Navigating the Peaks: Exploring the Significance of the Chinese Mountain Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Peaks: Exploring the Significance of the Chinese Mountain Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Peaks: Exploring the Significance of the Chinese Mountain Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Peaks: Exploring the Significance of the Chinese Mountain Map
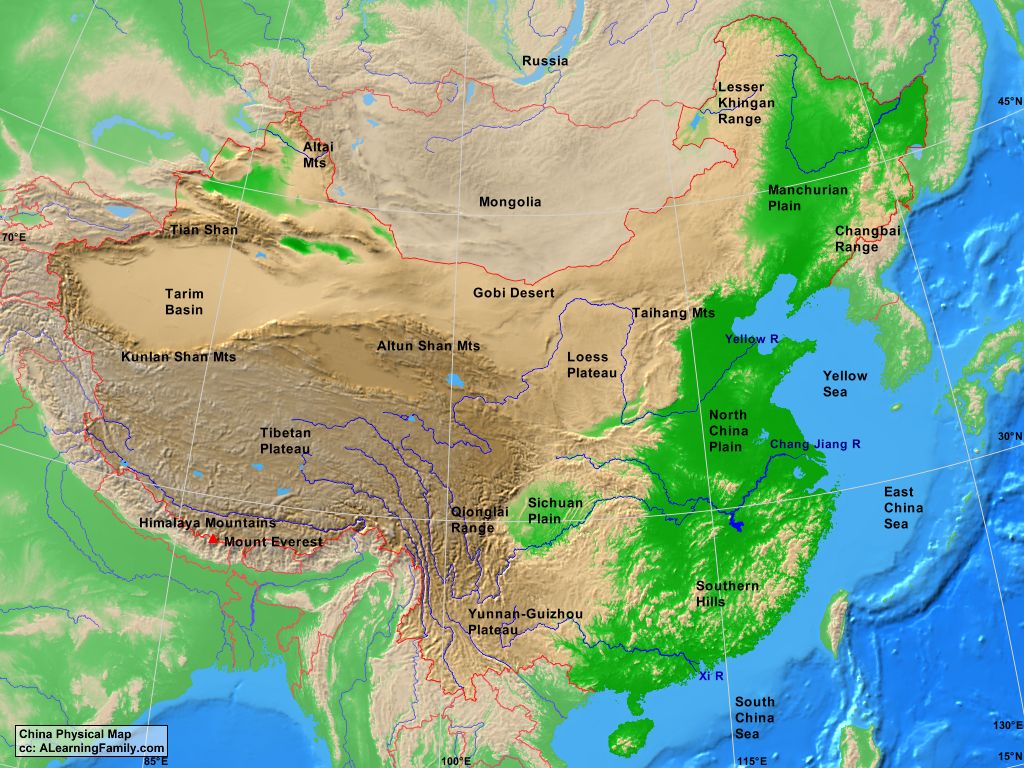
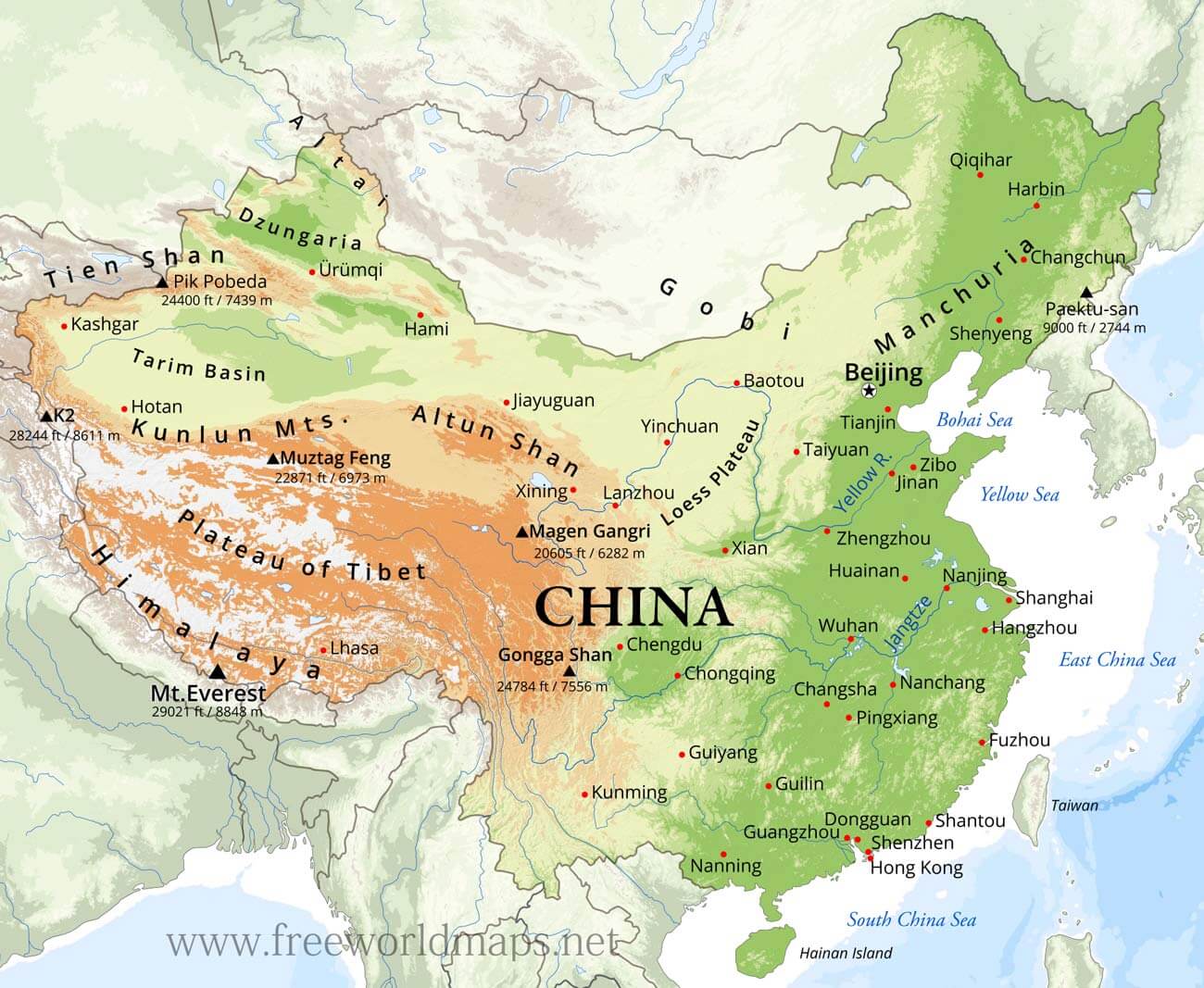
China, a land of vast landscapes and towering peaks, boasts a mountain range system of unparalleled scale and diversity. This intricate network of mountains, encompassing the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains, the Tian Shan, and many more, has profoundly shaped the country’s geography, climate, culture, and history. Understanding this mountainous terrain requires a comprehensive tool: the Chinese mountain map.
A Tapestry of Peaks and Valleys:
The Chinese mountain map is not simply a geographical representation. It is a visual narrative of the country’s geological evolution, a testament to the forces that shaped its landforms, and a reflection of the human stories interwoven with the mountains. It unveils the intricate network of mountain ranges, individual peaks, and valleys, revealing the interconnectedness of these features.
Geological Significance:
The map highlights the tectonic forces that have sculpted China’s landscape. The collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, a process that began millions of years ago, has resulted in the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and the Himalayas, the highest mountain range in the world. The map reveals the impact of this tectonic activity, showcasing the distribution of fault lines, volcanic zones, and the geological formations that define the country’s mountainous regions.
Climate and Biodiversity:
The Chinese mountain map reveals the intricate relationship between altitude and climate. As elevation increases, temperatures decrease, creating diverse microclimates within the mountain ranges. This climatic variability supports an astonishing array of plant and animal life, contributing to China’s remarkable biodiversity. The map allows researchers and conservationists to identify areas of high biodiversity, enabling targeted efforts for species protection and ecosystem management.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Beyond the physical landscape, the Chinese mountain map illuminates the cultural and historical connections with the mountains. For millennia, these peaks have served as a source of inspiration for art, literature, and philosophy. From the majestic landscapes depicted in ancient Chinese paintings to the philosophical concepts of Taoism, which find resonance in the harmonious balance of nature, mountains have played a central role in shaping Chinese cultural identity.
The map also reveals the historical significance of mountain passes and routes. These passages, often treacherous and challenging, served as vital trade routes, connecting different regions and cultures. The Silk Road, one of the most famous historical trade routes, traversed the mountains, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge across vast distances.
Modern-Day Importance:
In the modern era, the Chinese mountain map remains indispensable for various sectors. It serves as a crucial tool for:
- Resource Management: The map aids in identifying and managing natural resources like water, timber, and minerals found in mountainous regions.
- Infrastructure Development: It assists in planning and constructing roads, railways, and other infrastructure projects in challenging terrains.
- Disaster Mitigation: The map helps identify areas prone to landslides, earthquakes, and other natural disasters, enabling effective disaster preparedness and response.
- Tourism Development: It assists in promoting sustainable tourism, highlighting scenic areas and promoting responsible travel in mountainous regions.
FAQs Regarding the Chinese Mountain Map:
1. What are the most prominent mountain ranges on the Chinese mountain map?
The most prominent mountain ranges include the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains, the Tian Shan, the Qinling Mountains, the Hengduan Mountains, and the Nanling Mountains.
2. How is the Chinese mountain map used in environmental protection?
The map assists in identifying areas of high biodiversity and ecological sensitivity, enabling targeted conservation efforts and sustainable resource management.
3. How does the Chinese mountain map contribute to understanding the country’s climate?
The map reveals the impact of elevation on climate, highlighting the diverse microclimates within mountain ranges and their influence on local weather patterns.
4. What are some of the historical significance of the mountain passes depicted on the map?
Mountain passes have historically served as vital trade routes, connecting different regions and facilitating cultural exchange. The Silk Road, for instance, traversed the mountains, playing a crucial role in the spread of trade and ideas.
5. How does the Chinese mountain map assist in infrastructure development?
The map aids in planning and constructing roads, railways, and other infrastructure projects in challenging mountainous terrains, ensuring efficient and sustainable development.
Tips for Utilizing the Chinese Mountain Map:
- Explore the Map in Detail: Pay attention to the intricate details of the map, noting the elevation, mountain ranges, rivers, and other geographical features.
- Connect the Map to Historical and Cultural Context: Research the historical significance of specific mountains, passes, and regions, understanding their cultural and societal impact.
- Consider the Map’s Environmental Significance: Analyze the map’s representation of biodiversity, climate, and natural resources, recognizing the importance of sustainable resource management.
- Utilize the Map for Planning: Use the map to plan trips, research projects, or explore the potential for infrastructure development in mountainous regions.
Conclusion:
The Chinese mountain map is not merely a geographical tool; it is a window into the country’s geological history, cultural heritage, and environmental complexities. It reveals the intricate interplay of nature and human activity, highlighting the importance of understanding and appreciating the unique characteristics of China’s mountainous terrain. By utilizing the map’s insights, researchers, policymakers, and individuals can foster a deeper appreciation for the country’s natural wonders and promote sustainable development in these vital regions.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Peaks: Exploring the Significance of the Chinese Mountain Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!