Delineating the World: An Examination of National Borders on Global Maps
Related Articles: Delineating the World: An Examination of National Borders on Global Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delineating the World: An Examination of National Borders on Global Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delineating the World: An Examination of National Borders on Global Maps
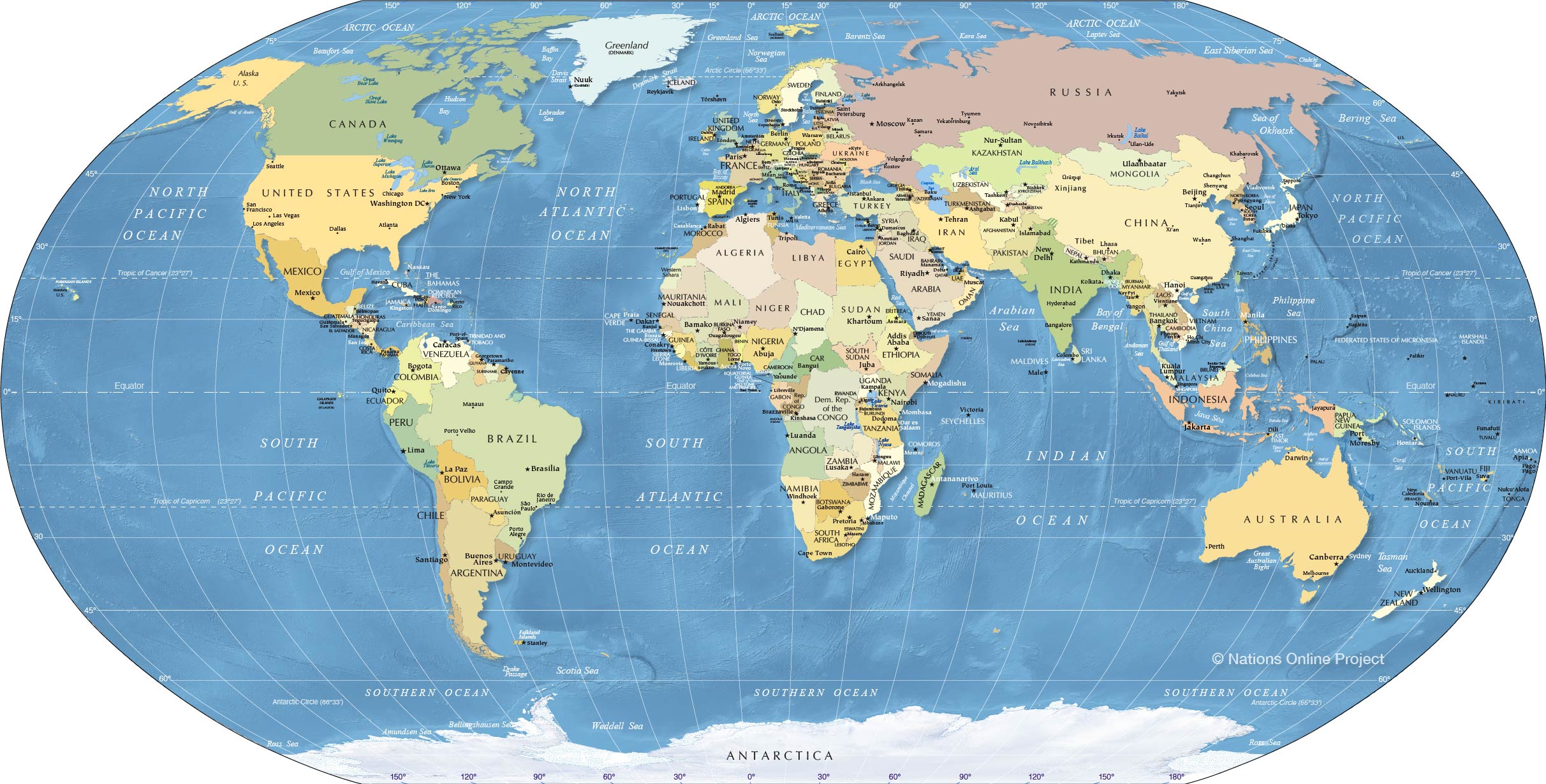
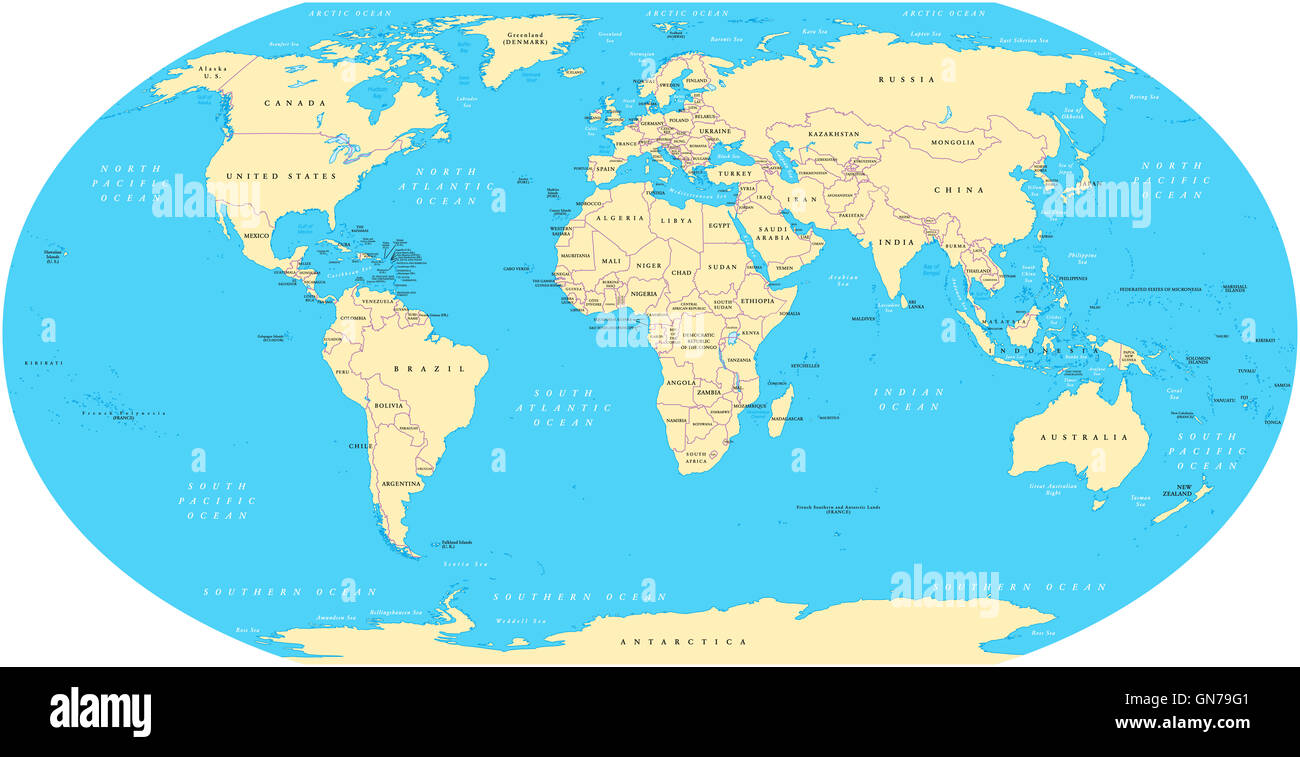
Cartography, the science and art of mapmaking, relies heavily on the accurate representation of national boundaries. These lines, often appearing as simple strokes on a map, represent complex geopolitical realities, historical events, and ongoing negotiations. Understanding how these lines are drawn and the implications of their depiction is crucial for interpreting global events, analyzing geopolitical dynamics, and appreciating the complexities of international relations.
The process of defining and displaying national borders on a world map is multifaceted. Initially, physical geography plays a significant role. Natural boundaries, such as rivers, mountain ranges, and coastlines, have historically served as convenient and often defensible demarcations. The Rhine River, for instance, forms parts of the borders of several European countries, while the Himalayas define a significant portion of the boundary between India and China. However, relying solely on physical features is often insufficient, leading to the incorporation of artificial boundaries.
Artificial boundaries, drawn without direct reference to physical geography, are often the product of treaties, agreements, and historical compromises. These lines frequently follow lines of latitude or longitude, or are drawn to accommodate specific political or economic interests. The straight-line borders between many African nations, often a legacy of colonial partitioning, exemplify this. These lines, drawn without regard for pre-existing ethnic or cultural divisions, have contributed to significant post-colonial instability and conflict. Similarly, the border between North and South Korea, a product of the Korean War, represents a stark division based on ideological differences rather than geographical realities.
The accuracy and precision of national boundaries on a world map depend heavily on the map’s scale and purpose. Large-scale maps, focusing on a specific region, can display borders with greater detail, incorporating finer nuances such as minor territorial disputes or enclaves. Small-scale world maps, conversely, necessitate simplification, often smoothing out intricate border details to maintain clarity and legibility. This simplification, however, can lead to a loss of information and potentially a misrepresentation of the complexities on the ground.
Furthermore, the representation of disputed territories poses a significant cartographic challenge. Areas with contested sovereignty, such as the South China Sea islands or the Kashmir region, require careful consideration. Different maps may depict these areas differently, reflecting the varying perspectives of the nations involved. The choice of representation—whether to show a disputed area as belonging to a particular nation, to leave it unclaimed, or to indicate the dispute explicitly—reflects political considerations and potentially contributes to the perpetuation of conflicting narratives.
The development of digital cartography has introduced new challenges and opportunities. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow for far greater precision and detail in the depiction of borders, integrating various data sources such as satellite imagery and census data. However, the increasing reliance on digital maps also raises concerns regarding data accuracy, potential biases in data collection, and the accessibility of this technology.
The importance of accurately depicting national borders on world maps cannot be overstated. These lines are not merely abstract lines on a page; they represent real-world consequences. They influence international relations, trade agreements, resource allocation, and the lives of millions of people. Inaccurate or misleading representations can have significant implications for political stability, economic development, and international cooperation.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How are disputed territories represented on world maps?
- A: The representation of disputed territories varies significantly depending on the map’s source and intended audience. Some maps may show the disputed territory as belonging to a particular nation, while others may leave it unclaimed or explicitly indicate the dispute through shading or labeling. The choice of representation reflects the mapmaker’s perspective and potential political biases.
-
Q: What is the role of technology in modern cartography of national borders?
- A: Technology, particularly GIS, has revolutionized the creation and updating of maps. High-resolution satellite imagery and other digital data sources allow for greater accuracy and detail in the depiction of borders. However, the reliance on digital technology also raises concerns regarding data quality, potential biases, and access to the technology itself.
-
Q: Why are some national borders straight lines while others follow natural features?
- A: Straight-line borders are often artificial boundaries, established through treaties or agreements without necessarily following natural geographical features. They often reflect political compromises or the imposition of boundaries by external powers, as seen in many post-colonial African nations. In contrast, borders following natural features, such as rivers or mountain ranges, are more often based on geographical realities and often existed before formal political boundaries were established.
-
Q: How often are world maps updated to reflect changes in national borders?
- A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the map’s purpose and the source. Maps intended for educational purposes or general use may be updated less frequently, while those used for navigational or geopolitical analysis require more regular updates to reflect changes resulting from treaties, conflicts, or other significant events.
Tips for Interpreting Maps Depicting National Boundaries
- Consider the map’s scale and projection: The scale affects the level of detail, while the projection can distort shapes and distances.
- Examine the map’s legend and metadata: This information provides crucial context about the data sources and potential limitations.
- Be aware of potential biases: Maps are not neutral; they reflect the perspectives and priorities of their creators.
- Cross-reference with multiple sources: Compare different maps to identify discrepancies and gain a more complete understanding.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical events that shaped national borders provides crucial insight into their current configuration.
Conclusion
The representation of national boundaries on world maps is a complex and multifaceted undertaking. These lines, seemingly simple on the surface, reflect a tapestry of historical events, geopolitical realities, and ongoing negotiations. Accurate and nuanced depiction of these boundaries is crucial for informed understanding of global dynamics, promoting international cooperation, and resolving conflicts. Critical analysis of map sources, careful consideration of scale and projection, and awareness of potential biases are essential for interpreting these representations effectively. The ongoing evolution of cartographic technologies necessitates a continuous reassessment of methodologies and a commitment to responsible and accurate representation of the world’s geopolitical landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating the World: An Examination of National Borders on Global Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!