Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Location Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Location Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Location Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Location Maps
The ability to pinpoint one’s location on a map has been a cornerstone of human exploration and navigation for centuries. From rudimentary star charts to sophisticated nautical maps, humanity has strived to understand its position within the vastness of the world. The advent of GPS technology, however, revolutionized this process, ushering in an era of unprecedented accuracy and accessibility. This article delves into the intricate workings of GPS location maps, exploring their multifaceted applications and the profound impact they have on our daily lives.
The Foundation of GPS: A Symphony of Satellites
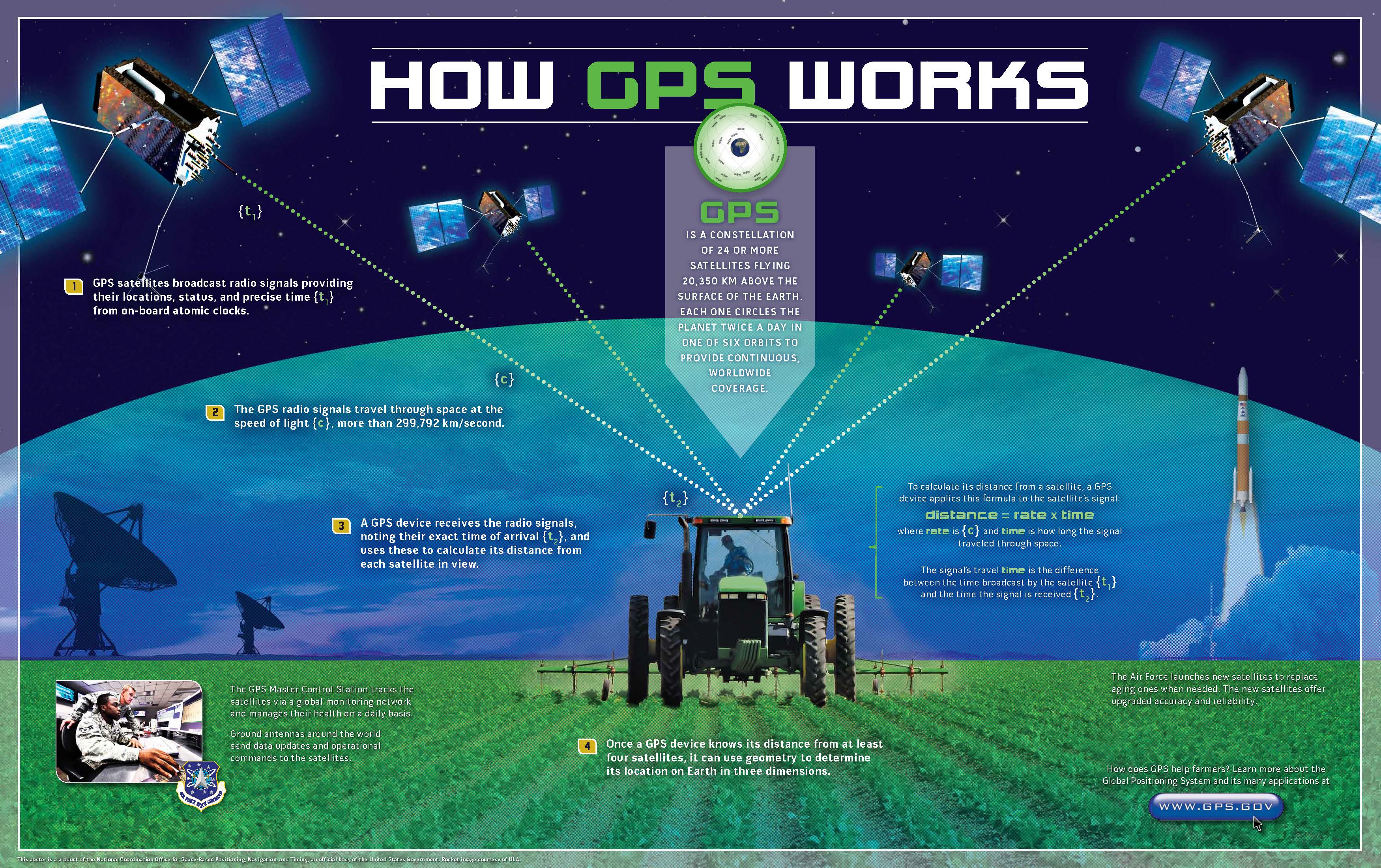
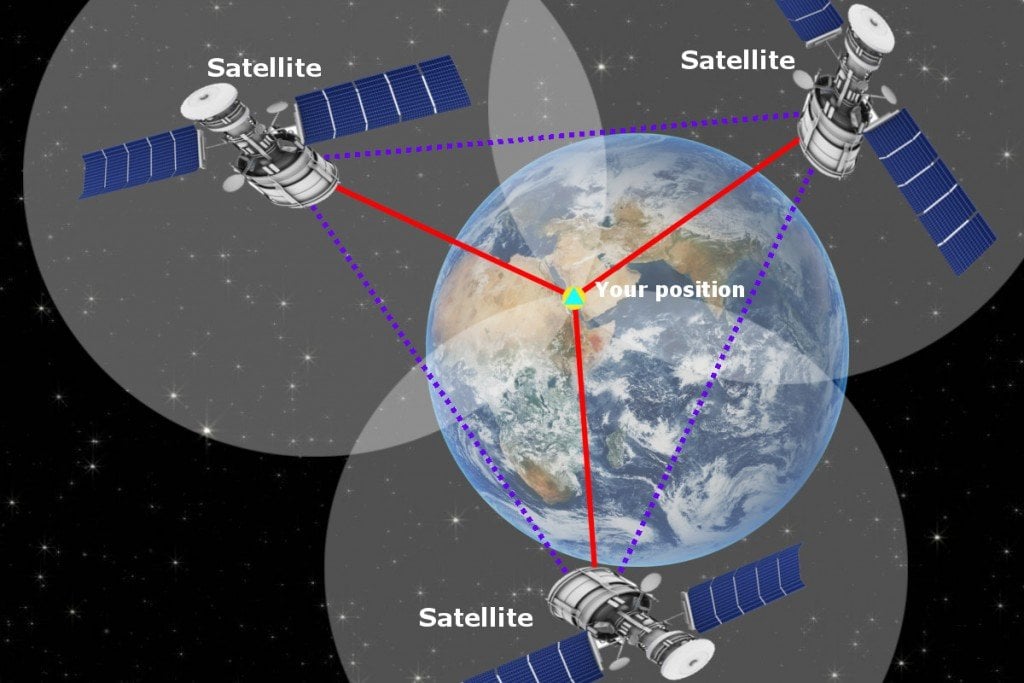
GPS, an acronym for Global Positioning System, is a network of 31 satellites orbiting Earth at an altitude of approximately 12,550 miles. These satellites constantly transmit radio signals, providing a constant stream of information about their precise location and time. Ground-based receivers, such as those found in smartphones and navigation devices, can pick up these signals, enabling them to calculate their own position with remarkable accuracy.
The core principle of GPS lies in trilateration, a method that utilizes the distances between three known points to determine an unknown location. In the case of GPS, the satellites serve as these known points. By measuring the time it takes for a signal to travel from each satellite to the receiver, the device can calculate its distance from each satellite. Combining these distances from three satellites, the receiver can pinpoint its location on the Earth’s surface.
Beyond the Basics: Refining Accuracy and Enhancing Functionality
While the core GPS system provides a foundation for location determination, advancements in technology have significantly refined its accuracy and expanded its capabilities.
1. Differential GPS (DGPS): DGPS utilizes ground-based reference stations to enhance the accuracy of GPS measurements. These stations receive signals from the GPS satellites and compare them to known positions on the ground. This information is then transmitted to nearby receivers, allowing them to correct for errors in the satellite signals and achieve significantly higher accuracy.
2. Assisted GPS (A-GPS): A-GPS leverages cellular networks to accelerate the process of acquiring satellite signals. By utilizing information about the receiver’s approximate location from the cellular network, A-GPS can significantly reduce the time it takes to lock onto satellite signals, particularly in areas with limited satellite visibility.
3. Real-Time Kinematic (RTK): RTK is a highly precise method used in surveying and other applications requiring centimeter-level accuracy. It involves two receivers, one acting as a base station with a known position and the other as a rover. By exchanging data between the two receivers, RTK can eliminate errors caused by atmospheric conditions and other factors, achieving exceptional accuracy.
4. GPS-enabled Mapping Applications: The integration of GPS with mapping software has revolutionized navigation and location-based services. These applications utilize GPS data to provide real-time location information, route guidance, traffic updates, and various other features, transforming how we navigate our surroundings.
The Unseen Impact: GPS Location Maps in Our Lives
GPS location maps have become an integral part of our modern world, seamlessly woven into the fabric of our daily lives. Their applications extend far beyond navigation, influencing numerous sectors and profoundly shaping our interactions with the world.
1. Transportation and Logistics: GPS technology is the backbone of modern transportation systems. From ride-sharing services and delivery platforms to fleet management and traffic control, GPS location maps enable efficient routing, real-time tracking, and optimized logistics, revolutionizing how goods and people move around the world.
2. Emergency Services and Public Safety: GPS plays a critical role in emergency response and public safety. Law enforcement agencies utilize GPS tracking to locate suspects and monitor crime scenes. Emergency medical services rely on GPS for rapid dispatch and navigation to accident sites, saving valuable time and potentially lives.
3. Agriculture and Resource Management: GPS technology has transformed agricultural practices, enabling precision farming and efficient resource management. Farmers can use GPS-guided equipment to optimize fertilizer application, minimize pesticide use, and maximize crop yields. GPS also facilitates land surveying, resource monitoring, and wildlife tracking, contributing to sustainable land management practices.
4. Urban Planning and Development: GPS location maps are essential tools for urban planners and developers. They provide valuable data for traffic analysis, infrastructure planning, and the development of smart cities. GPS-based mapping applications can help identify areas with high pedestrian traffic, analyze traffic patterns, and optimize urban design for improved mobility and livability.
5. Scientific Research and Exploration: GPS technology has become indispensable for scientific research and exploration. Researchers use GPS to track animal movements, monitor environmental changes, and study geological formations. GPS-enabled devices are essential for navigation in remote areas and for precise location data collection in various scientific disciplines.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about GPS Location Maps
Q: How accurate is GPS?
A: The accuracy of GPS depends on various factors, including the number of satellites in view, atmospheric conditions, and the quality of the receiver. Standard GPS systems typically achieve an accuracy of around 10 meters, while more advanced methods like DGPS and RTK can achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
Q: Can GPS be used indoors?
A: Standard GPS systems are designed for outdoor use and may not function accurately indoors due to obstructions from buildings and other structures. However, some indoor positioning systems utilize Wi-Fi or Bluetooth signals to provide location information within buildings.
Q: Are there any privacy concerns associated with GPS tracking?
A: The widespread use of GPS technology has raised privacy concerns about the potential for unauthorized tracking and data collection. It is essential to be aware of the privacy settings on your devices and to consider the implications of sharing your location data with various applications.
Q: What are some tips for using GPS effectively?
Tips for Effective GPS Usage:
- Ensure a clear view of the sky: GPS receivers need a clear view of the sky to receive satellite signals. Avoid using GPS in areas with dense foliage or tall buildings.
- Calibrate your device regularly: Regular calibration helps ensure the accuracy of your GPS readings.
- Use reliable mapping applications: Choose mapping applications with a proven track record for accuracy and reliability.
- Be aware of battery life: GPS usage can drain battery life quickly. Ensure your device has sufficient charge before embarking on long journeys.
- Understand the limitations of GPS: GPS is not always perfect and can be affected by various factors. It is essential to be aware of these limitations and use other sources of information when navigating.
Conclusion: A Transformative Technology Shaping Our World
GPS location maps have emerged as a transformative technology, profoundly impacting our lives and shaping our interactions with the world. Their applications extend far beyond navigation, influencing various sectors and driving innovation in countless fields. From optimizing transportation and logistics to enhancing emergency response and facilitating scientific research, GPS technology has become an integral part of our modern world, paving the way for a future filled with unprecedented connectivity and efficiency. As GPS technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of our interconnected world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Location Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!