Kindergarten Assessment: Measuring Early Literacy and Numeracy
Related Articles: Kindergarten Assessment: Measuring Early Literacy and Numeracy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Kindergarten Assessment: Measuring Early Literacy and Numeracy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Kindergarten Assessment: Measuring Early Literacy and Numeracy

Kindergarten marks a pivotal transition in a child’s educational journey. It’s the foundational year where fundamental literacy and numeracy skills are cultivated, setting the stage for future academic success. Comprehensive assessment at this stage is crucial for identifying individual learning needs, tailoring instruction, and ensuring equitable access to appropriate support. This necessitates the use of robust assessment tools capable of providing detailed insights into a child’s developmental trajectory. These assessments play a vital role in informing pedagogical approaches and resource allocation within the educational system.
One commonly used assessment method involves standardized tests, often designed to measure a range of skills across various domains. These tests typically incorporate a variety of question types, including multiple-choice, short-answer, and performance-based tasks. The results provide a snapshot of a child’s current abilities, highlighting areas of strength and weakness. This data is then used to inform instructional decisions, allowing educators to focus on specific skill development and provide targeted interventions where necessary.
The design of these assessments is meticulously planned. Development involves rigorous psychometric analysis to ensure reliability and validity. Reliability refers to the consistency of the test results over time and across different administrations. Validity, on the other hand, refers to the extent to which the test accurately measures what it intends to measure. These qualities are essential for ensuring the accuracy and usefulness of the assessment data. Furthermore, the assessment instruments are often designed to align with established learning standards, providing a benchmark against which student performance can be compared.
The data obtained from these assessments provide valuable insights for multiple stakeholders. Teachers can use the information to personalize learning experiences, adapting their instructional strategies to meet the diverse needs of their students. Administrators utilize the data to evaluate the effectiveness of school-wide programs and identify areas needing improvement. Parents also benefit from receiving clear and concise reports, enabling them to better understand their child’s progress and collaborate with educators to support their learning. Early identification of learning gaps through these assessments allows for timely intervention, potentially preventing more significant challenges later on.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
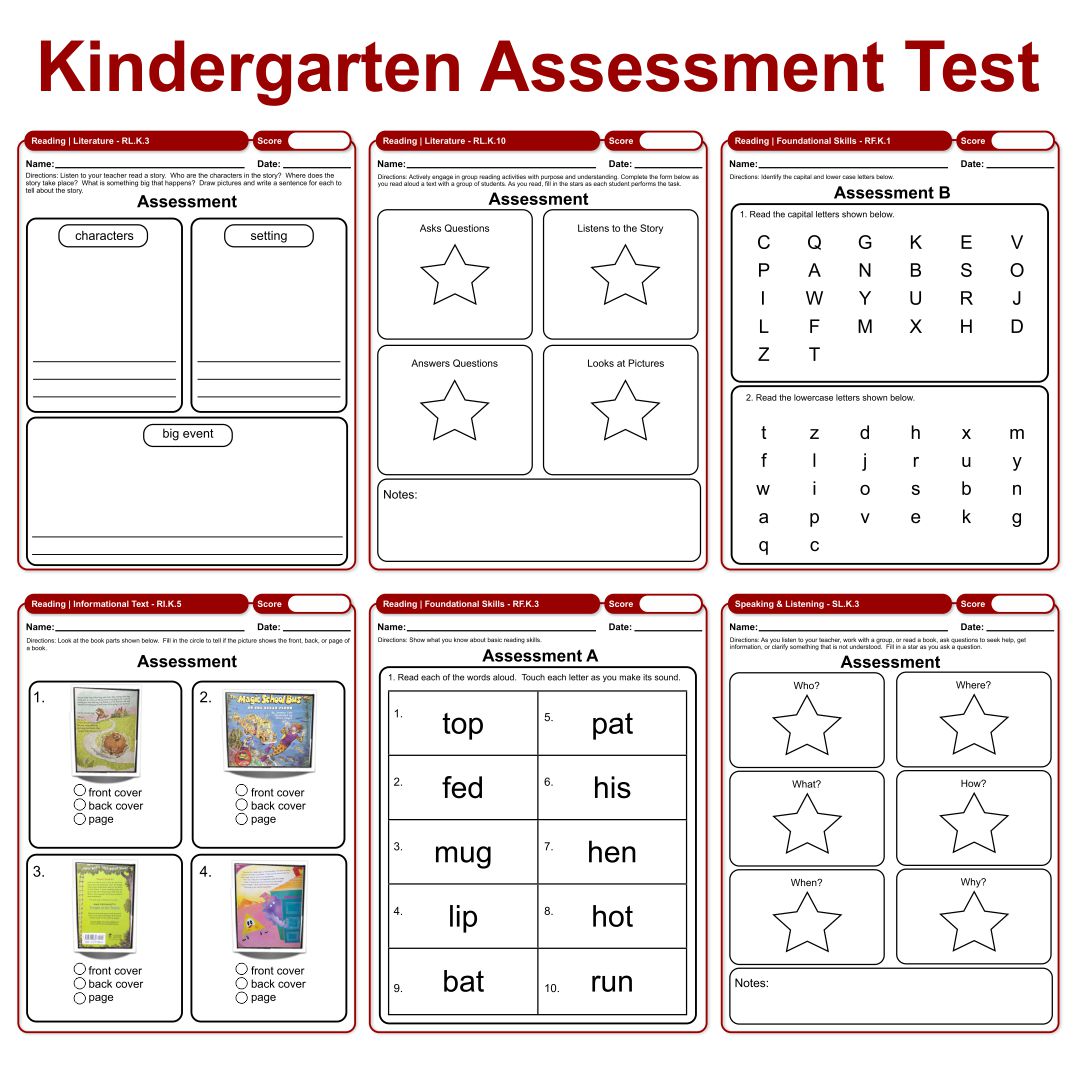
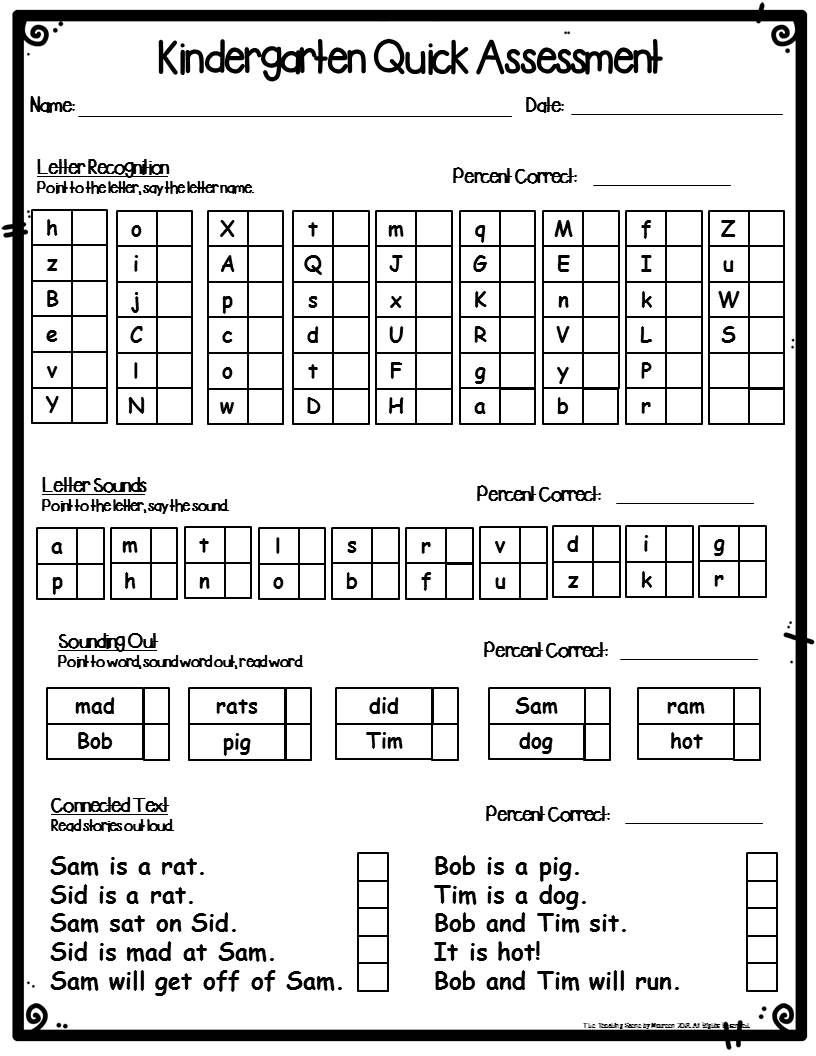
What skills are typically assessed in kindergarten-level assessments? Assessments typically cover a range of foundational skills in literacy and numeracy. Literacy assessments often focus on phonological awareness (identifying and manipulating sounds in words), letter recognition, print awareness (understanding the function of print), and early reading skills. Numeracy assessments frequently assess number recognition, counting, simple addition and subtraction, and spatial reasoning.
-
How are the results of these assessments used? Assessment results are primarily used to inform instructional decisions. Teachers use the data to identify students who may need additional support or enrichment, allowing for differentiated instruction tailored to individual needs. The data also informs school-wide programming and resource allocation, ensuring that resources are directed where they are most needed.
-
What types of questions are included in these assessments? A variety of question types are commonly used, including multiple-choice questions, matching exercises, short-answer questions, and performance-based tasks that require students to demonstrate their skills through hands-on activities.
-
Are these assessments standardized? Many kindergarten assessments are standardized, meaning that they are administered and scored in a consistent manner across different settings. This standardization ensures that results are comparable across different schools and classrooms.
-
How can parents access their child’s assessment results? Parents typically receive a report summarizing their child’s performance on the assessment. This report usually provides a clear explanation of the results and recommendations for supporting their child’s learning. Open communication between teachers and parents is encouraged to discuss the results and create a collaborative learning plan.
Tips for Supporting Kindergarten Learning
-
Foster a love of reading: Regularly reading aloud to children, visiting libraries, and providing access to a variety of books can significantly impact literacy development.
-
Engage in playful learning activities: Incorporate numeracy and literacy into everyday activities through games, songs, and interactive experiences.
-
Encourage active participation: Create a supportive and engaging learning environment where children feel comfortable taking risks and participating actively.
-
Collaborate with educators: Maintain open communication with teachers to understand your child’s progress and work together to support their learning.
-
Provide a consistent and supportive home environment: Establish a routine that supports learning and provides a stable and nurturing environment conducive to academic success.
Conclusion
Comprehensive assessment in kindergarten is not merely a process of evaluation; it’s a critical component of a holistic approach to early childhood education. The data generated provides invaluable insights into a child’s developmental progress, informing individualized instruction and fostering a supportive learning environment. By utilizing assessment data effectively, educators can identify and address learning gaps early on, promoting equitable access to quality education and setting the stage for future academic success. The ultimate goal is to equip every child with the necessary foundational skills to thrive in their educational journey. The continuous refinement of assessment methodologies and the collaborative efforts of educators, parents, and administrators are essential for maximizing the benefits of these assessments and ensuring that all children reach their full potential.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Kindergarten Assessment: Measuring Early Literacy and Numeracy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!