Defining the Circle of Influence: Understanding Radius on a Map
Related Articles: Defining the Circle of Influence: Understanding Radius on a Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Defining the Circle of Influence: Understanding Radius on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining the Circle of Influence: Understanding Radius on a Map

The concept of a radius around a point on a map might seem simple, but it holds immense power in various fields, from urban planning and logistics to environmental analysis and disaster response. It is a fundamental tool that enables us to visualize and quantify the spatial extent of influence or reach around a specific location.
Imagine a stone dropped into a pond, creating ripples that expand outwards. These ripples represent the radius – the distance from a central point to its surrounding area. On a map, this radius can be a physical distance measured in miles, kilometers, or other units, or it can be a conceptual representation of influence, such as the coverage area of a cell tower or the potential impact zone of a natural disaster.
Understanding the Concept of Radius
At its core, the concept of radius is based on the geometric definition of a circle. A circle is defined as the set of all points that are equidistant from a central point. This distance from the center to any point on the circle is called the radius.
On a map, this radius can be applied in various ways:
- Defining a geographic area: A radius can be used to define a circular area around a specific point. This could be the service area of a business, the potential impact zone of a hurricane, or the catchment area of a school.
- Measuring distance: The radius can be used to measure the distance from a central point to any other point within the defined area. This is useful for calculating travel times, determining the proximity of locations, and analyzing spatial relationships.
- Visualizing influence: The radius can be used to visualize the extent of influence or reach of a particular location or entity. For instance, the radius of a cell tower represents the area within which the tower can provide cellular service.
Applications of Radius in Various Fields
The concept of radius finds applications in a wide range of fields, each with its unique requirements and benefits:
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Determining service areas: Radius calculations help urban planners define service areas for public facilities like hospitals, schools, and fire stations. This ensures optimal accessibility and distribution of resources.
- Identifying potential development zones: By analyzing population density and proximity to amenities using radius calculations, planners can identify areas suitable for residential or commercial development.
- Assessing traffic congestion: Understanding the radius of influence of major intersections and road networks helps planners address traffic congestion and optimize transportation infrastructure.
2. Logistics and Transportation:
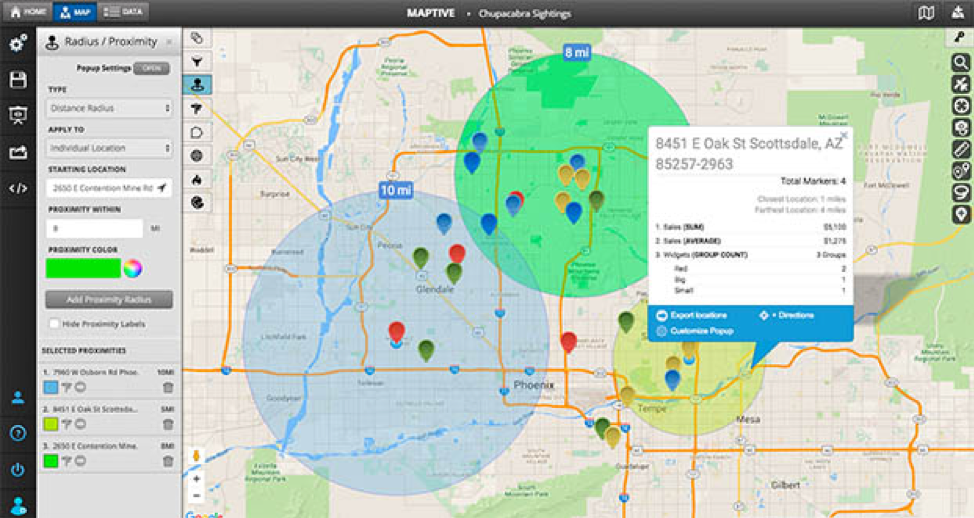
- Optimizing delivery routes: Logistics companies utilize radius calculations to determine the most efficient delivery routes for their vehicles, minimizing travel time and costs.
- Managing fleet operations: Radius-based analysis helps fleet managers monitor the location and movement of vehicles, optimizing resource allocation and ensuring timely service delivery.
- Identifying potential supply chain disruptions: By analyzing the radius of influence of natural disasters or other disruptions, logistics companies can develop contingency plans to mitigate potential supply chain disruptions.
3. Environmental Analysis and Management:
- Mapping pollution zones: Radius calculations are crucial for identifying and mapping areas affected by pollution from industrial sites, traffic, or other sources. This information helps in implementing mitigation strategies and protecting public health.
- Assessing environmental impact: By defining the radius of influence of development projects, environmental analysts can assess the potential impact on ecosystems, wildlife, and water resources.
- Monitoring wildlife populations: Radius analysis helps wildlife biologists track animal movements and understand their habitat ranges, aiding in conservation efforts.
4. Disaster Response and Emergency Management:
- Determining evacuation zones: During natural disasters, radius calculations are vital for defining evacuation zones and providing timely warnings to residents within the affected area.
- Deploying emergency resources: Radius analysis helps emergency responders determine the most efficient routes for deploying resources like ambulances, fire trucks, and search and rescue teams.
- Assessing post-disaster impact: By analyzing the radius of influence of a disaster, authorities can assess the extent of damage, prioritize relief efforts, and allocate resources effectively.
5. Marketing and Business Strategy:
- Targeting local customers: Businesses use radius calculations to target their marketing efforts to customers within a specific geographic area, maximizing reach and effectiveness.
- Analyzing customer demographics: Radius-based analysis helps businesses understand the demographics and purchasing habits of customers within their service area, informing marketing strategies and product development.
- Identifying potential expansion opportunities: By analyzing the radius of influence of existing businesses, companies can identify potential markets for expansion and assess the feasibility of new ventures.
FAQs about Radius Around a Point on a Map
1. How is radius measured on a map?
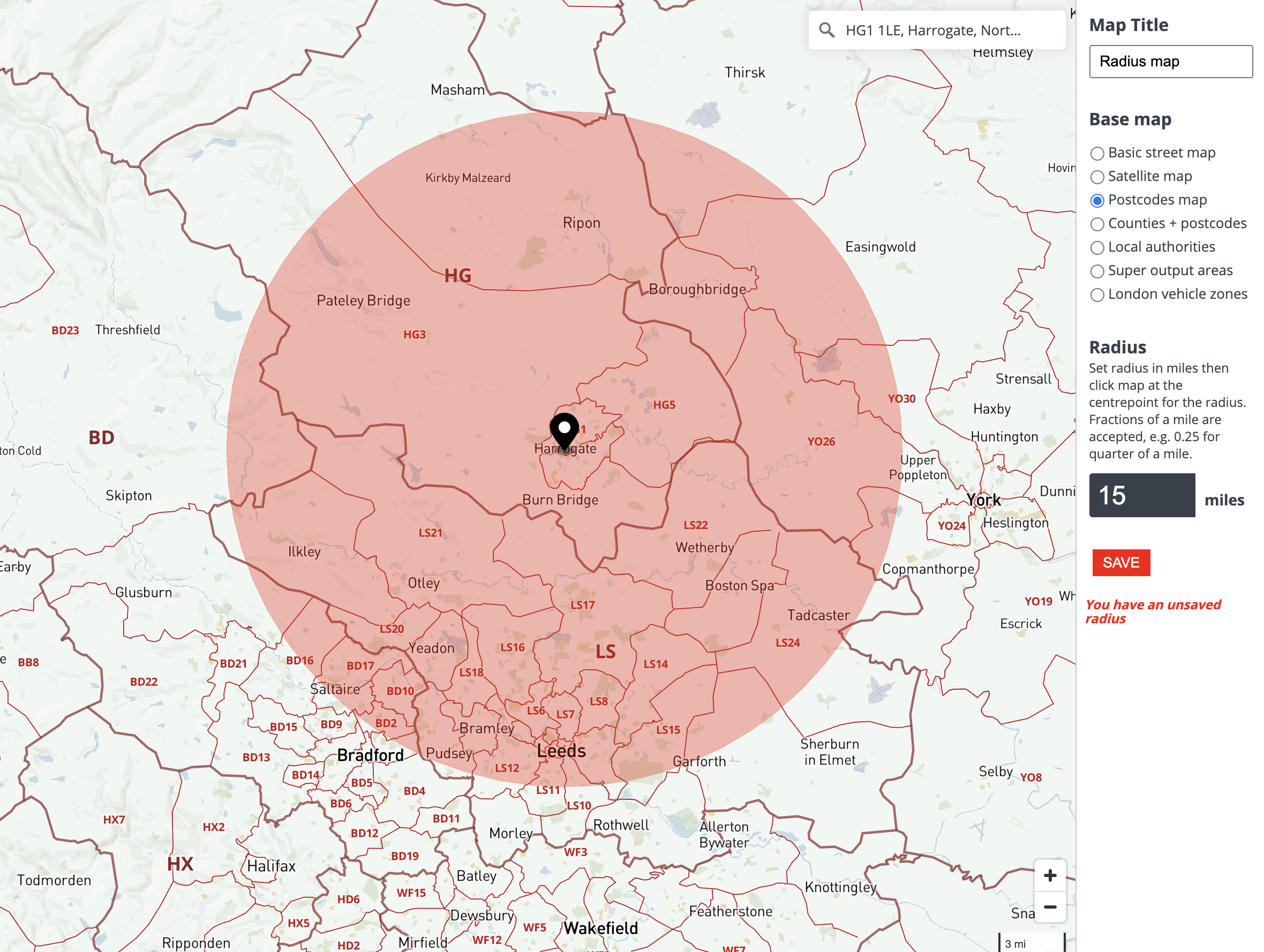
Radius is typically measured in units of distance, such as miles, kilometers, or meters. It can be calculated using various tools, including:
- Map software: Many online mapping platforms and GIS software offer tools for measuring radius and creating circular areas.
- GPS devices: GPS devices can measure the distance between two points, which can be used to determine the radius of a circle.
- Mathematical formulas: Using the coordinates of the center point and the desired radius, mathematical formulas can be used to calculate the perimeter and area of the circle.
2. What factors influence the choice of radius?
The choice of radius depends on the specific application and the factors being considered. Some key factors include:
- Purpose of the analysis: The radius should be chosen based on the specific objective of the analysis, such as identifying service areas, assessing environmental impact, or targeting customers.
- Scale of the map: The radius should be appropriate for the scale of the map. A radius of 1 mile may be suitable for a local map, while a radius of 100 miles may be more appropriate for a regional map.
- Data availability: The availability of relevant data, such as population density, traffic patterns, or environmental conditions, can influence the choice of radius.
3. What are the limitations of using radius on a map?
While radius is a powerful tool, it has some limitations:
- Oversimplification: Radius calculations can oversimplify complex spatial relationships, as they assume a uniform influence or reach within the defined area.
- Ignoring terrain and barriers: Radius calculations do not account for terrain features, obstacles, or other barriers that may affect the actual influence or reach of a location.
- Lack of context: Radius calculations alone do not provide context about the specific characteristics or conditions within the defined area.
Tips for Using Radius Effectively on a Map
- Define your objective: Clearly define the purpose of your analysis and choose a radius that is relevant to your objective.
- Consider the scale: Select an appropriate radius based on the scale of your map and the area you are analyzing.
- Use data sources: Utilize relevant data sources, such as population density, traffic patterns, or environmental conditions, to inform your radius calculations.
- Visualize the results: Use mapping software or other visualization tools to create clear and informative maps that showcase the radius and its implications.
Conclusion
The concept of radius around a point on a map is a fundamental tool that empowers us to visualize and quantify spatial relationships, influencing a wide range of fields. By understanding the principles of radius and its applications, we can make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and address complex spatial challenges. From urban planning and logistics to environmental analysis and disaster response, radius calculations provide valuable insights into the extent of influence, reach, and impact of locations and entities on the map. By embracing this powerful tool, we can unlock new possibilities for spatial analysis and decision-making.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining the Circle of Influence: Understanding Radius on a Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!