A Verdant Tapestry: Exploring the Global Distribution of Rainforests
Related Articles: A Verdant Tapestry: Exploring the Global Distribution of Rainforests
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Verdant Tapestry: Exploring the Global Distribution of Rainforests. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Verdant Tapestry: Exploring the Global Distribution of Rainforests

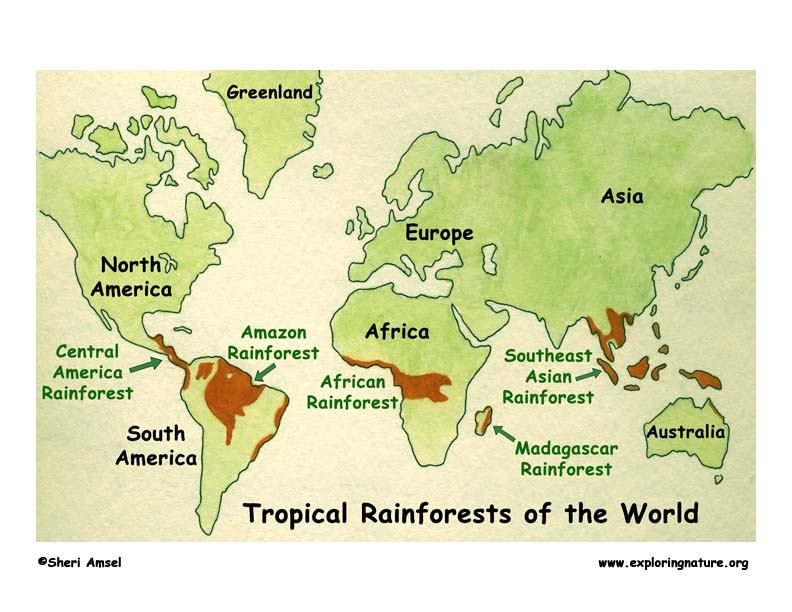
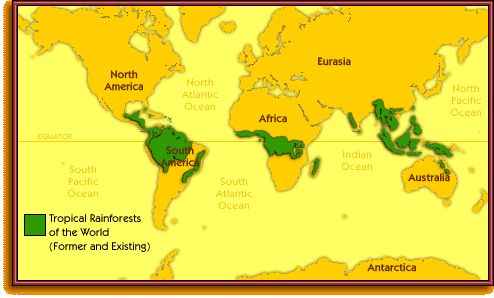
Rainforests, the emerald jewels of our planet, are vast, vibrant ecosystems teeming with life. These lush landscapes, characterized by high rainfall and year-round warmth, harbor an astonishing diversity of plant and animal species, playing a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate and providing essential resources for humankind. A global map of rainforests reveals their distribution, highlighting their significance for both the planet’s health and human well-being.
The Global Tapestry of Rainforests:
The world’s rainforests are not evenly distributed, but rather form distinct bands across the globe, primarily concentrated in the equatorial regions. These regions experience high levels of solar radiation, leading to consistent warmth and abundant rainfall. The major rainforest regions include:
-
Amazon Rainforest: This colossal expanse, spanning over 7 million square kilometers, covers parts of nine South American countries. It is the largest rainforest on Earth, home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species.
-
Congo Basin Rainforest: Located in Central Africa, the Congo Basin rainforest is the second largest in the world, covering over 2 million square kilometers. It is renowned for its dense canopy and rich biodiversity, harboring a vast array of primates, reptiles, and birds.
-
Southeast Asian Rainforest: This region encompasses rainforests across Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Myanmar. It is characterized by a high diversity of plant life, including valuable timber species and medicinal plants.
-
Australasian Rainforest: This region includes the rainforests of Papua New Guinea, northeastern Australia, and the islands of Melanesia. It boasts a unique combination of ancient and modern species, with a high degree of endemism.
-
Central American Rainforest: This region encompasses the rainforests of Central America, including Belize, Costa Rica, and Panama. It is characterized by its diverse landscapes, ranging from lush lowlands to towering cloud forests.
The Vital Role of Rainforests:
Rainforests are not merely scenic wonders; they are vital for the health of our planet and the well-being of humanity. Their ecological importance is multifaceted:
-
Climate Regulation: Rainforests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
-
Biodiversity Hotspot: Rainforests are home to an astonishing array of plant and animal species, many of which are yet to be discovered. Their rich biodiversity contributes to the stability and resilience of ecosystems.
-
Water Cycle Regulation: Rainforests play a critical role in the global water cycle. They release vast amounts of water vapor into the atmosphere, influencing rainfall patterns across continents.
-
Medicinal Resources: Rainforests are a treasure trove of medicinal plants, providing a wealth of natural remedies for various ailments. Many modern pharmaceuticals have their origins in rainforest plants.
-
Cultural Significance: Rainforests have been home to indigenous communities for millennia. These communities hold deep cultural and spiritual connections to the forest, relying on its resources for sustenance and well-being.
Threats to Rainforests:
Despite their immense importance, rainforests are facing unprecedented threats:
-
Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban development is a major driver of rainforest loss. This loss not only destroys habitat but also releases stored carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change.
-
Climate Change: Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns are impacting rainforest ecosystems, leading to increased droughts, wildfires, and insect infestations.
-
Mining and Oil Extraction: The exploitation of natural resources, such as minerals and oil, often involves clearing forests, contaminating water sources, and disrupting the ecological balance.
-
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: The illegal hunting and trade of wildlife, including endangered species, poses a significant threat to rainforest biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the crucial role of rainforests and the threats they face, global efforts are underway to protect and conserve these vital ecosystems:
-
Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, helps safeguard rainforest ecosystems from human activities.
-
Sustainable Forest Management: Implementing sustainable forestry practices, such as selective logging and reforestation, can reduce the impact of logging on rainforest ecosystems.
-
Community-Based Conservation: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, empowering them to manage and protect their forests, is essential for long-term success.
-
International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and international organizations are crucial for addressing transboundary issues, such as deforestation and illegal wildlife trade.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the main causes of deforestation?
A: The primary drivers of deforestation include agricultural expansion, particularly for cattle ranching and palm oil plantations, logging for timber and paper production, and infrastructure development, such as roads and dams.
Q: How do rainforests contribute to climate regulation?
A: Rainforests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. This process helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
Q: What are the implications of rainforest loss for biodiversity?
A: The loss of rainforests results in habitat fragmentation and destruction, leading to a decline in species populations and potentially extinctions. This loss of biodiversity undermines the stability and resilience of ecosystems.
Q: What can individuals do to help protect rainforests?
A: Individuals can contribute to rainforest conservation by supporting sustainable products, reducing their consumption of products that contribute to deforestation, advocating for policies that protect rainforests, and donating to organizations working to conserve rainforest ecosystems.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating Rainforests:
-
Explore Rainforest Maps: Utilize online maps and resources to visualize the global distribution of rainforests and understand their geographic context.
-
Learn About Rainforest Biodiversity: Research the fascinating diversity of life in rainforests, focusing on specific species, their ecological roles, and the threats they face.
-
Support Rainforest Conservation Organizations: Contribute to organizations working to protect rainforests through donations, volunteering, or advocacy.
-
Embrace Sustainable Consumption: Choose products that are sustainably sourced and do not contribute to deforestation.
-
Educate Others: Share your knowledge about the importance of rainforests and the threats they face with friends, family, and community members.
Conclusion:
The world map of rainforests reveals a vibrant tapestry of life, a testament to the planet’s remarkable biodiversity. These lush ecosystems are not merely beautiful landscapes; they are vital for the health of our planet and the well-being of humanity. Their contribution to climate regulation, biodiversity, and human well-being cannot be overstated. As we face the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, protecting and conserving rainforests is more crucial than ever. By understanding their importance, supporting conservation efforts, and making informed choices in our daily lives, we can ensure that these emerald jewels of our planet continue to thrive for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Verdant Tapestry: Exploring the Global Distribution of Rainforests. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!