Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude on Maps
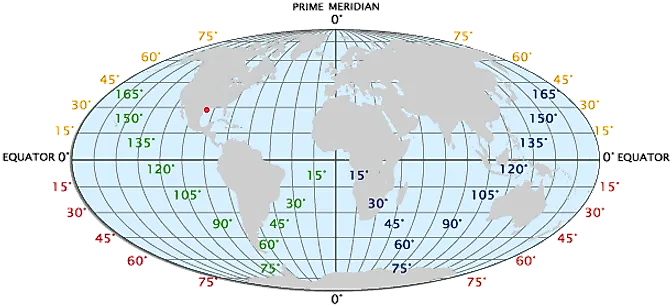
Maps, those flat representations of our three-dimensional world, are powerful tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding our planet. At the heart of their effectiveness lies a system of coordinates: longitude and latitude. These invisible lines, crisscrossing the globe, provide a precise way to pinpoint any location on Earth.
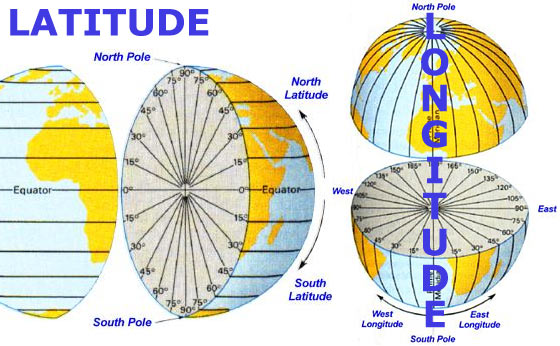
Longitude: The Lines of East and West
Imagine slicing an orange into segments. Each slice represents a line of longitude. These lines run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, forming semi-circles that converge at the poles. The prime meridian, a designated line passing through Greenwich, England, serves as the zero-degree longitude. Locations east of the prime meridian are assigned positive values, while those to the west receive negative values.
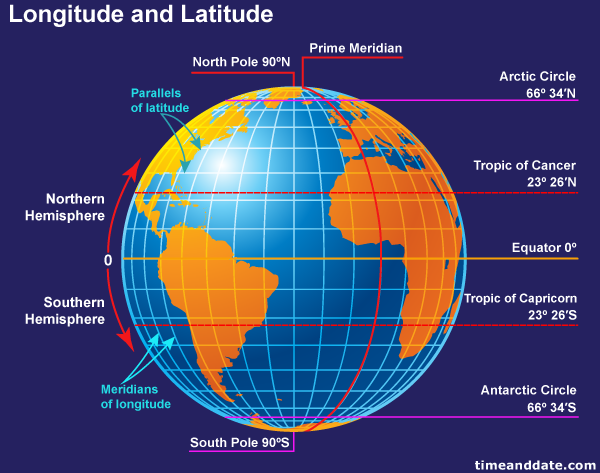
Latitude: The Lines of North and South
Now, imagine cutting the orange horizontally, creating circles around the equator. These circles represent lines of latitude. They run parallel to the equator, which is assigned a value of zero degrees. Locations north of the equator receive positive values, while those south receive negative values. The North Pole is at 90 degrees north, and the South Pole at 90 degrees south.
Understanding the Grid System
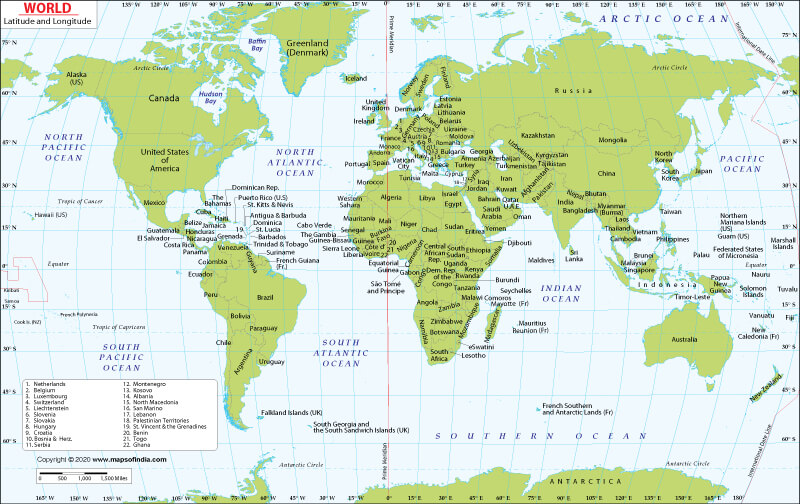
The intersection of longitude and latitude lines creates a grid system, akin to a giant chessboard covering the Earth. Each point on the globe can be identified by its unique combination of longitude and latitude coordinates. This system, known as the geographic coordinate system, is fundamental to navigation and geographical data analysis.
Reading a Map’s Coordinates
To read a map’s coordinates, look for the lines representing longitude and latitude. These lines are usually marked with numbers indicating their degree values. The location of a specific point is determined by finding the intersection of the corresponding longitude and latitude lines.
Example: Finding a Location on a Map
Let’s say you want to locate a city with coordinates 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W.
- Find the latitude line: Locate the line representing 40.7128° North.
- Find the longitude line: Locate the line representing 74.0060° West.
- Locate the intersection: The point where these two lines intersect represents the location of the city.
Benefits of Understanding Longitude and Latitude
The ability to read and interpret longitude and latitude coordinates offers numerous benefits:
- Accurate Navigation: Longitude and latitude are crucial for accurate navigation, guiding ships, planes, and even cars.
- Precise Location Identification: They provide a precise way to identify and record the location of any point on Earth.
- Geographic Data Analysis: These coordinates are essential for various geographic data analysis tasks, including mapping, weather forecasting, and environmental studies.
- Understanding Geographic Phenomena: Understanding longitude and latitude helps comprehend various geographic phenomena, such as time zones, climate patterns, and the distribution of natural resources.
- Global Communication: They facilitate communication and collaboration between people across different geographical locations.
FAQs on Reading Longitude and Latitude
Q: How are longitude and latitude measured?
A: Longitude and latitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. A degree is divided into 60 minutes, and a minute is divided into 60 seconds. For example, 40.7128° N can be expressed as 40 degrees, 42 minutes, and 46.08 seconds North.
Q: Why are there negative values for longitude and latitude?
A: Negative values are used to distinguish locations west of the prime meridian and south of the equator.
Q: How do I convert decimal degrees to degrees, minutes, and seconds?
A: To convert decimal degrees to degrees, minutes, and seconds:
- The whole number represents the degrees.
- Multiply the decimal part by 60 to get the minutes.
- Multiply the decimal part of the minutes by 60 to get the seconds.
Q: How accurate do coordinates need to be?
A: The required accuracy depends on the application. For general navigation, a few decimal places are sufficient. For precise applications like surveying or mapping, more decimal places are needed.
Tips for Reading Longitude and Latitude
- Practice: The best way to learn is through practice. Use online maps or atlases to identify locations based on their coordinates.
- Use a compass: A compass can help you visualize the cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) and understand how longitude and latitude relate to them.
- Study maps: Examine different types of maps and pay attention to how longitude and latitude lines are displayed.
- Utilize online tools: Many online tools and websites offer interactive maps and coordinate conversion features.
Conclusion
Understanding longitude and latitude is crucial for navigating our world, analyzing geographical data, and gaining a deeper understanding of our planet. By mastering the ability to read and interpret these coordinates, you unlock a powerful tool for exploration, discovery, and knowledge. From pinpointing locations on maps to understanding the complexities of our world, longitude and latitude play a fundamental role in our understanding of the Earth and our place within it.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!