Canada’s Arteries of Life: Exploring the Majestic River Programs of a Huge Land
Canada, a land of immense scale and breathtaking pure magnificence, is carved and nourished by an enormous community of rivers. These waterways, extra than simply picturesque options of the panorama, are the arteries of life, shaping the surroundings, influencing human settlement, and driving the Canadian economic system. From the mighty Mackenzie flowing north to the Arctic Ocean to the historic St. Lawrence connecting the Nice Lakes to the Atlantic, Canada’s rivers inform a narrative of exploration, commerce, and the enduring energy of nature.
This text explores the various and important river techniques of Canada, offering a glimpse into their geographical significance, historic significance, ecological roles, and financial contributions. We’ll delve into the foremost river basins, highlighting the distinctive traits of a number of the most important waterways, and contemplate the challenges they face in a quickly altering world.
Mapping Canada’s Liquid Panorama: Key River Basins
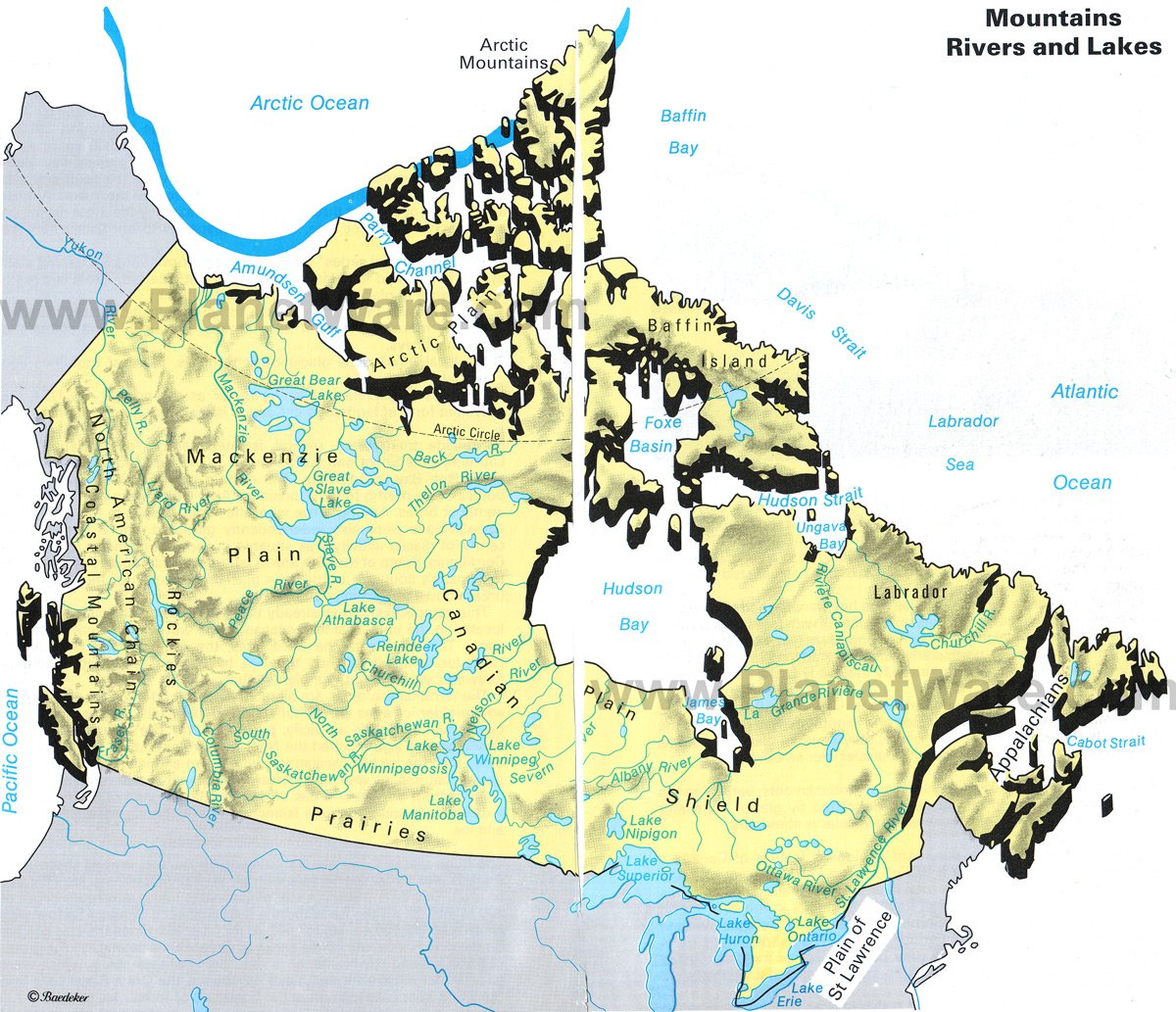
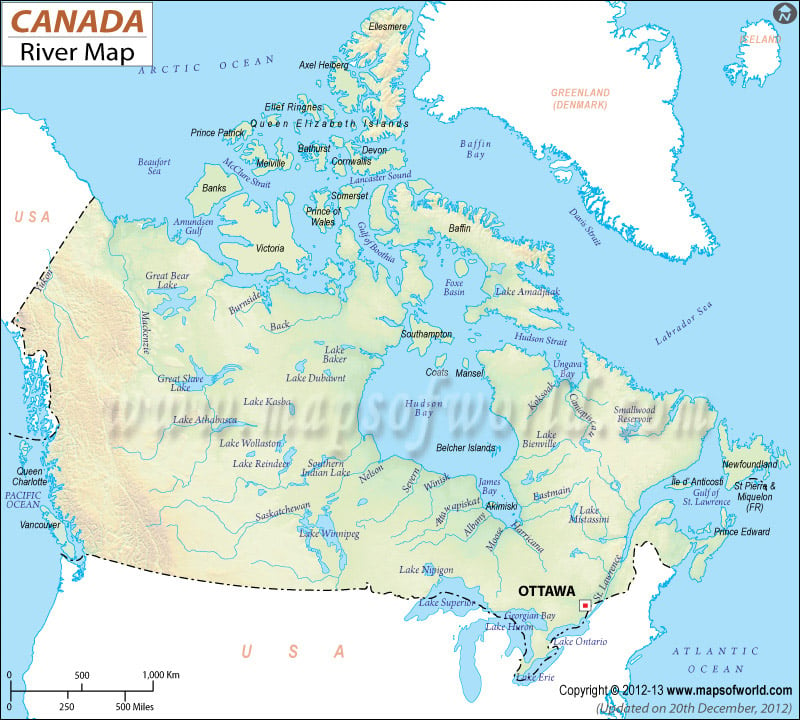
Understanding Canada’s river techniques requires acknowledging the vastness of the nation and the distinct geographical areas that affect their formation and circulate. The nation could be broadly divided into a number of main drainage basins, every characterised by distinctive local weather, topography, and geological historical past:
-
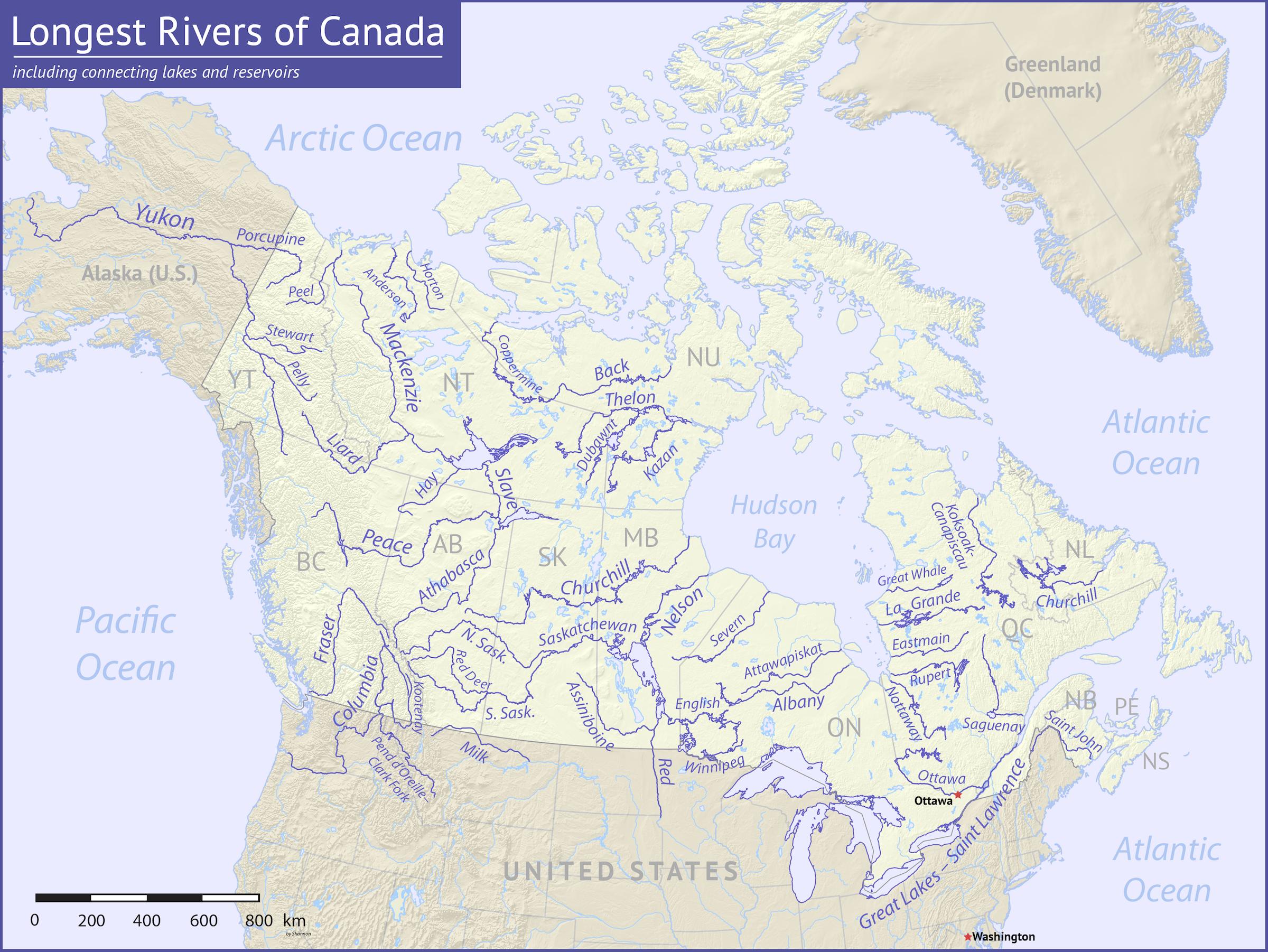
The Arctic Drainage Basin: Dominated by the Mackenzie River, this basin drains an enormous space of the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and components of Alberta and British Columbia. The rivers listed below are characterised by lengthy, chilly winters and brief, intense summer time soften seasons. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada and second longest in North America, is the principal waterway, amassing water from quite a few tributaries and in the end emptying into the Beaufort Sea.
-
The Atlantic Drainage Basin: This basin encompasses the japanese provinces of Canada, together with Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, and components of Quebec. The St. Lawrence River, arguably probably the most traditionally and economically important river in Canada, varieties the spine of this basin, connecting the Nice Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. Different important rivers on this basin embrace the Saint John River, the Restigouche River, and the Churchill River (Labrador).
-
The Hudson Bay Drainage Basin: An unlimited, low-lying space, this basin drains components of Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and Nunavut. The Nelson River, the second-largest river in Canada by discharge quantity, is the first waterway, draining Lake Winnipeg and flowing into Hudson Bay. Different essential rivers on this basin embrace the Churchill River (Manitoba/Saskatchewan), the Hayes River, and the Albany River.
-
The Pacific Drainage Basin: Confined to the mountainous western province of British Columbia and components of Yukon, this basin is characterised by steep, fast-flowing rivers that carve by means of rugged terrain. The Fraser River, the longest river totally inside British Columbia, is the dominant waterway. Different important rivers embrace the Columbia River (shared with the US), the Skeena River, and the Nass River.
-
The Gulf of Mexico Drainage Basin: A small portion of southern Alberta and Saskatchewan drains into the Milk River, which flows into the Missouri River and finally into the Gulf of Mexico. That is the one a part of Canada that drains into the Atlantic Ocean through the Gulf of Mexico.
Iconic Rivers: Profiles of Energy and Significance
Let’s discover a few of Canada’s most iconic rivers in additional element:
-
The Mackenzie River: Because the longest river in Canada, the Mackenzie holds immense ecological and cultural significance. Its huge drainage basin helps a various array of wildlife, together with migratory birds, fish populations, and numerous mammal species. For hundreds of years, Indigenous peoples have relied on the Mackenzie River for transportation, sustenance, and cultural practices. The river can also be essential for useful resource improvement, notably oil and gasoline exploration within the Mackenzie Delta.
-
The St. Lawrence River: The St. Lawrence River is the lifeblood of Japanese Canada. It varieties a significant transportation hall, connecting the Nice Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean and facilitating worldwide commerce. The St. Lawrence Seaway, a system of canals and locks, permits giant ships to navigate the river, connecting main industrial and agricultural facilities in Canada and the US. The river can also be a major supply of hydroelectric energy and helps a various ecosystem, together with beluga whales within the St. Lawrence Estuary.
-
The Fraser River: Flowing totally inside British Columbia, the Fraser River is famend for its spectacular salmon runs. Tens of millions of salmon migrate up the river every year to spawn, supporting a thriving fishing business and offering a vital meals supply for wildlife. The Fraser River additionally performs a significant position in agriculture, offering irrigation water for crops within the Fraser Valley. Its dramatic canyons and rapids make it a well-liked vacation spot for whitewater rafting and different leisure actions.
-
The Nelson River: Draining Lake Winnipeg, the Nelson River is a significant supply of hydroelectric energy in Manitoba. A number of giant dams and producing stations have been constructed alongside the river, offering electrical energy to the province and past. Nevertheless, these developments have additionally had important environmental impacts, together with altering the pure circulate regime and affecting fish populations.
-
The Columbia River: Shared with the US, the Columbia River is one other main supply of hydroelectric energy and irrigation water. Quite a few dams have been constructed alongside the river in each international locations, creating giant reservoirs and altering the river’s pure circulate. The Columbia River can also be essential for navigation and helps a various vary of fish and wildlife.
Rivers as Highways: Historical past, Commerce, and Transportation
Canada’s rivers have performed a pivotal position in shaping the nation’s historical past and improvement. For hundreds of years, Indigenous peoples relied on rivers for transportation, commerce, and communication. European explorers and fur merchants adopted these identical waterways, establishing buying and selling posts and settlements alongside their banks. Rivers served as important transportation routes, permitting entry to distant areas and facilitating the motion of products and other people.
The fur commerce, specifically, was closely reliant on rivers. Voyageurs, expert canoeists, navigated the waterways, transporting furs from the inside to buying and selling posts alongside the coasts. The St. Lawrence River, the Ottawa River, and the Churchill River have been all main arteries of the fur commerce.
Even with the arrival of railways and highways, rivers proceed to play an essential position in transportation, notably for bulk commodities comparable to grain, minerals, and timber. The St. Lawrence Seaway, for instance, stays a vital transportation hall for worldwide commerce.
Ecological Significance: Biodiversity and Ecosystem Companies
Canada’s rivers help a wealthy range of aquatic life, together with fish, invertebrates, and aquatic vegetation. They supply habitat for quite a few species, together with migratory birds, waterfowl, and mammals. Rivers additionally play a vital position in sustaining water high quality, regulating nutrient cycles, and offering different important ecosystem providers.
River ecosystems are notably susceptible to air pollution, habitat destruction, and local weather change. Dams and diversions can alter the pure circulate regime, affecting fish populations and disrupting ecosystem processes. Air pollution from industrial and agricultural sources can contaminate water and hurt aquatic life. Local weather change can also be having a major impression on rivers, altering water temperatures, circulate patterns, and ice cowl.
Financial Contributions: Useful resource Improvement and Business
Rivers contribute considerably to the Canadian economic system in numerous methods. They’re a supply of hydroelectric energy, offering a clear and renewable power supply. They’re additionally used for irrigation, supporting agriculture in lots of areas. Rivers help business and leisure fisheries, offering jobs and meals. They’re used for transportation, facilitating the motion of products and other people. Moreover, rivers are essential for tourism and recreation, attracting guests from around the globe.
Nevertheless, the financial advantages derived from rivers have to be balanced with the necessity to shield their ecological integrity. Sustainable administration practices are important to make sure that rivers proceed to supply financial and environmental advantages for future generations.
Challenges and Conservation: Defending Canada’s Rivers
Canada’s rivers face quite a few challenges within the twenty first century. Air pollution, habitat destruction, local weather change, and over-exploitation of assets all threaten the well being and integrity of those important ecosystems.
- Air pollution: Industrial and agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and mining actions can all pollute rivers, harming aquatic life and affecting water high quality.
- Habitat Destruction: Dams, diversions, and shoreline improvement can destroy vital habitat for fish and different aquatic species.
- Local weather Change: Rising water temperatures, altered circulate patterns, and elevated frequency of maximum climate occasions are all impacting river ecosystems.
- Over-Exploitation of Sources: Overfishing, extreme water withdrawals, and unsustainable logging practices can all degrade river ecosystems.
Defending Canada’s rivers requires a multi-faceted strategy that features:
- Strengthening environmental rules: Implementing stricter rules to regulate air pollution and shield habitat.
- Selling sustainable useful resource administration: Adopting sustainable fishing, forestry, and agricultural practices.
- Investing in water therapy infrastructure: Upgrading wastewater therapy vegetation to cut back air pollution.
- Restoring degraded river ecosystems: Eradicating dams, restoring riparian vegetation, and implementing different restoration tasks.
- Addressing local weather change: Decreasing greenhouse gasoline emissions and adapting to the impacts of local weather change.
Conclusion: A Name for Stewardship
Canada’s rivers are a nationwide treasure, important for the nation’s economic system, surroundings, and cultural heritage. Understanding their geographical significance, historic significance, ecological roles, and financial contributions is essential for guaranteeing their sustainable administration. As stewards of this huge and treasured useful resource, Canadians should work collectively to guard and preserve these arteries of life for future generations. By embracing sustainable practices, investing in restoration efforts, and addressing the challenges of air pollution, habitat destruction, and local weather change, we are able to make sure that Canada’s rivers proceed to circulate robust, supporting wholesome ecosystems and affluent communities for hundreds of years to return.