The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents
Related Articles: The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents
- 3.1 A Geographical Overview
- 3.2 Historical Significance: A Gateway to Global Trade
- 3.3 Strategic Importance: A Geopolitical Hub
- 3.4 Economic Benefits: A Vital Revenue Stream
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Suez Canal’s Importance
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Link for Global Connectivity
- 4 Closure
The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents
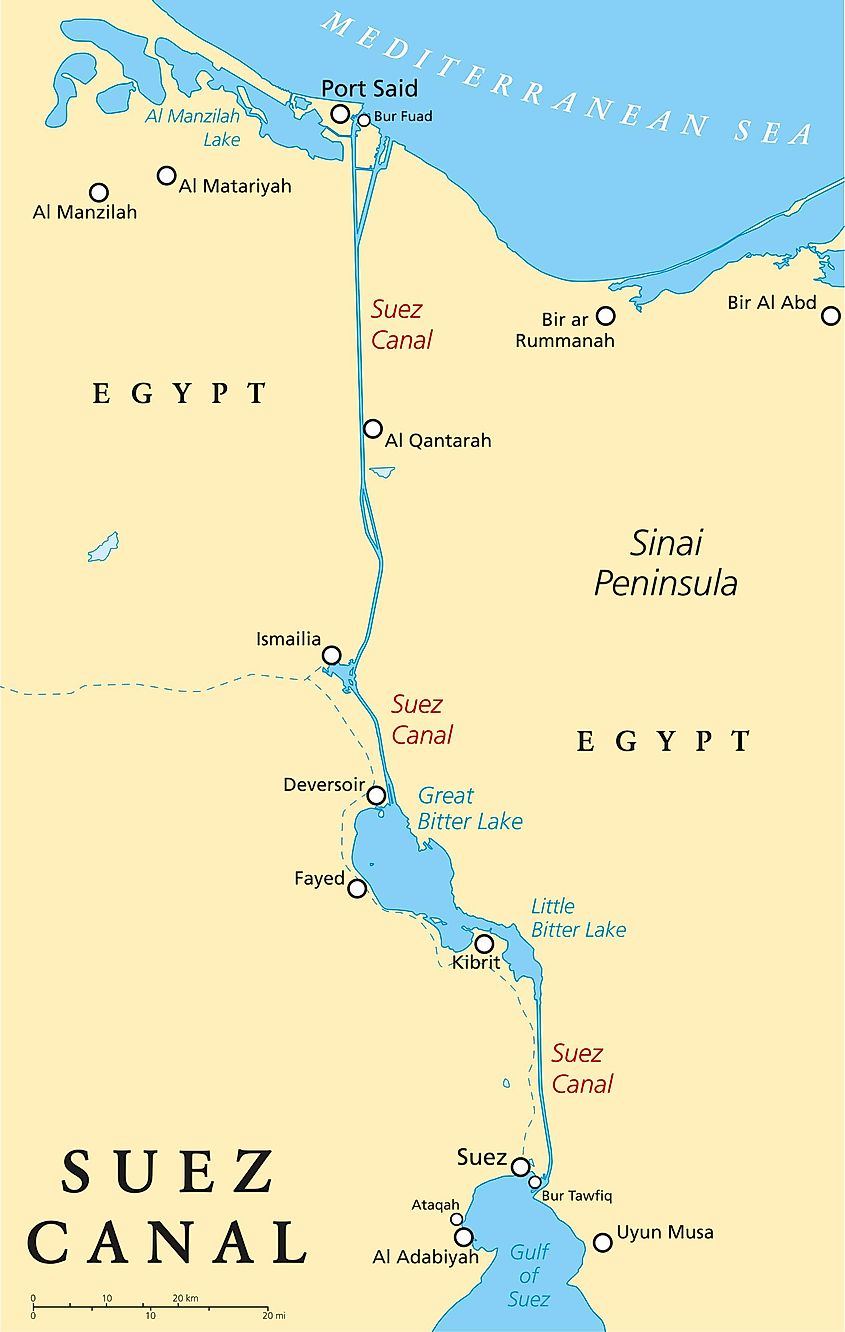
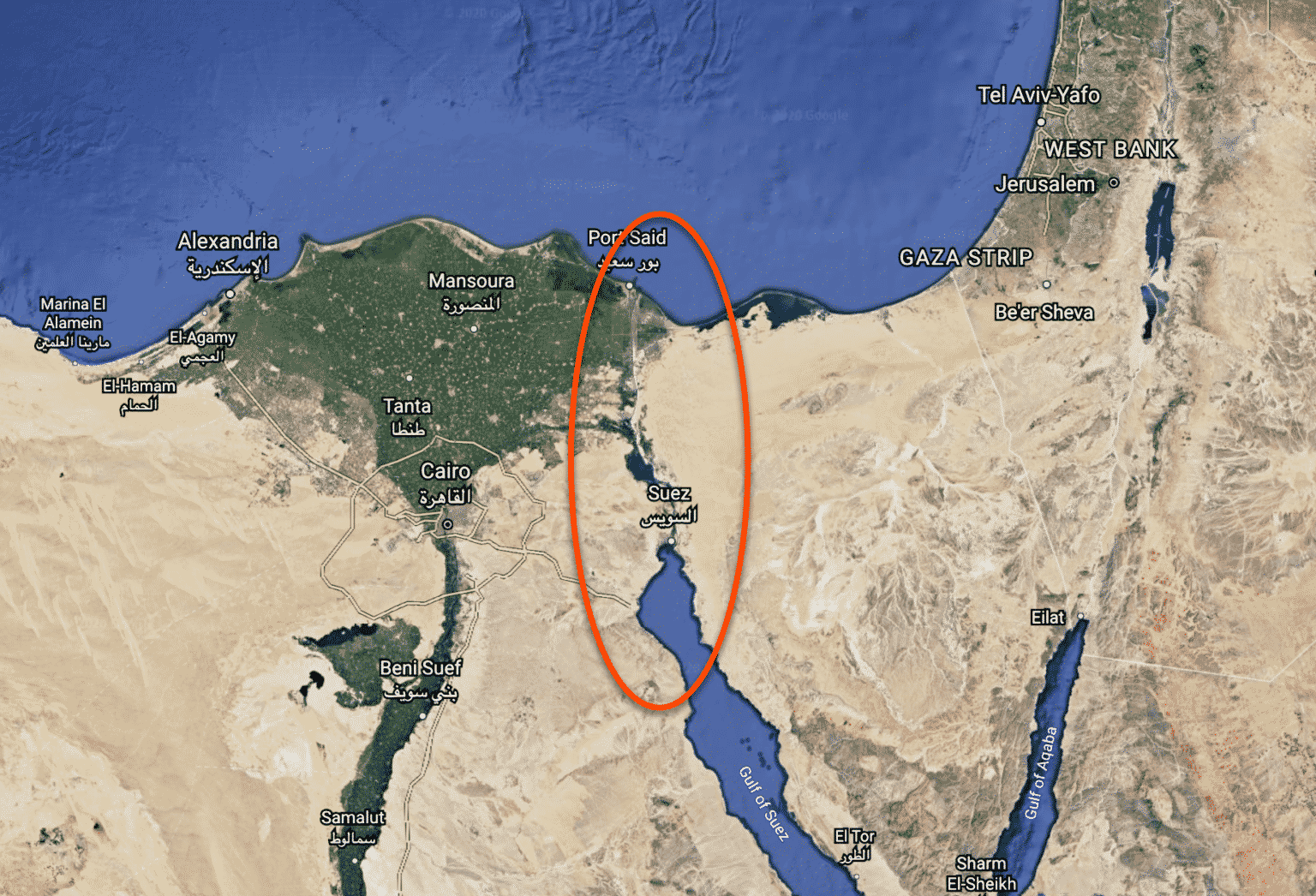
The Suez Canal, a 120-mile waterway traversing the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, serves as a crucial link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, effectively connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Indian Ocean. This artificial waterway, a marvel of engineering, significantly shortens maritime routes, reducing travel time and distance for ships traveling between Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its strategic location has made it a vital artery for global trade and a focal point of geopolitical interest for centuries.
A Geographical Overview
The Suez Canal’s location is central to its significance. It cuts through the narrow strip of land separating the continents of Africa and Asia, specifically the Sinai Peninsula. The canal’s northern terminus lies at Port Said, a city on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt, while its southern end connects to the city of Suez on the Red Sea. The canal’s route traverses a diverse landscape, including the Bitter Lakes, a series of saline lakes, and the Great Bitter Lake, the largest and deepest lake in the canal.
Navigating the Canal:
The Suez Canal is a single-lane waterway, with a series of passing places strategically positioned along its length to facilitate the movement of ships in both directions. The canal features a minimum width of 205 meters (672 feet) and a depth of 24 meters (79 feet), accommodating vessels with a maximum draft of 16 meters (52 feet). The canal is maintained by the Suez Canal Authority (SCA), responsible for its operation, dredging, and expansion projects.
Historical Significance: A Gateway to Global Trade
The Suez Canal’s history is deeply intertwined with global trade and the development of maritime transportation. The ancient Egyptians recognized the strategic importance of the Isthmus of Suez, building a series of canals to connect the Red Sea to the Nile River, facilitating trade between Egypt and the East. However, these early canals fell into disuse over time.
The modern Suez Canal, as we know it today, was constructed in the mid-19th century under the leadership of Ferdinand de Lesseps, a French diplomat and engineer. Construction began in 1859 and was completed in 1869, marking a significant milestone in global maritime trade. The canal’s opening dramatically shortened the sea route between Europe and Asia, eliminating the need for ships to circumnavigate the African continent, thereby reducing travel time and costs.
Strategic Importance: A Geopolitical Hub
The Suez Canal’s location has made it a strategic asset throughout history, attracting interest from various powers. The canal’s control has shifted hands several times, with Egypt ultimately gaining full control in 1956. The canal’s strategic importance is further highlighted by its role in facilitating the flow of energy resources, with significant volumes of oil and gas transported through it.
Impact on Global Trade:
The Suez Canal’s impact on global trade is undeniable. It facilitates the transportation of goods between continents, playing a crucial role in the global supply chain. Approximately 10% of global trade, by volume, transits through the canal annually. The canal’s efficiency and strategic location have made it a vital artery for the movement of goods, including manufactured products, agricultural commodities, and energy resources.
Economic Benefits: A Vital Revenue Stream
The Suez Canal generates significant revenue for Egypt, contributing to its economic development. Transit fees paid by ships passing through the canal are a major source of income for the country. The canal’s economic benefits extend beyond revenue generation, fostering job creation in related industries and boosting tourism.
Challenges and Developments:
The Suez Canal, despite its significant benefits, faces challenges. The increasing size of modern container ships has led to calls for widening and deepening the canal to accommodate larger vessels. The canal’s vulnerability to disruptions, such as the grounding of the Ever Given container ship in 2021, highlights the need for robust contingency plans and infrastructure development to mitigate potential disruptions.
Future Prospects:
The Suez Canal Authority is committed to expanding and modernizing the canal to meet the growing demands of global trade. Plans are underway to further widen and deepen the canal, as well as develop new infrastructure, including a new parallel channel, to enhance capacity and efficiency. These initiatives aim to solidify the canal’s position as a crucial artery for global trade and ensure its continued relevance in the future.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the Suez Canal’s significance in international trade?
A: The Suez Canal significantly shortens maritime routes, reducing travel time and costs for ships traveling between Europe, Asia, and Africa. It facilitates the transportation of goods between continents, playing a crucial role in the global supply chain.
Q: How does the Suez Canal impact global energy markets?
A: The Suez Canal plays a vital role in facilitating the flow of energy resources, with significant volumes of oil and gas transported through it. Its closure or disruption can have a significant impact on global energy markets, potentially leading to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Suez Canal?
A: The Suez Canal faces challenges related to the increasing size of modern container ships, the need for continuous maintenance and dredging, and the potential for disruptions caused by accidents or geopolitical events.
Q: What are the future prospects for the Suez Canal?
A: The Suez Canal Authority is committed to expanding and modernizing the canal to meet the growing demands of global trade. Plans are underway to further widen and deepen the canal, as well as develop new infrastructure, including a new parallel channel, to enhance capacity and efficiency.
Tips for Understanding the Suez Canal’s Importance
- Visualize the location: Use online maps or globes to understand the geographical location of the Suez Canal and its connection between continents.
- Explore historical context: Research the history of the canal, its construction, and its impact on global trade and geopolitical dynamics.
- Consider global trade flows: Analyze the flow of goods and resources through the canal, understanding its role in the global supply chain.
- Analyze geopolitical factors: Understand the canal’s strategic importance, its role in energy transportation, and the geopolitical considerations surrounding its control.
- Stay informed about developments: Follow news and updates about the Suez Canal, including ongoing expansion projects, potential disruptions, and its impact on the global economy.
Conclusion: A Vital Link for Global Connectivity
The Suez Canal, a marvel of engineering and a testament to human ingenuity, stands as a crucial link connecting continents and facilitating global trade. Its strategic location, historical significance, and economic benefits have made it a vital artery for the movement of goods and resources, contributing significantly to global prosperity. As the world continues to grow and global trade expands, the Suez Canal will undoubtedly remain a critical element in shaping the future of international commerce and connectivity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Suez Canal: A Maritime Lifeline Connecting Continents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!