A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Native American Tribes of California
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Native American Tribes of California
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Native American Tribes of California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Native American Tribes of California

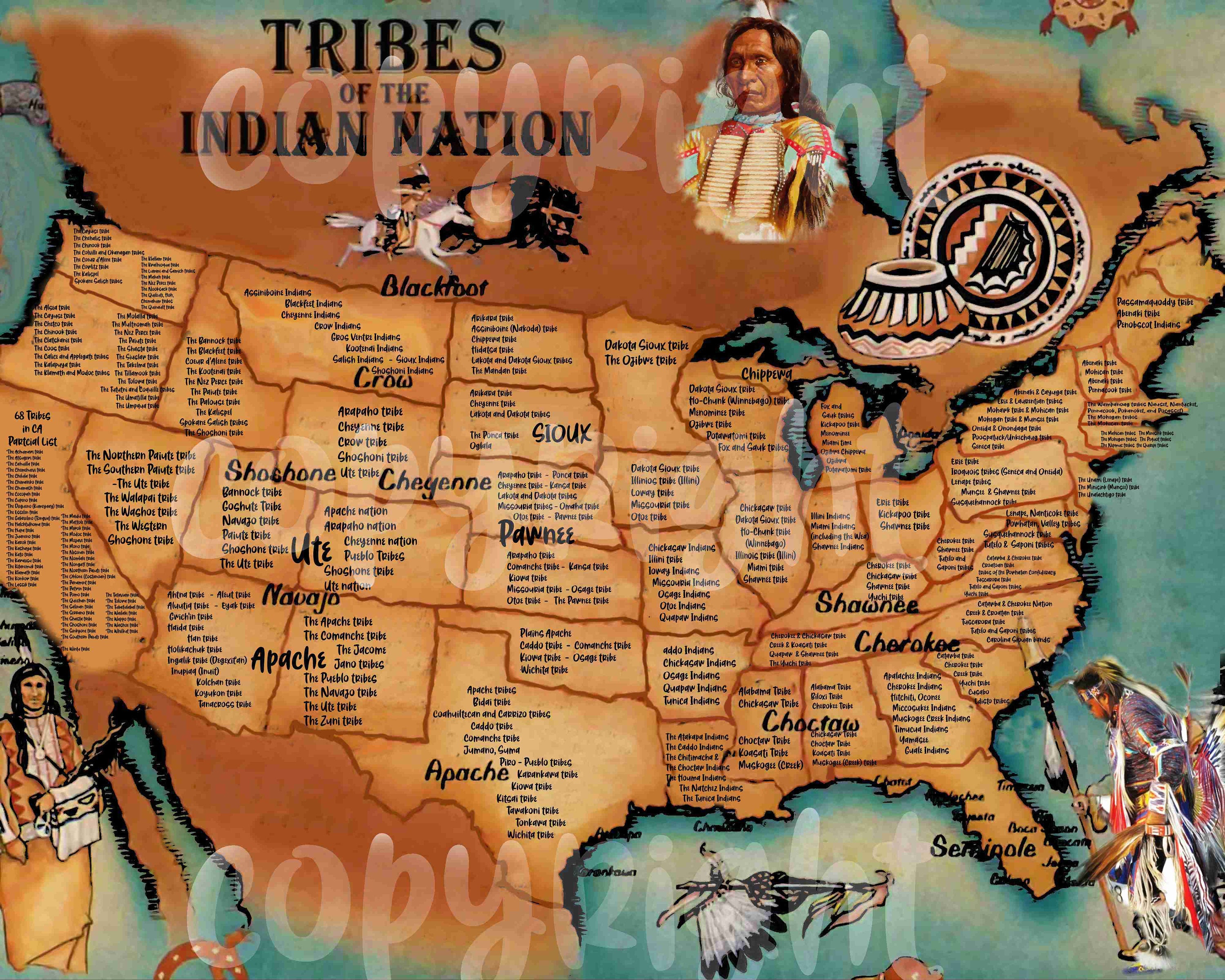
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and vibrant modern culture, is also home to a rich and complex tapestry of Native American heritage. For centuries, indigenous peoples thrived across the state, adapting to the unique environments from the towering redwoods of the north to the arid deserts of the south. Understanding the geographical distribution and cultural nuances of these tribes is essential for appreciating the state’s true history and fostering a deeper understanding of its present.
A Diverse Landscape, Diverse Peoples:
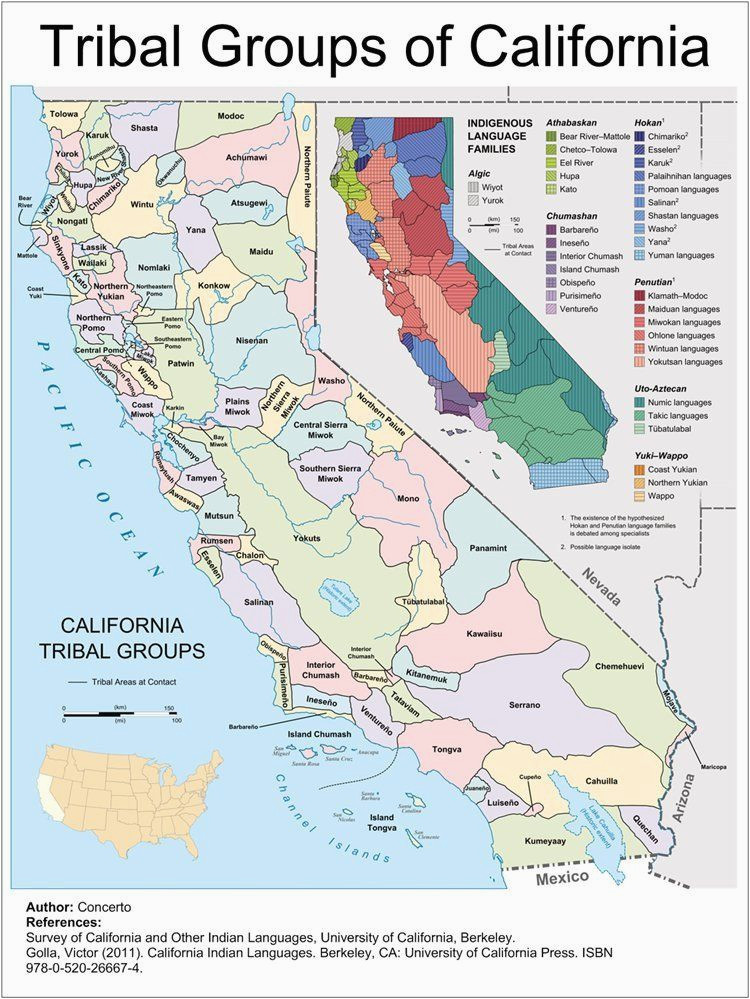
California’s varied geography fostered a remarkable diversity of cultures. The state’s indigenous population is divided into 105 distinct federally recognized tribes, each with its own unique language, traditions, and relationship with the land. These tribes are further grouped into larger linguistic families, reflecting the shared ancestry and historical connections between groups.
Key Linguistic Families of California:
- Penutian: This is the largest linguistic family in California, encompassing over 40 languages spoken throughout the state. The Penutian family includes tribes such as the Miwok, Maidu, and Wintun.
- Hokan: This family includes tribes from the coast, the deserts, and the Sierra Nevada mountains. Notable Hokan tribes include the Yurok, Karuk, and Chumash.
- Uto-Aztecan: This family, primarily found in the southern and eastern parts of the state, includes tribes like the Cahuilla, Serrano, and Luiseño.
- Algic: The Algic family is represented by the Wiyot tribe, located on the north coast of California.
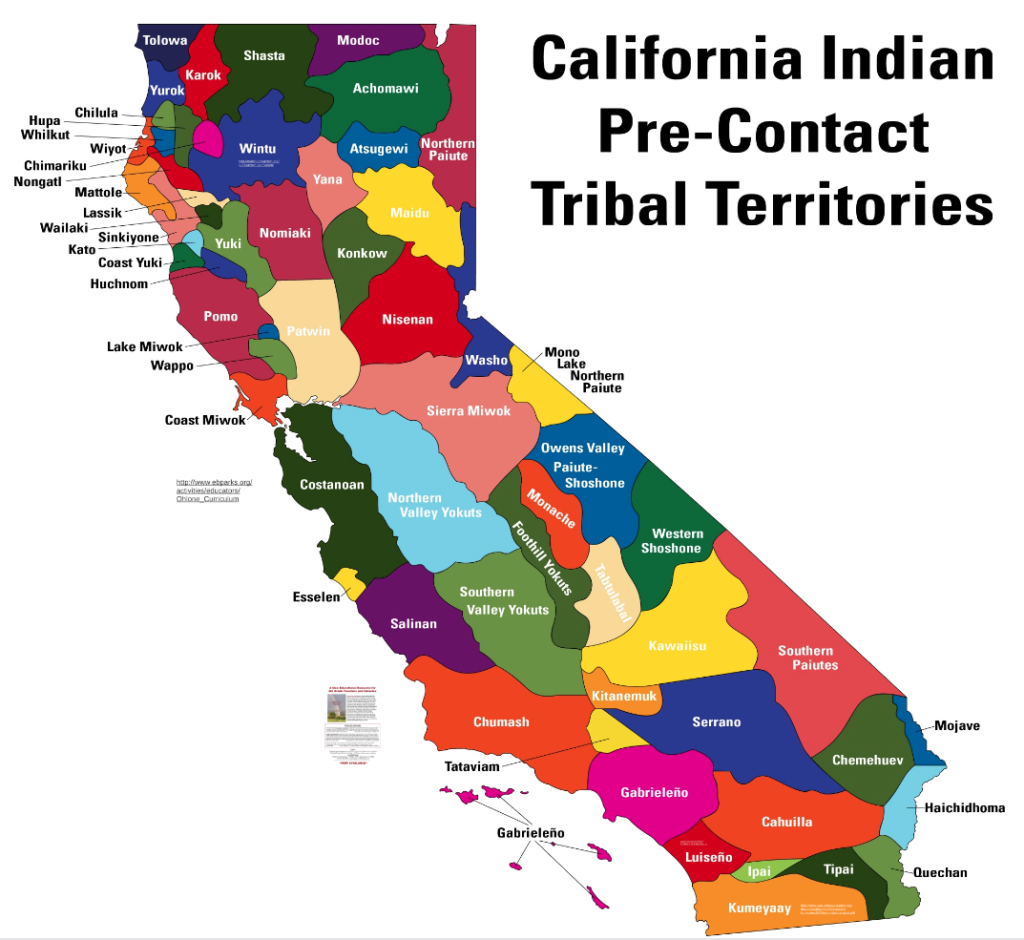
Visualizing the Tapestry: The California Native American Tribes Map
The California Native American Tribes Map is a powerful tool for understanding the geographic distribution of these diverse cultures. It visually illustrates the location of each tribe, showcasing their unique territories and their historical connections to the land. This map offers a valuable resource for:
- Historical Research: The map provides a visual framework for understanding the pre-colonial landscape of California, illuminating the intricate relationships between tribes and their territories.
- Cultural Preservation: It serves as a visual reminder of the enduring presence of indigenous cultures in California, highlighting the importance of preserving traditions and languages.
- Education: The map can be a valuable tool for teaching students about the rich history and cultural diversity of California’s indigenous peoples.
Beyond Geography: Understanding Cultural Diversity
While the map provides a visual representation of tribal territories, it is crucial to understand that each tribe has its own distinct cultural identity. This includes their language, traditions, spiritual beliefs, and social structures.
Examples of Cultural Diversity:
- Language: California was once home to over 100 distinct Native American languages. While many of these languages are now endangered, efforts are underway to revitalize and preserve them.
- Art and Crafts: Each tribe developed its own unique art forms, including basket weaving, pottery, beadwork, and carving. These crafts often reflected the natural materials and cultural traditions of the tribe.
- Ceremonies and Rituals: Native American tribes in California held a variety of ceremonies and rituals, often related to the natural world, such as the changing seasons, the harvest, and the spirit world.
The Impact of Colonization
The arrival of European colonists in California had a devastating impact on Native American populations. Diseases, forced displacement, and cultural suppression led to a significant decline in population and the loss of many traditions.
The Legacy of Resilience:
Despite these challenges, Native American tribes in California have shown remarkable resilience. They have continued to fight for their rights, preserve their cultures, and advocate for their communities.
The Importance of Understanding and Respect:
Understanding the history and culture of Native American tribes in California is not just about appreciating the past; it is about fostering respect and understanding in the present. By recognizing the enduring presence of indigenous cultures and their contributions to the state’s history and identity, we can create a more inclusive and equitable future for all Californians.
FAQs about Native American Tribes in California:
Q: How many Native American tribes are in California?
A: There are currently 105 federally recognized Native American tribes in California.
Q: What are some of the most well-known Native American tribes in California?
A: Some of the most well-known tribes include the Chumash, Yurok, Karuk, Miwok, Maidu, and Cahuilla.
Q: What is the significance of the California Native American Tribes Map?
A: The map visually represents the geographic distribution of California’s indigenous tribes, showcasing their historical territories and cultural connections to the land.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Native American tribes in California today?
A: Challenges include poverty, lack of access to healthcare and education, and the ongoing struggle for land rights and self-determination.
Q: How can I learn more about Native American tribes in California?
A: You can visit tribal websites, museums, cultural centers, and attend events organized by Native American communities.
Tips for Understanding Native American Tribes in California:
- Engage with tribal websites and resources: Many tribes have their own websites and social media pages, offering insights into their history, culture, and current initiatives.
- Visit tribal museums and cultural centers: These institutions offer exhibits and programs that showcase the rich cultural heritage of California’s indigenous peoples.
- Attend events organized by Native American communities: Participate in powwows, cultural festivals, and other events to experience the vibrant traditions and contemporary expressions of Native American culture.
- Support Native American-owned businesses: Patronize businesses owned and operated by Native American entrepreneurs to contribute to the economic well-being of tribal communities.
- Respect tribal sovereignty and self-determination: Acknowledge the right of tribes to govern themselves and make decisions about their own futures.
Conclusion:
The California Native American Tribes Map is a valuable tool for understanding the rich history and cultural diversity of California’s indigenous peoples. It serves as a visual reminder of the enduring presence of these cultures and the importance of respecting their traditions, languages, and sovereignty. By recognizing and appreciating the contributions of Native American tribes to California’s history and identity, we can foster a more inclusive and equitable future for all Californians.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Native American Tribes of California. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!