Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization
Related Articles: Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization
- 3.1 The Power Grid Map: A Visual Representation of Energy Flow
- 3.2 Types of Power Grid Maps
- 3.3 Key Features of Power Grid Maps
- 3.4 Benefits of Power Grid Maps
- 3.5 FAQs about Power Grid Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Power Grid Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: Power Grid Maps – A Foundation for a Sustainable Future
- 4 Closure
Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization

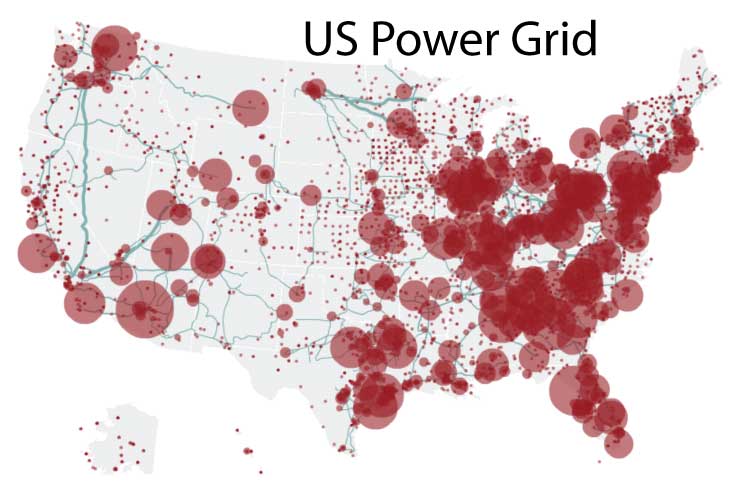
Power grids are the intricate networks that deliver electricity to homes, businesses, and industries across the globe. These complex systems, often spanning vast distances, are the lifeblood of modern society, enabling everything from basic lighting to sophisticated technological advancements. Understanding the intricate web of power grids is crucial for ensuring a reliable and efficient energy supply, and power grid maps serve as essential tools for visualizing and analyzing these critical systems.
The Power Grid Map: A Visual Representation of Energy Flow
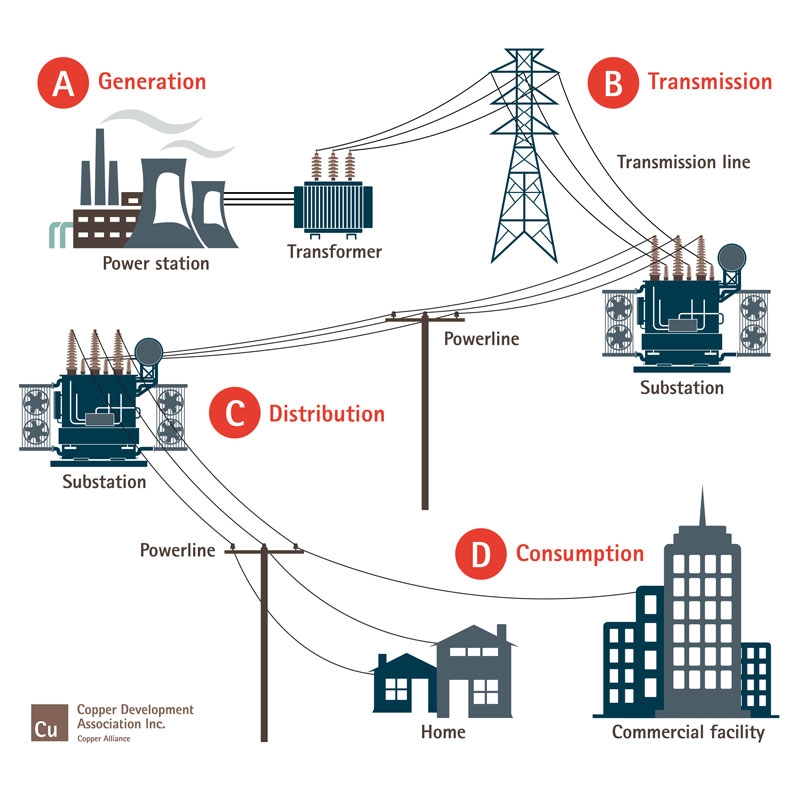
Power grid maps provide a visual representation of the interconnectedness of power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure. They depict the flow of electricity from power plants to consumers, showcasing the intricate network of power lines, substations, transformers, and other critical components. These maps serve as a vital reference for various stakeholders, including:
- Utilities: Power grid maps allow utilities to monitor their systems in real-time, identify potential bottlenecks, and plan for future expansion. They are essential for efficient operation and maintenance of the grid.
- Regulators: Regulatory agencies utilize power grid maps to assess the reliability and security of the electricity infrastructure, ensuring compliance with safety standards and environmental regulations.
- Researchers: Scientists and engineers utilize power grid maps to study the impact of renewable energy integration, analyze grid stability, and develop innovative solutions for improving grid efficiency.
- Policymakers: Power grid maps inform policy decisions regarding energy infrastructure development, grid modernization, and the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Types of Power Grid Maps
Power grid maps can be categorized into various types based on their purpose and level of detail:
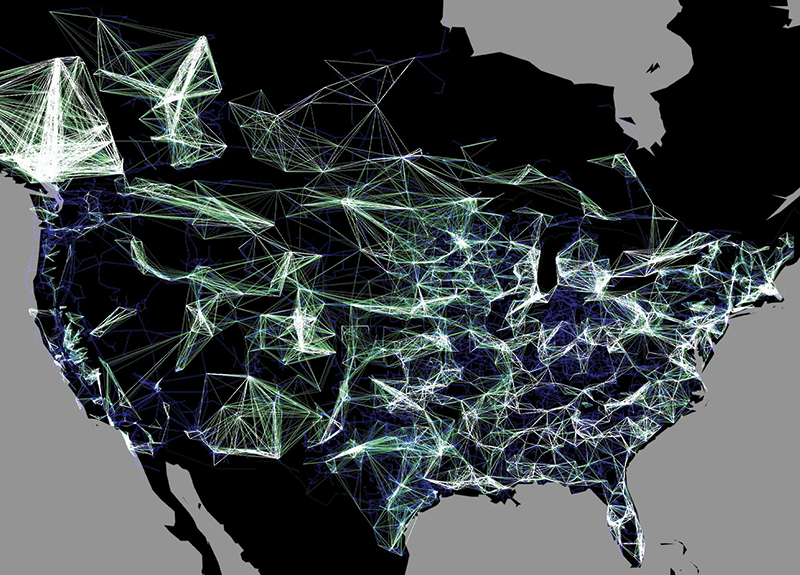
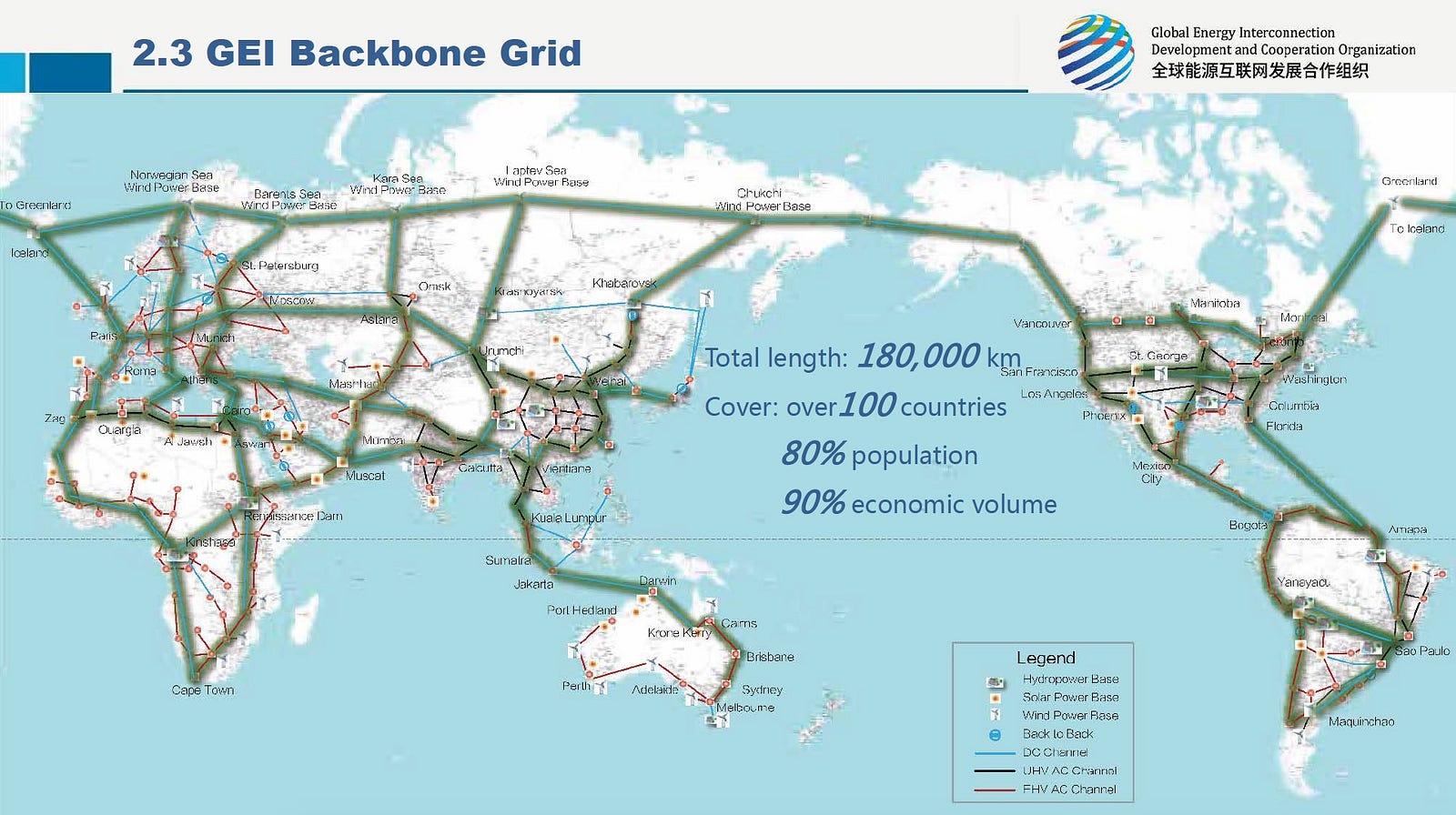
- Transmission System Maps: These maps focus on the high-voltage transmission lines that carry electricity over long distances. They depict the major power plants, substations, and transmission corridors, providing a comprehensive overview of the national or regional electricity network.
- Distribution System Maps: These maps detail the lower-voltage distribution networks that carry electricity from substations to individual consumers. They showcase the intricate network of distribution lines, transformers, and feeder circuits, providing a detailed view of the local electricity infrastructure.
- Real-Time Operational Maps: These maps display real-time data on power flow, voltage levels, and other operational parameters. They provide a dynamic view of the grid’s performance, enabling utilities to monitor and control the system effectively.
- Historical Grid Maps: These maps showcase the evolution of power grids over time, providing valuable insights into the growth and development of the electricity infrastructure. They are essential for understanding the historical context of grid planning and development.
Key Features of Power Grid Maps
Power grid maps incorporate various features to provide a comprehensive understanding of the electricity infrastructure:
- Geographic Location: Power grid maps are overlaid on geographical maps, providing a clear spatial representation of the grid’s location and extent.
- Power Plant Locations: The maps highlight the locations of various power plants, including fossil fuel, nuclear, hydroelectric, and renewable energy sources.
- Transmission Lines: Power lines are depicted with varying line thicknesses or colors to represent voltage levels and transmission capacity.
- Substations: Substations are marked on the map, indicating key locations for voltage transformation and grid control.
- Transformers: Transformers are represented as symbols, showcasing the crucial role they play in voltage conversion.
- Load Centers: Areas with high electricity demand, such as urban centers and industrial zones, are identified on the map.
- Real-Time Data: Operational maps incorporate real-time data on power flow, voltage, frequency, and other critical parameters.
Benefits of Power Grid Maps
Power grid maps offer numerous benefits for various stakeholders, enabling them to:
- Visualize Complex Systems: Power grid maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of the intricate network of power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure.
- Identify Bottlenecks and Vulnerabilities: By analyzing power flow patterns and load distribution, maps help identify potential bottlenecks, congested areas, and vulnerabilities within the grid.
- Plan for Future Expansion: Power grid maps facilitate the planning and development of future grid infrastructure, ensuring adequate capacity to meet growing electricity demand.
- Optimize Grid Operations: Real-time operational maps provide valuable insights into grid performance, enabling utilities to optimize power flow, voltage control, and system reliability.
- Improve Grid Security: By identifying potential vulnerabilities, power grid maps support efforts to enhance grid security and resilience against cyberattacks and natural disasters.
- Facilitate Renewable Energy Integration: Maps aid in the planning and integration of renewable energy sources, ensuring a smooth transition to a more sustainable energy future.
- Promote Public Awareness: Power grid maps can be used to educate the public about the complex and interconnected nature of the electricity infrastructure, fostering a greater appreciation for the vital role it plays in modern society.
FAQs about Power Grid Maps
Q: What are the different types of power grid maps?
A: Power grid maps can be categorized into transmission system maps, distribution system maps, real-time operational maps, and historical grid maps, each offering a specific perspective on the grid’s infrastructure and operation.
Q: How are power grid maps used in grid planning and development?
A: Power grid maps are essential tools for planning and developing future grid infrastructure, ensuring adequate capacity to meet growing electricity demand and integrating renewable energy sources.
Q: What data is included in real-time operational power grid maps?
A: Real-time operational maps display data on power flow, voltage levels, frequency, and other critical parameters, providing a dynamic view of the grid’s performance.
Q: What are the benefits of using power grid maps for grid security?
A: Power grid maps help identify potential vulnerabilities and facilitate the development of strategies to enhance grid security against cyberattacks and natural disasters.
Q: How can power grid maps be used to promote public awareness of the electricity infrastructure?
A: Power grid maps can be used to educate the public about the complex and interconnected nature of the electricity infrastructure, fostering a greater appreciation for its vital role in modern society.
Tips for Using Power Grid Maps Effectively
- Understand the map’s purpose and scale: Before using a power grid map, it’s crucial to understand its intended purpose and the geographic area it covers.
- Identify key features: Pay attention to the map’s legend, identifying symbols representing power plants, transmission lines, substations, and other critical components.
- Analyze power flow patterns: Observe the direction and intensity of power flow on the map to gain insights into load distribution and grid performance.
- Identify potential bottlenecks and vulnerabilities: Analyze the map for areas with high power flow density, indicating potential bottlenecks or vulnerable points in the grid.
- Explore real-time data: For operational maps, utilize real-time data to monitor grid performance, identify anomalies, and respond to potential issues.
- Compare maps over time: By comparing historical and current power grid maps, you can gain valuable insights into the evolution of the electricity infrastructure and identify trends in grid development.
Conclusion: Power Grid Maps – A Foundation for a Sustainable Future
Power grid maps are essential tools for understanding, managing, and improving the vital electricity infrastructure that powers modern society. They provide a visual representation of the complex network of power generation, transmission, and distribution, enabling informed decision-making for grid planning, operation, security, and sustainability. As we transition to a more sustainable energy future, power grid maps will play an increasingly crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources, optimizing grid efficiency, and ensuring a reliable and resilient electricity supply for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Power Grid Maps: A Vital Blueprint for Modern Civilization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!