Navigating the Archipelago: A Regional Exploration of Japan
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Regional Exploration of Japan
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Regional Exploration of Japan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Regional Exploration of Japan
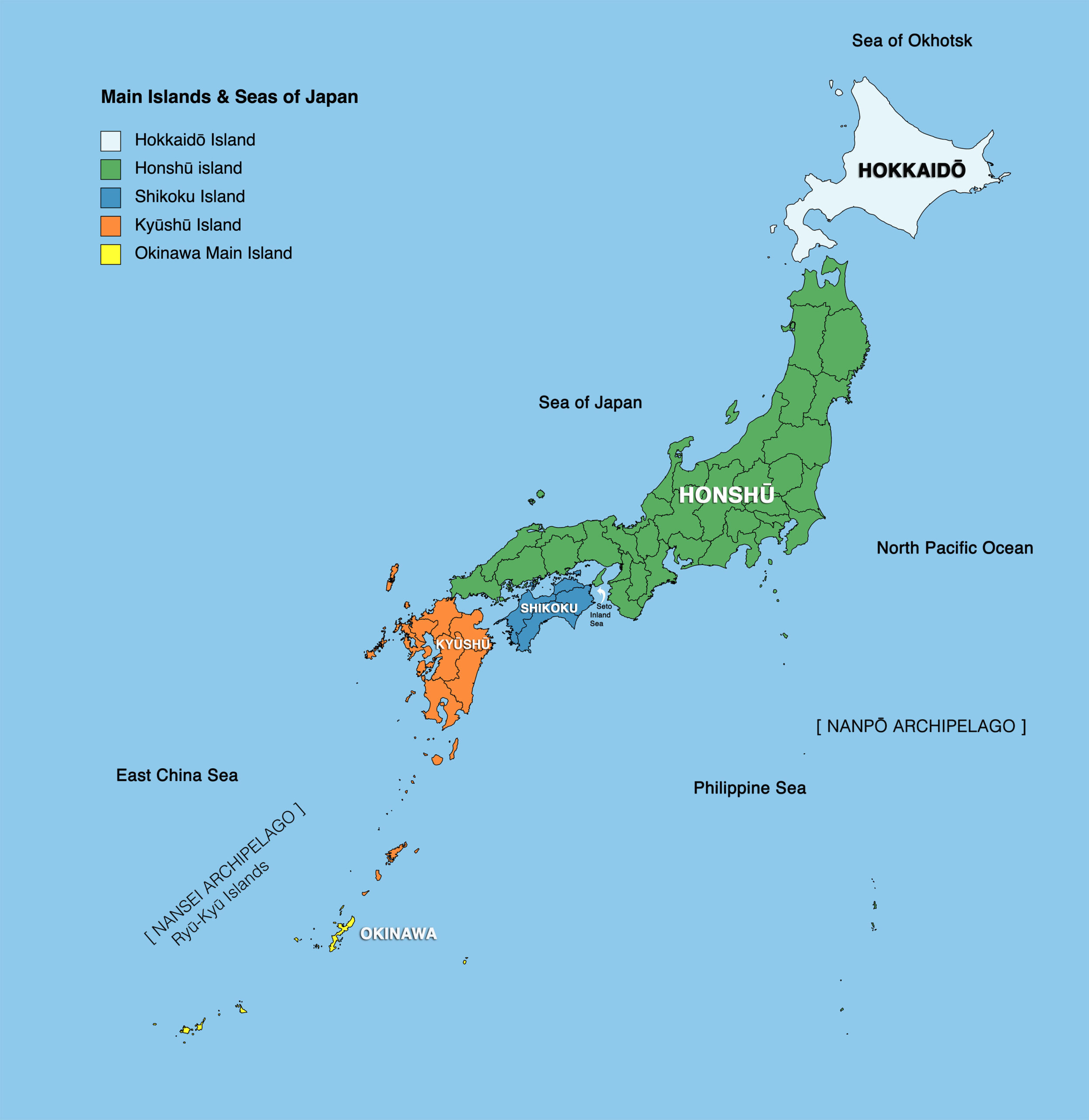
Japan’s geography is as complex and fascinating as its culture. A geographically diverse nation, understanding its regional divisions is crucial for appreciating its multifaceted history, unique characteristics, and economic dynamism. The archipelago’s arrangement, stretching thousands of kilometers, naturally lends itself to regional distinctions, reflected in variations in climate, dialect, cuisine, and traditions. This analysis explores these regional divisions, highlighting the unique attributes of each area.
Regional Divisions: A Geographical Overview
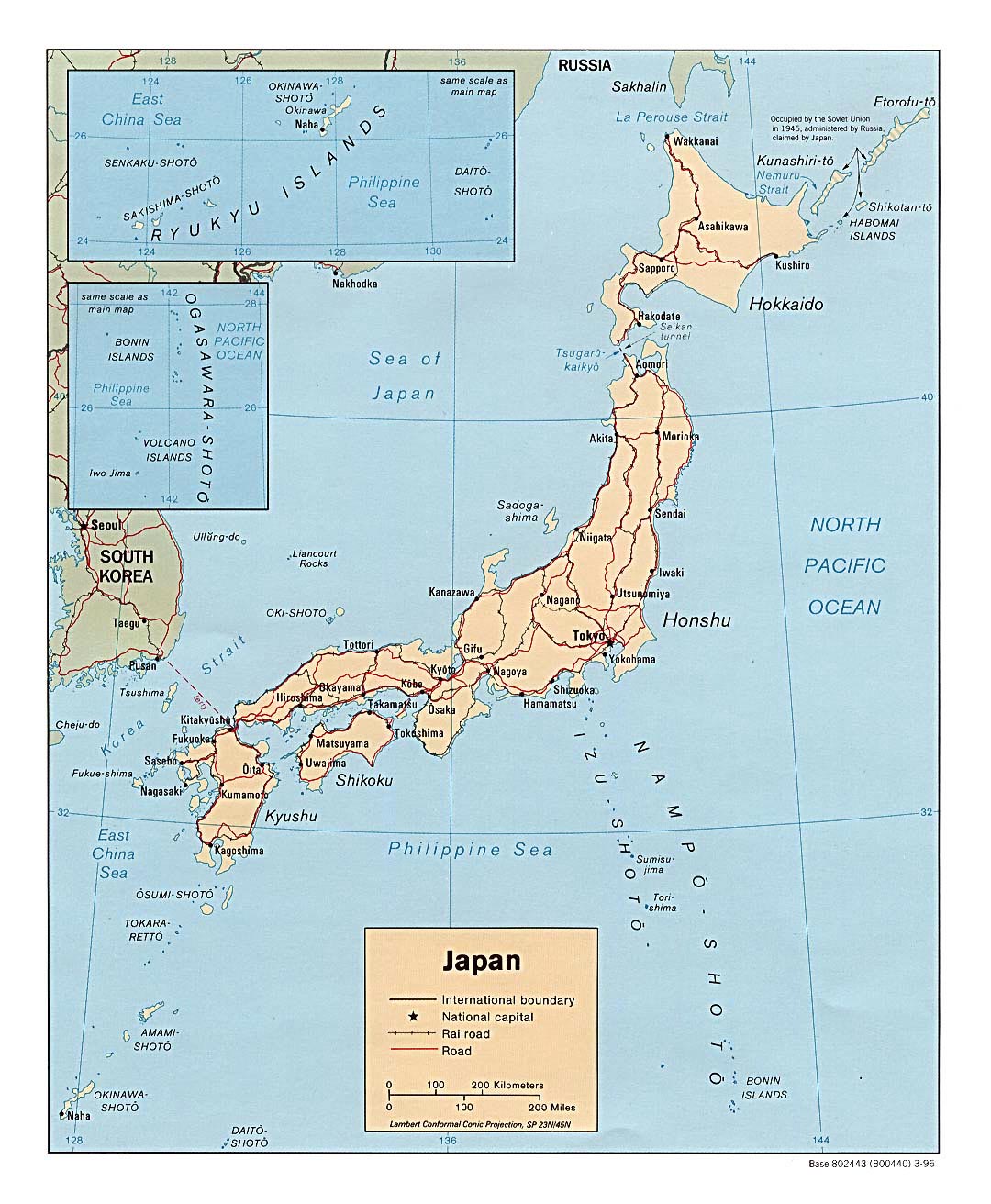
While numerous classifications exist, a common approach divides Japan into eight major regions: Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu-Okinawa. This framework provides a useful starting point for understanding the country’s spatial organization.
1. Hokkaido: The northernmost island, Hokkaido, is characterized by a cooler, more continental climate compared to the rest of Japan. Vast expanses of wilderness, volcanic landscapes, and abundant natural resources define this region. Its economy relies heavily on agriculture, fisheries, and tourism, with Sapporo serving as its largest city. The Ainu people, indigenous to the island, have a rich cultural heritage that continues to be celebrated and preserved.
2. Tohoku: Situated on the northern Honshu island, Tohoku is known for its rugged mountains, pristine coastlines, and onsen (hot springs). Agriculture, particularly rice cultivation, plays a significant role in the regional economy, alongside forestry and fisheries. The region is also gaining recognition for its burgeoning tourism sector, showcasing its natural beauty and traditional crafts. The region’s history is marked by strong samurai traditions and distinct regional dialects.
3. Kanto: Home to Tokyo, Japan’s capital, Kanto is the country’s most populous and economically powerful region. It encompasses a diverse landscape, ranging from the sprawling metropolis to mountainous areas and coastal plains. Manufacturing, finance, and technology are key industries, while cultural institutions and historical sites attract visitors from around the world. The region’s influence on national politics and culture is undeniable.
4. Chubu: Located in the central Honshu, Chubu is a mountainous region known for its spectacular scenery, including the Japanese Alps. Traditional crafts, such as pottery and textiles, are prevalent, along with industries related to tourism and manufacturing. The region’s diverse geography supports a variety of agricultural activities. Historically, Chubu served as a crucial link between eastern and western Japan.
5. Kansai: Often considered the cultural heartland of Japan, Kansai encompasses Kyoto, Osaka, and Kobe. This region boasts a rich history, renowned temples and shrines, and a vibrant culinary scene. Manufacturing, particularly in Osaka, plays a significant role in the economy, along with tourism and traditional arts. Kansai’s dialect and cultural traditions are distinct from those found in other parts of the country.
6. Chugoku: Located on the western side of Honshu, Chugoku is characterized by its mountainous terrain and coastal areas. Historically significant as a gateway to the Inland Sea, the region has a rich history and cultural heritage, reflected in its numerous castles and temples. Agriculture, fishing, and light manufacturing are key economic drivers.
7. Shikoku: The smallest of Japan’s four main islands, Shikoku is known for its serene landscapes, pilgrimage routes, and unique cultural traditions. Agriculture, forestry, and fishing are important economic activities, while tourism is increasingly significant. The region’s less densely populated areas offer a slower pace of life and a connection to nature.
8. Kyushu-Okinawa: Kyushu, the southernmost of the main islands, is a region of volcanic activity and diverse landscapes. Agriculture, particularly the cultivation of tea and citrus fruits, is important, along with industries related to tourism and manufacturing. Okinawa, a separate island chain, possesses a unique culture and history, distinct from the rest of Japan. Its subtropical climate and marine resources are central to its economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the key differences between the regions? Significant variations exist in climate, dialect, cuisine, and cultural traditions across the regions. Economic activities also differ based on geography and historical development.
-
How does geography influence regional development? Geographical factors, such as climate, terrain, and coastal access, heavily influence agricultural practices, industrial development, and overall economic activity.
-
What are the major cities in each region? Each region boasts significant urban centers, with Tokyo (Kanto) being the most populous, followed by Osaka (Kansai) and Nagoya (Chubu).
-
What is the significance of the regional dialects? Regional dialects, or "ben," reflect unique historical developments and cultural identities, adding to the richness and diversity of Japanese language.
-
How does regionalism impact national identity? Regionalism contributes to a nuanced understanding of national identity, demonstrating that a unified Japan is also a collection of diverse regional cultures and traditions.
Tips for Regional Exploration
-
Consider the time of year: Japan experiences distinct seasonal variations, impacting the suitability of certain activities and destinations.
-
Research regional specialties: Each region offers unique culinary experiences and traditional crafts.
-
Learn basic Japanese phrases: While English is spoken in major tourist areas, knowing basic phrases will enhance interactions with locals.
-
Utilize public transportation: Japan’s public transportation system is efficient and extensive, making it easy to explore different regions.
-
Respect local customs and traditions: Showing respect for local customs and traditions ensures a positive and enriching travel experience.
Conclusion
Understanding Japan’s regional divisions provides a crucial framework for appreciating the nation’s diverse geography, history, and culture. The variations in climate, landscape, economic activities, and cultural traditions across the eight major regions highlight the complexity and richness of the Japanese archipelago. Further exploration of these regions reveals a nation that is both unified and remarkably diverse. This multifaceted nature contributes significantly to Japan’s unique identity and enduring appeal.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Regional Exploration of Japan. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!