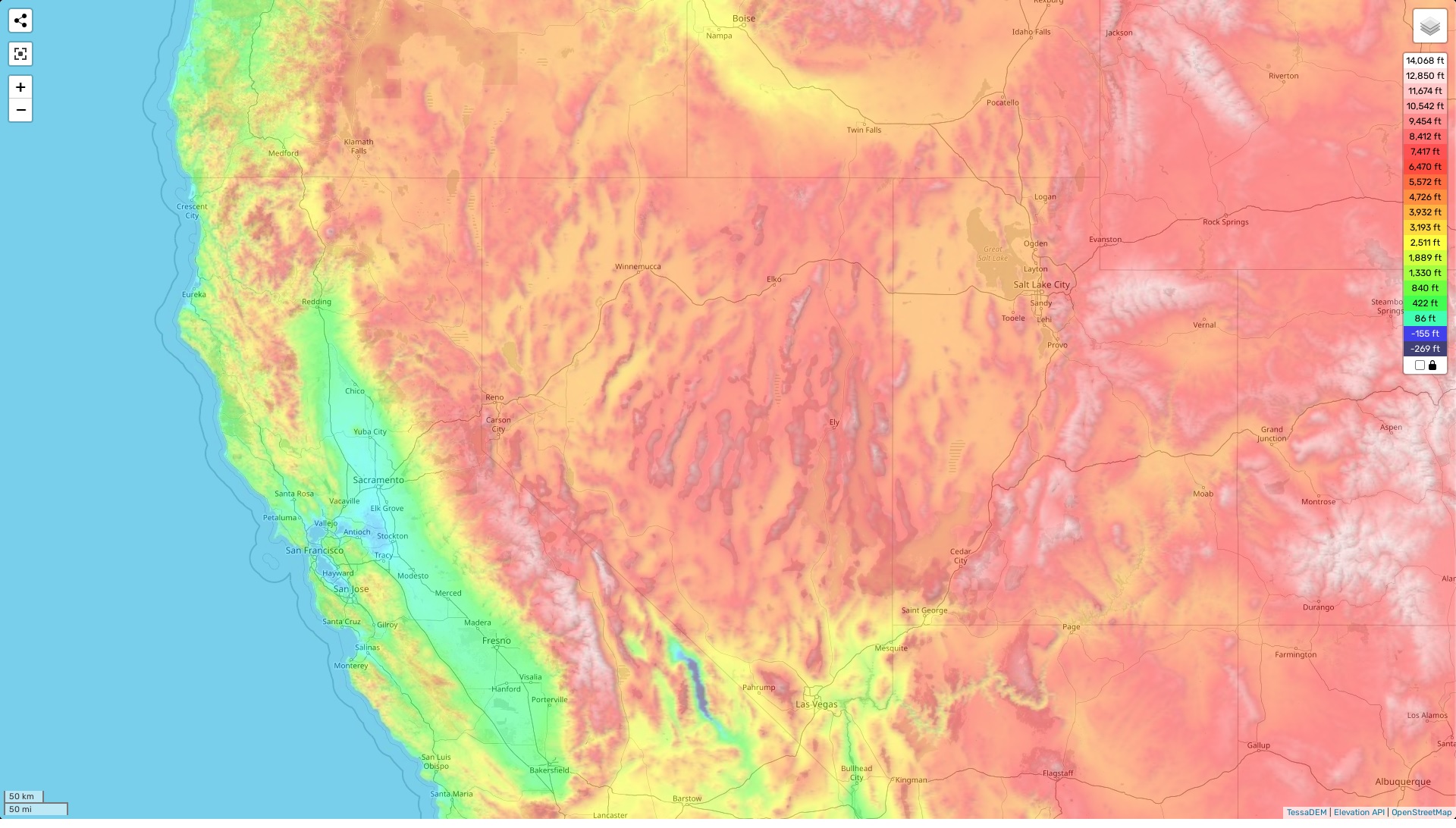
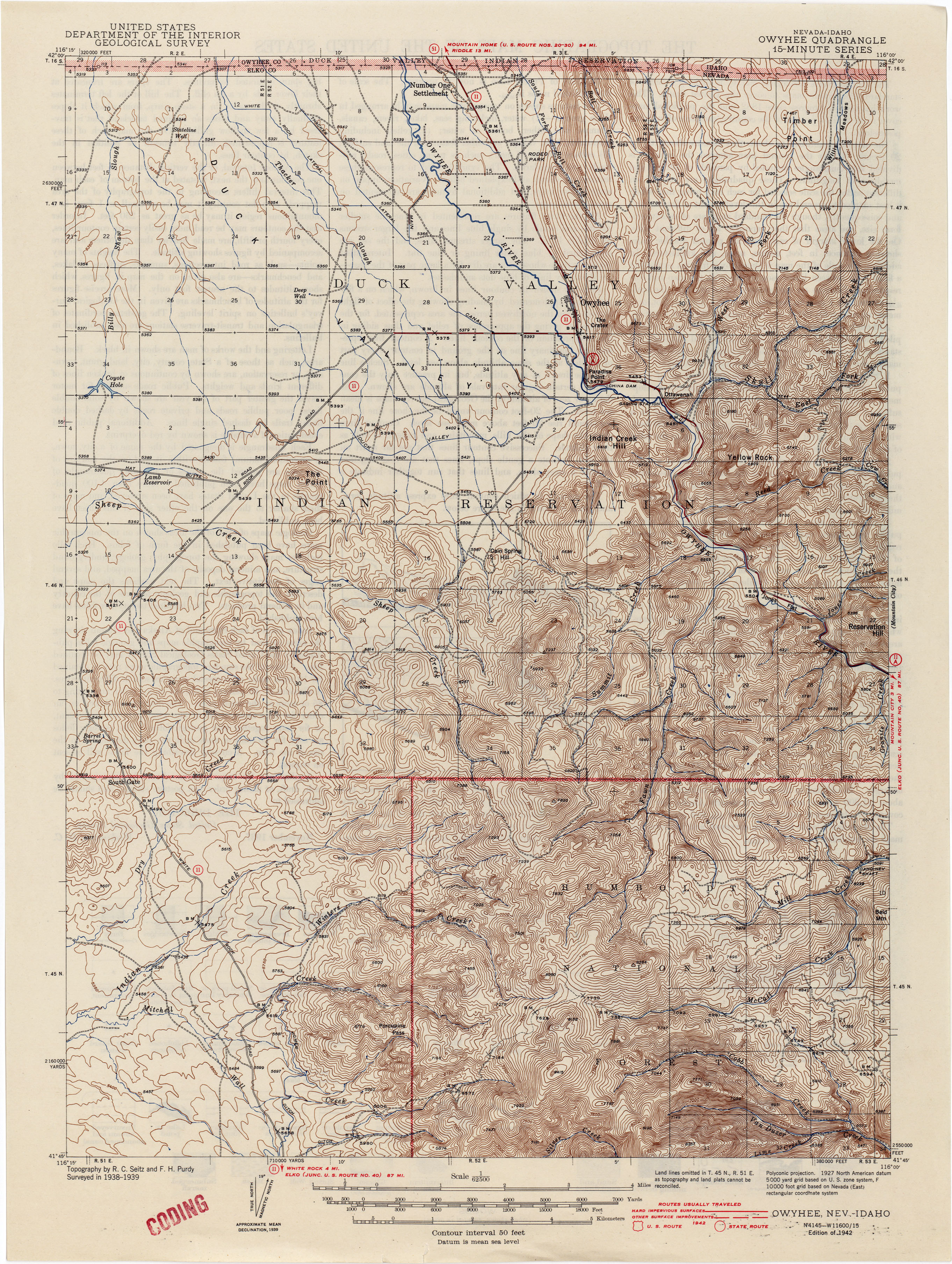
Topographic maps are not simply static images; they are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing both its horizontal and vertical dimensions. Contour lines, the hallmark of these maps, are lines connecting points of equal elevation. These lines, like the rings of a tree trunk, reveal the contours of the land, tracing the rise and fall of hills, valleys, and plateaus. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
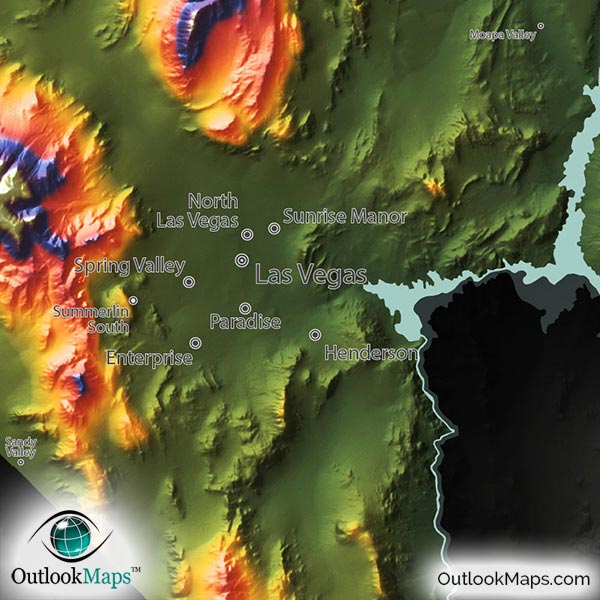
Beyond contour lines, topographic maps utilize a rich array of symbols to depict diverse features. Roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation are all represented with specific icons, providing a comprehensive overview of the landscape. The use of color also plays a vital role, with different hues representing varying elevations, allowing for quick visual interpretation of terrain changes.
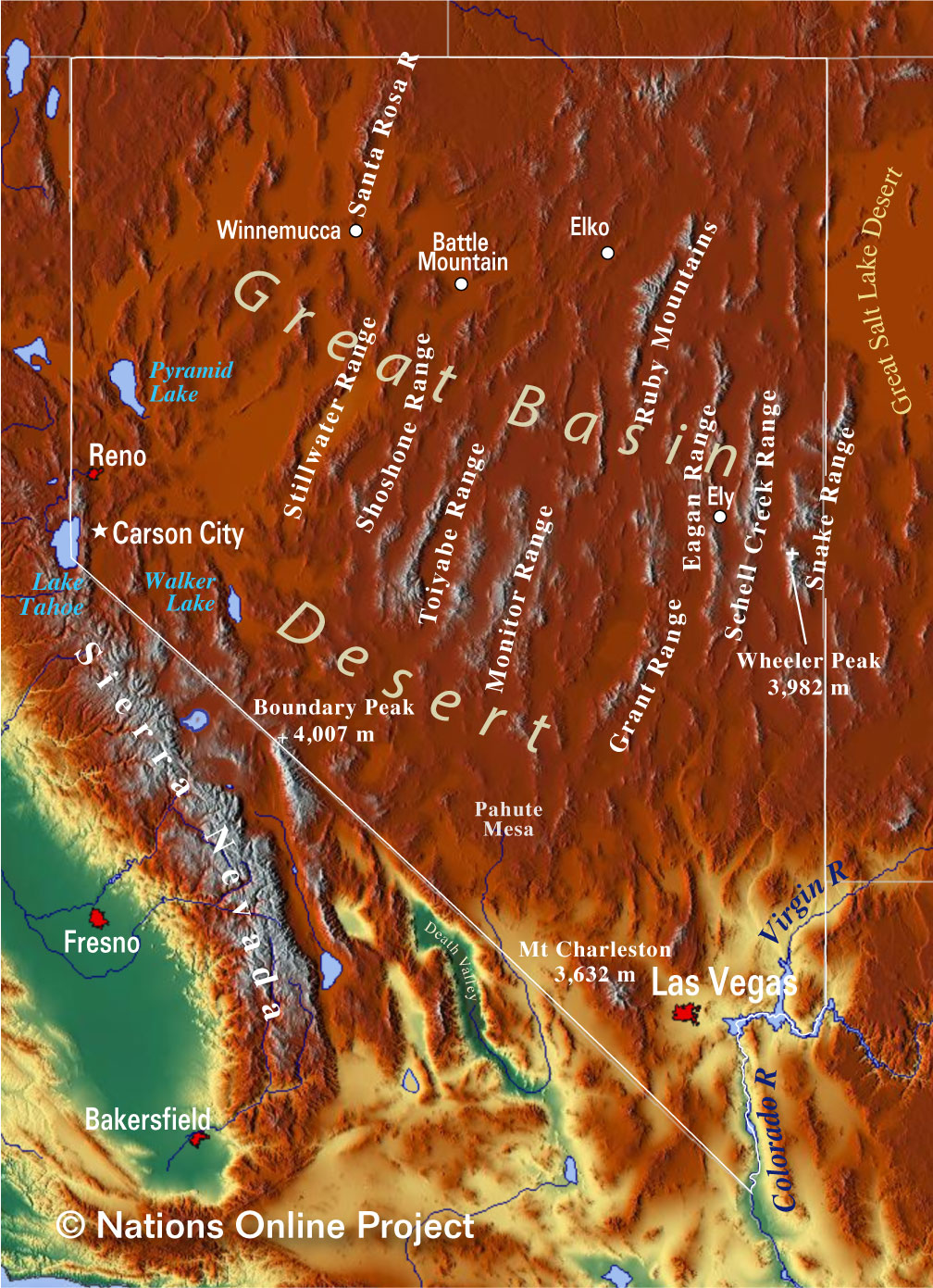
Nevada’s Topography: A Story Told Through Contour Lines
The topographic map of Nevada is a testament to the state’s geological history and diverse ecosystems. The Sierra Nevada, a dominant feature on the western border, is represented by densely packed contour lines, showcasing its dramatic elevation changes. The majestic peaks, including Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States, stand out as sharp, pointed peaks on the map.
Moving east, the landscape transitions to the Great Basin, a vast, arid region characterized by numerous mountain ranges and valleys. The topographic map reveals the intricate network of fault lines that have shaped this region, creating its distinctive topography. The Basin and Range province, with its alternating mountain ranges and valleys, is a fascinating example of tectonic forces at work, vividly depicted in the map’s contour lines.
The Mojave Desert, a vast expanse of low-lying terrain, is represented by widely spaced contour lines, indicating its generally flat topography. However, the map also highlights the presence of isolated mountain ranges and canyons, showcasing the desert’s hidden complexities.
The Importance of Topographic Maps in Nevada
The topographic map of Nevada serves as a crucial tool for various sectors, playing a vital role in:
1. Resource Management: The state’s mineral wealth, including gold, silver, and lithium, is concentrated in specific geological formations. Topographic maps help geologists identify promising areas for exploration, ensuring efficient and responsible resource extraction.
2. Water Management: Nevada, a semi-arid state, faces significant challenges in water resource management. Topographic maps help identify watersheds, assess water flow patterns, and plan for efficient water distribution systems.
3. Infrastructure Development: From roads and highways to power lines and pipelines, infrastructure projects require careful planning and environmental considerations. Topographic maps provide vital information about terrain, elevation, and potential hazards, enabling engineers to design resilient and sustainable infrastructure.
4. Emergency Response: During natural disasters like wildfires or earthquakes, topographic maps are essential for first responders. They provide detailed information about terrain, access routes, and potential hazards, facilitating rapid and efficient rescue operations.
5. Outdoor Recreation: Nevada is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts, attracting hikers, climbers, and off-road adventurers. Topographic maps are indispensable for planning trips, identifying trails, and navigating challenging terrain.
6. Urban Planning: As Nevada’s population grows, urban planning becomes increasingly crucial. Topographic maps help identify suitable locations for development, assess potential hazards like flooding or landslides, and ensure sustainable urban growth.
FAQs about Topographic Maps of Nevada
Q: How can I obtain a topographic map of Nevada?
A: Topographic maps of Nevada are available from various sources, including the United States Geological Survey (USGS), online mapping services like Google Maps, and specialized map retailers.
Q: What is the scale of a topographic map?
A: The scale of a topographic map refers to the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Different maps have different scales, with larger scales providing more detail.
Q: How can I read contour lines on a topographic map?
A: Contour lines represent points of equal elevation. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline. Closed contour lines indicate hills or peaks, while depressions are often represented by hachure marks.
Q: Are there any online resources for learning about topographic maps?
A: Yes, numerous online resources offer tutorials and interactive exercises for learning how to read and interpret topographic maps. The USGS website and other educational institutions provide comprehensive resources for map literacy.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps of Nevada
1. Choose the Right Scale: Select a map scale that provides the level of detail needed for your specific purpose. For detailed hiking trails, a larger scale map is preferable, while a smaller scale map may be suitable for planning a road trip.
2. Understand the Map Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the various symbols used on topographic maps to represent features like roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation.
3. Use a Compass and Altimeter: For accurate navigation, especially in remote areas, a compass and altimeter are essential tools to complement your topographic map.
4. Plan Your Route Carefully: Before embarking on any outdoor adventure, carefully plan your route, considering elevation changes, potential hazards, and emergency procedures.
5. Respect the Environment: When exploring Nevada’s landscapes, be mindful of the fragile ecosystems and practice Leave No Trace principles to minimize your impact.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Nevada is more than just a collection of lines and symbols; it is a window into the state’s complex and captivating landscape. By understanding the language of contour lines and map symbols, we can unlock the secrets of Nevada’s diverse topography, appreciate its geological history, and make informed decisions for resource management, infrastructure development, and outdoor recreation. The topographic map, in its intricate detail, serves as a powerful tool for understanding and appreciating the beauty and complexity of Nevada’s natural environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Nevada’s Landscape: Unveiling the Secrets of Topographic Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!