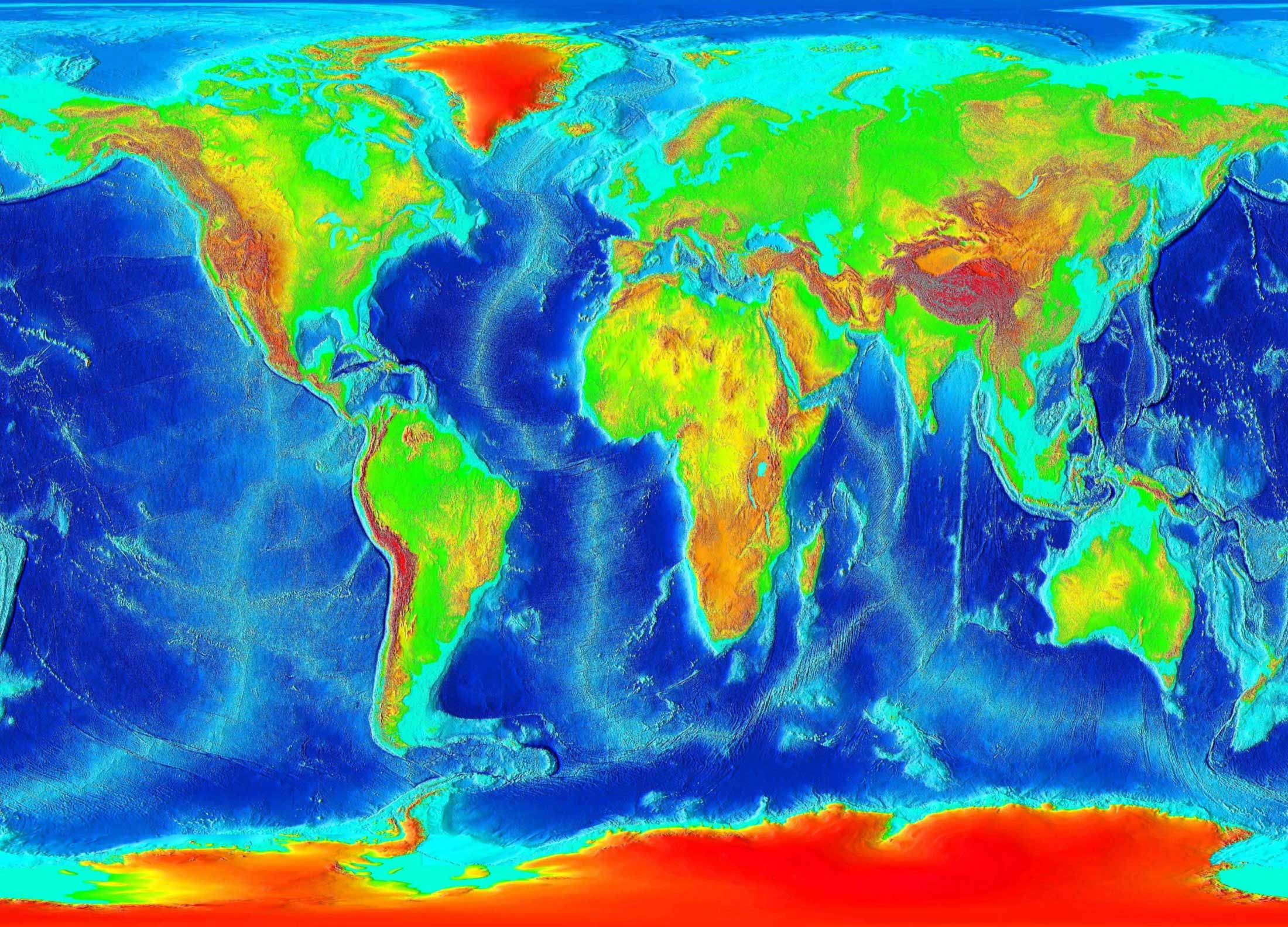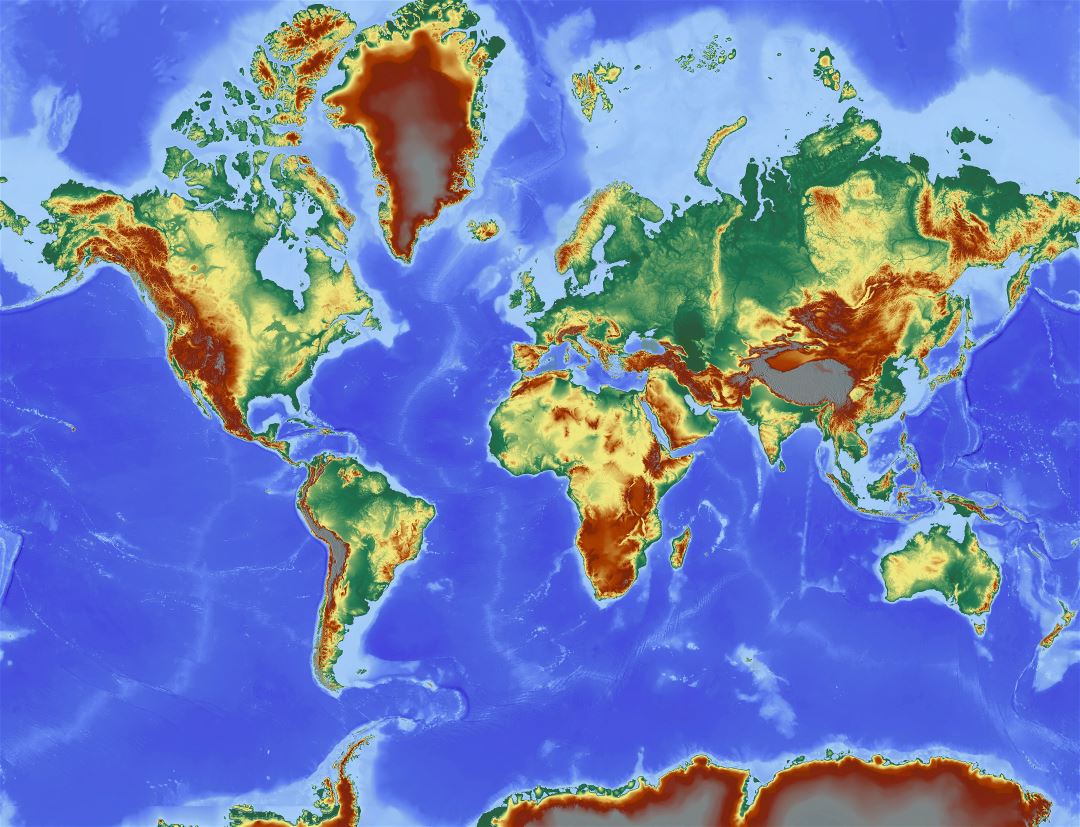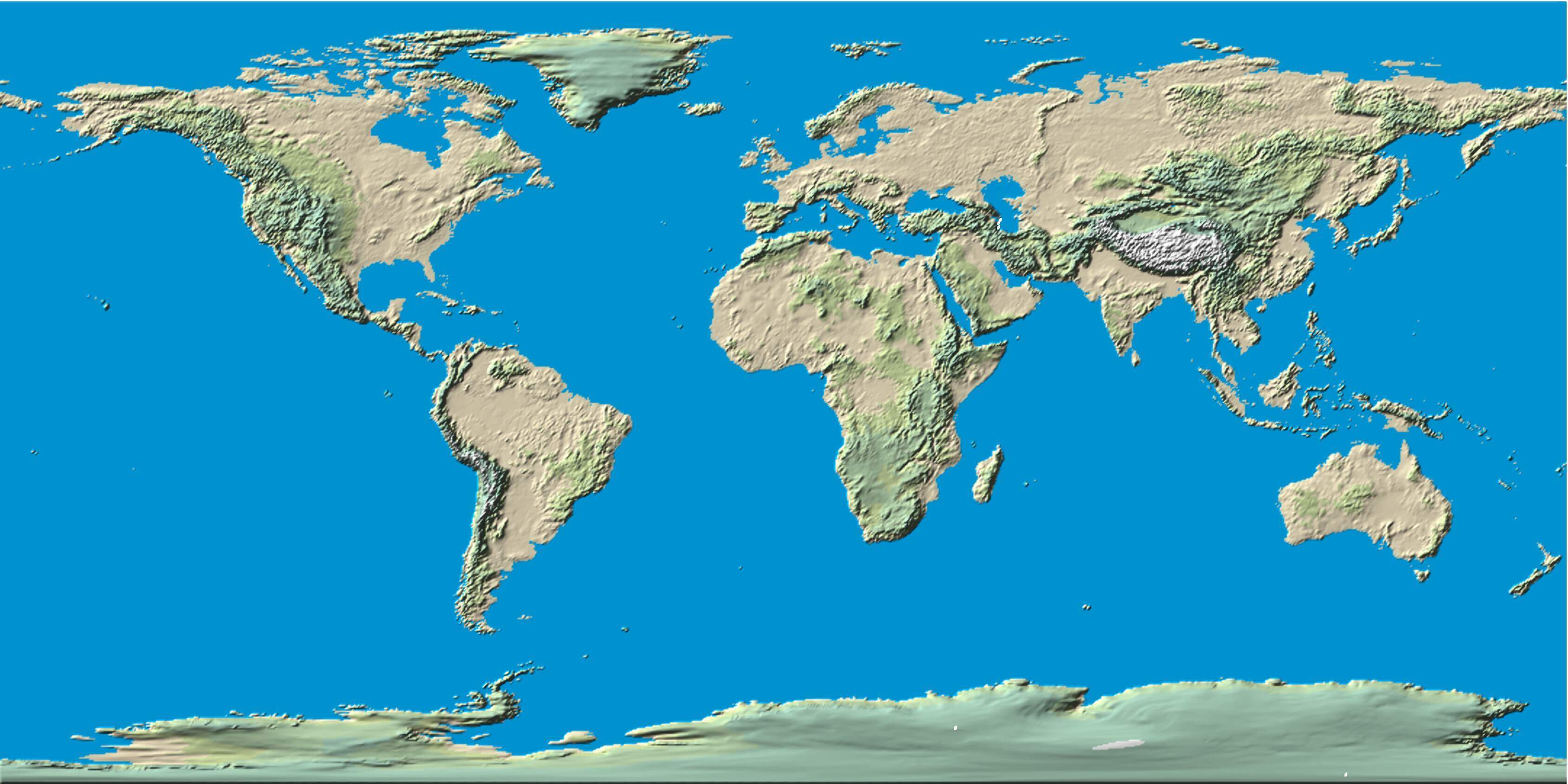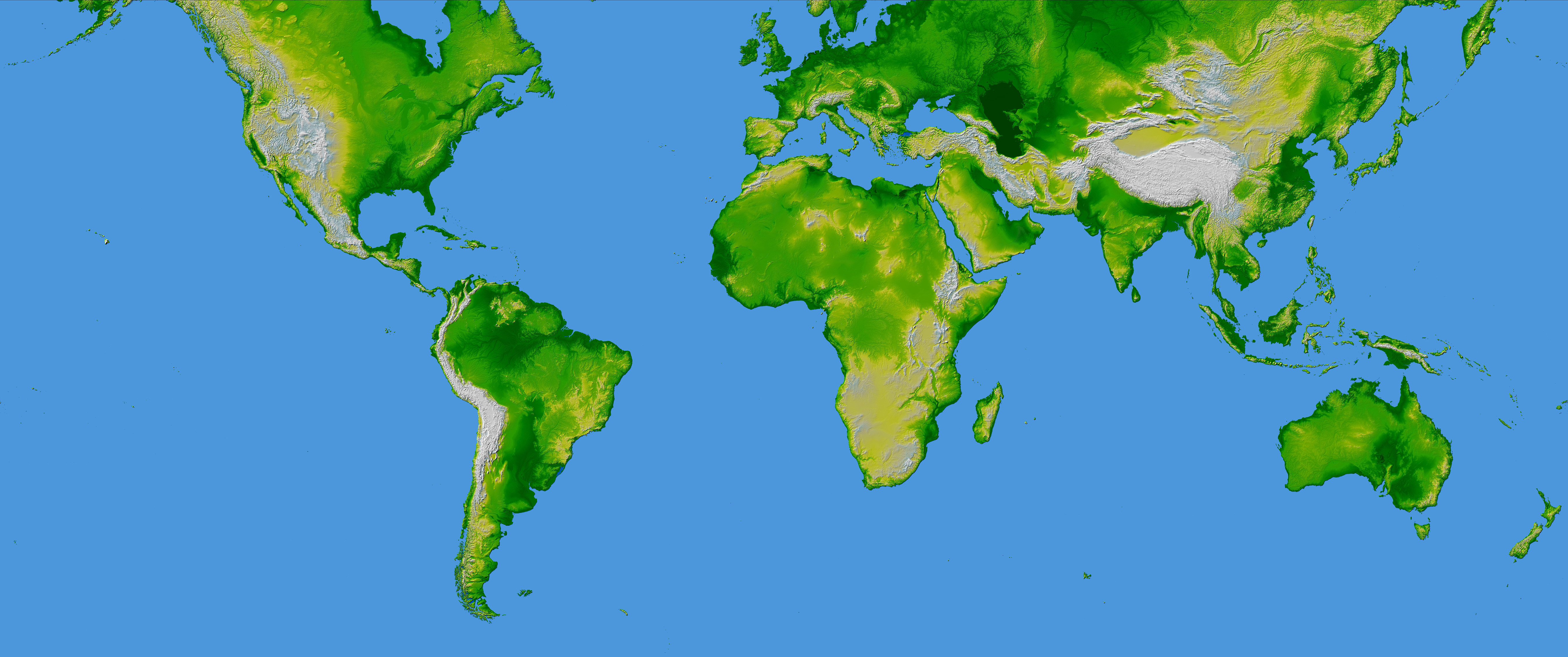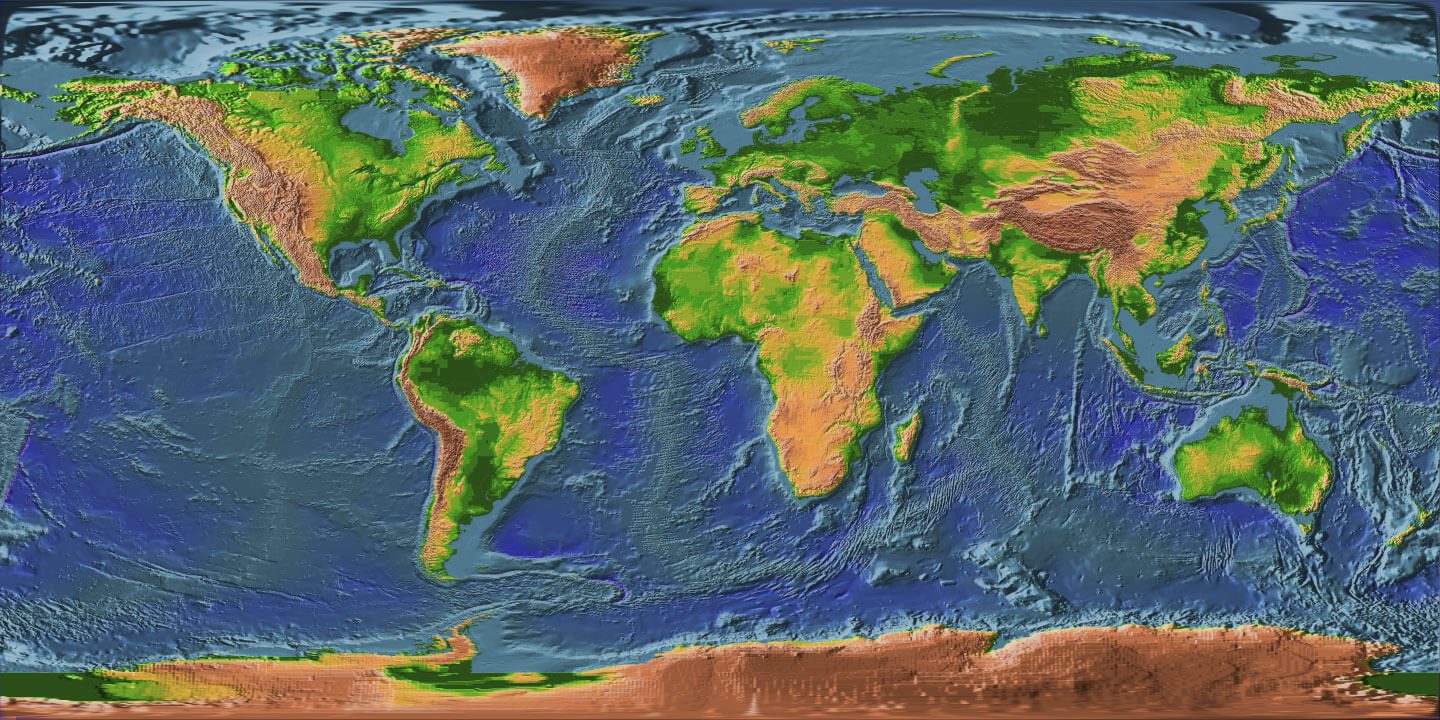
Elevation maps, also known as topographic maps or relief maps, depict the vertical dimension of the Earth’s surface. They use various techniques, such as color shading, contour lines, and digital elevation models (DEMs), to represent the height of different locations relative to a reference point, typically sea level. By studying these maps, we can identify mountain ranges, valleys, plateaus, and other landforms, gaining insights into the geological processes that shaped our planet.
What is Elevation?
Elevation refers to the height of a point above a reference level, most commonly mean sea level. It is a fundamental concept in geography and is essential for understanding various phenomena, such as climate patterns, water flow, and vegetation distribution. Elevation is typically measured in meters or feet.
Why are Elevation Maps Important?
- Geographic Studies: They provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, aiding in the study of landforms, drainage patterns, and regional variations.
- Geological Surveys: Elevation data helps geologists understand the structure and composition of the Earth’s crust, identify fault lines, and assess the risk of earthquakes and landslides.
- Environmental Monitoring: Elevation maps are used to monitor changes in land surface, such as glacier retreat, coastal erosion, and deforestation.
- Urban Planning: They assist urban planners in designing infrastructure, managing water resources, and mitigating the impact of natural disasters.
- Navigation and Aviation: Pilots and navigators rely on elevation data to plan routes, avoid obstacles, and ensure safe passage.
Creating Elevation Maps: Methods and Technologies
Traditional Surveying
Traditional surveying methods, such as using levels and theodolites, have been used for centuries to measure elevation. These methods involve establishing a network of benchmarks with known elevations and then using instruments to determine the height of other points relative to those benchmarks. While accurate, traditional surveying is time-consuming and labor-intensive, making it impractical for large-scale mapping.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing techniques, such as satellite imagery and airborne LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), have revolutionized the creation of elevation maps. These methods allow for the rapid and efficient collection of elevation data over large areas.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with sensors can capture images of the Earth’s surface from space. By analyzing these images, scientists can create digital elevation models (DEMs) that represent the terrain.
- LiDAR: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure the distance to the Earth’s surface. Airborne LiDAR systems can generate highly accurate and detailed elevation data, even in vegetated areas.
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs)
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface that stores elevation data as a grid of values. DEMs are the foundation for creating many types of elevation maps and are used in a variety of applications.
Interpreting Elevation Maps: Understanding the Visual Language
Elevation maps use various visual cues to represent elevation differences. Understanding these cues is essential for interpreting the information presented on the map.
Color Shading
Color shading is a common technique used in elevation maps to represent height. Typically, lower elevations are represented by green or blue colors, while higher elevations are represented by yellow, orange, or brown colors. The specific color scheme used can vary depending on the map.
Contour Lines
Contour lines are lines that connect points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. Contour lines can be used to identify hills, valleys, and other landforms.
Hypsometric Tinting
Hypsometric tinting is a technique that uses different colors to represent different elevation ranges. This technique can make it easier to visualize the overall topography of an area.
Relief Shading
Relief shading, also known as hillshading, simulates the effect of sunlight illuminating the terrain. This technique can enhance the visual representation of landforms and make it easier to identify subtle elevation changes.
Extreme Elevations: The Highest and Lowest Points on Earth
The Earth’s surface exhibits a wide range of elevations, from the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the deep trenches of the ocean floor.
Mount Everest: The Highest Point
Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas, is the highest point on Earth, with a summit elevation of approximately 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) above sea level. This iconic peak attracts climbers from all over the world, but its extreme altitude and harsh conditions make it a challenging and dangerous climb.
The Mariana Trench: The Lowest Point
The Mariana Trench, located in the western Pacific Ocean, is the deepest part of the world’s oceans. Its deepest point, the Challenger Deep, reaches a depth of approximately 10,929 meters (35,853 feet) below sea level. The pressure at this depth is immense, and only a few manned submersibles have ever ventured to the bottom of the trench.
Other Notable High and Low Points
- Aconcagua (South America): The highest peak in the Americas, reaching approximately 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
- Dead Sea (Middle East): The lowest land elevation on Earth, approximately 430.5 meters (1,412 feet) below sea level.
- K2 (Asia): The second-highest mountain in the world, known for its treacherous climbing conditions.
Applications of World Elevation Data
- Climate Modeling: Elevation influences temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. Elevation data is crucial for creating accurate climate models.
- Hydrology: Elevation data is used to model water flow, predict floods, and manage water resources.
- Agriculture: Elevation affects soil type, drainage, and sunlight exposure. This information is used to optimize crop selection and irrigation practices.
- Infrastructure Development: Elevation data helps engineers plan and design roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Disaster Management: Elevation maps are used to identify areas at risk of landslides, floods, and other natural disasters.
Commonly Asked Questions About World Elevation Maps
How are elevation maps created?
Elevation maps are created using a variety of methods, including traditional surveying, remote sensing (satellite imagery and LiDAR), and digital elevation models (DEMs).
What is the difference between elevation and altitude?
Elevation refers to the height of a point above a reference level, typically sea level. Altitude refers to the height of an object above the Earth’s surface.
What are contour lines?
Contour lines are lines that connect points of equal elevation on an elevation map. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope.
How can I find the elevation of a specific location?
You can find the elevation of a specific location using online mapping tools, topographic maps, or GPS devices.
What is a digital elevation model (DEM)?
A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface that stores elevation data as a grid of values.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Earth’s Topographic Diversity
A map of world elevation is more than just a visual representation of height; it’s a window into the geological history, environmental processes, and human activities that have shaped our planet. By understanding how these maps are created and interpreted, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s topographic diversity and its influence on our lives. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the hidden depths of the ocean trenches, elevation variations play a crucial role in shaping our world, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human settlements. By continuing to develop and refine elevation mapping technologies, we can gain even greater insights into the complex and dynamic nature of our planet.
Understanding the concepts of elevation, altitude, and topography is crucial in various fields, from geography and geology to urban planning and environmental science. Elevation maps, digital elevation models (DEMs), and remote sensing technologies like LiDAR provide valuable tools for visualizing and analyzing the Earth’s surface. These tools enable us to study landforms, monitor environmental changes, plan infrastructure projects, and mitigate the impact of natural disasters. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and accurate elevation data, leading to a deeper understanding of our planet and its diverse landscapes.