The Equatorial Divide: Understanding the Earth’s Zero Degree Line
Related Articles: The Equatorial Divide: Understanding the Earth’s Zero Degree Line
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equatorial Divide: Understanding the Earth’s Zero Degree Line. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equatorial Divide: Understanding the Earth’s Zero Degree Line

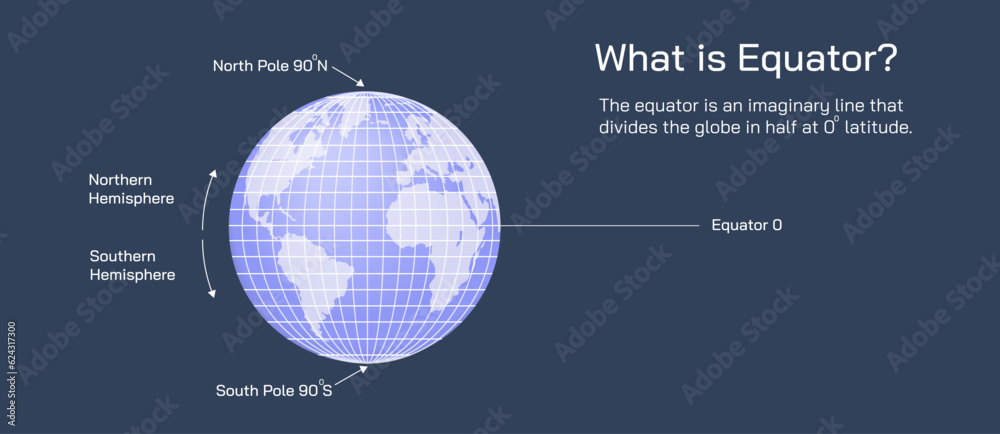
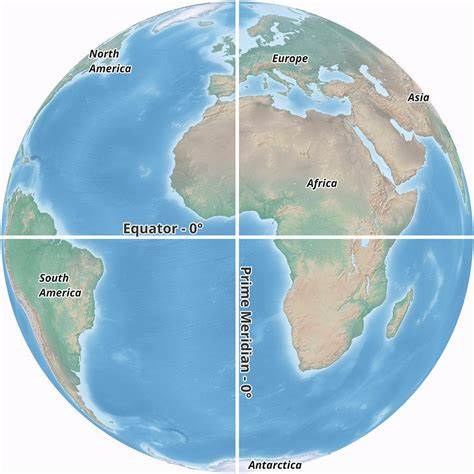
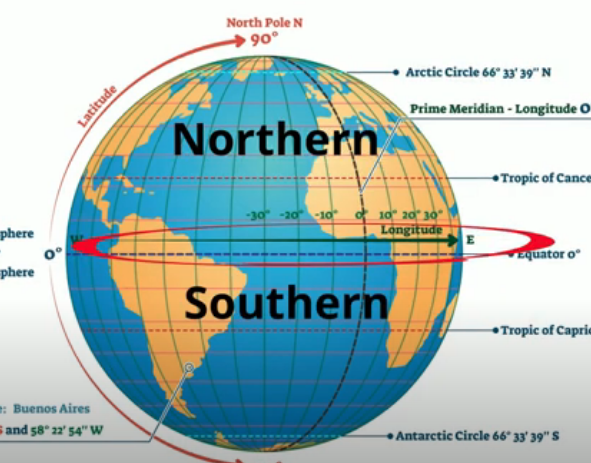
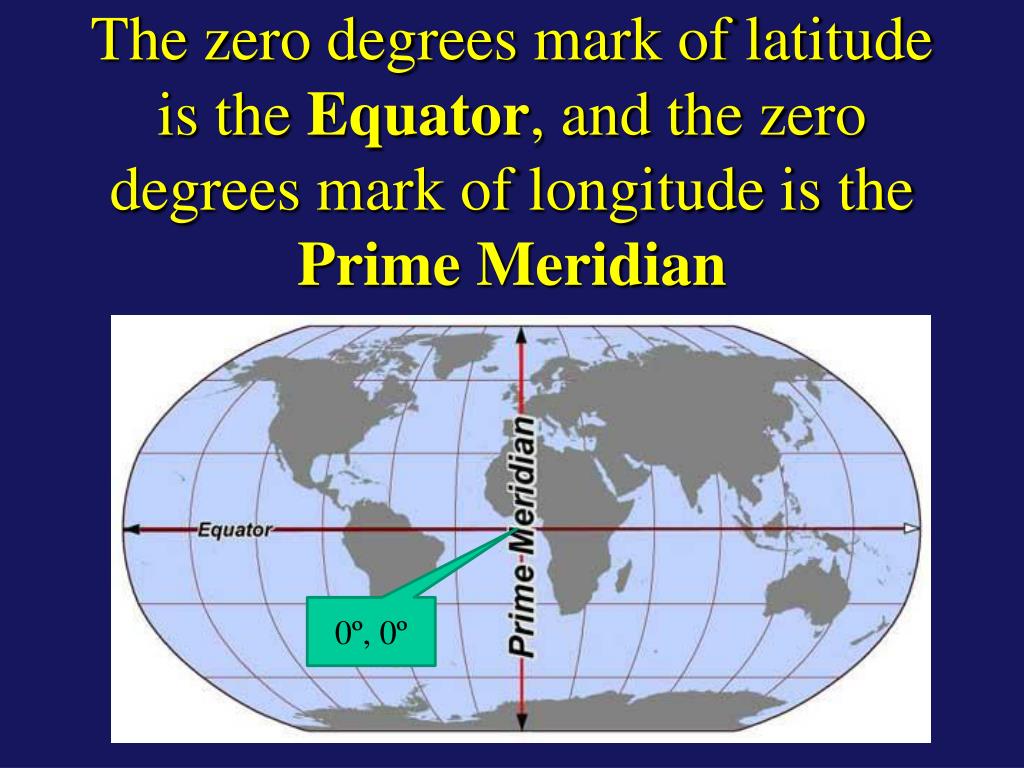
The Earth, a sphere rotating on its axis, is divided by an imaginary line known as the equator. This line, situated at 0 degrees latitude, encircles the globe, splitting it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. While invisible, the equator is a fundamental geographical concept, influencing climate, ecosystems, and even human societies.
A Line of Significance:
The equator is not merely a symbolic boundary; it plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s physical characteristics and influencing life across the globe. Its significance can be understood through the following aspects:
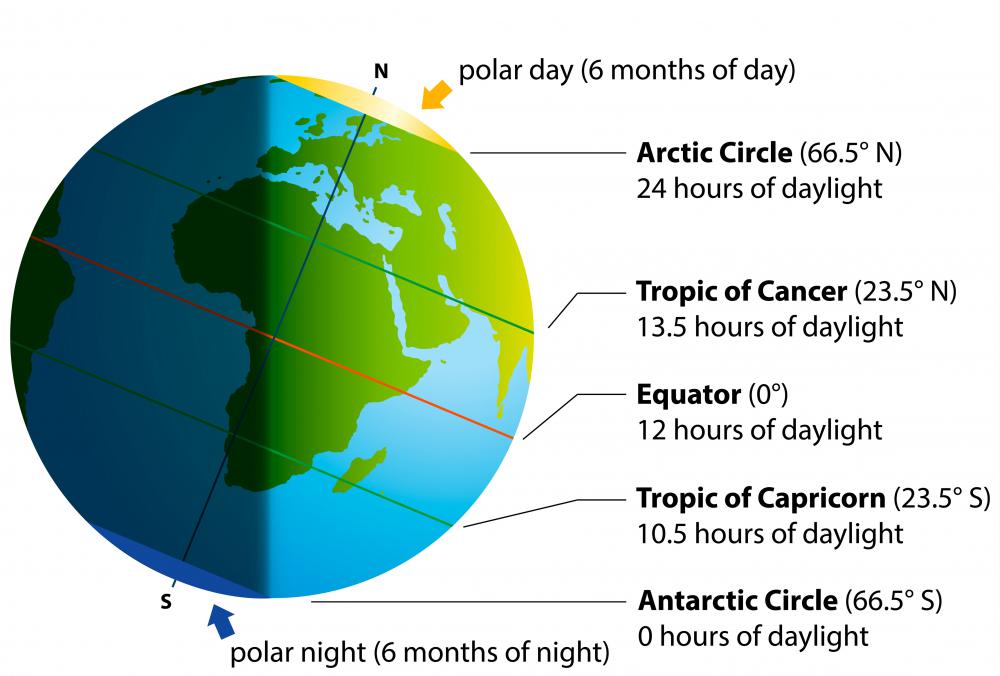
1. Climate: The equator experiences the most intense solar radiation due to its direct alignment with the sun. This leads to consistent high temperatures and heavy rainfall, creating tropical climates characterized by lush vegetation and diverse biodiversity. The consistent sunlight and warmth fuel a thriving ecosystem, supporting a wide array of plant and animal life.
2. Time Zones: The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each spanning 15 degrees of longitude. The prime meridian, another imaginary line, passes through Greenwich, England, serving as the starting point for these zones. The equator acts as a reference point for these time zones, with the time at the equator serving as the basis for calculating time across the globe.
3. Navigation: The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation. Sailors and explorers have long used its location to determine their position and direction. Navigational charts and maps rely on the equator as a zero point for latitude measurements, enabling accurate navigation across oceans and continents.
4. Cultural Significance: The equator has held cultural and symbolic significance for various civilizations throughout history. In ancient cultures, the equator was often associated with the celestial equator, marking the path of the sun across the sky. The equator’s symbolic importance continues to resonate in various cultures, representing a line of balance, unity, and connection.
5. Global Distribution of Resources: The equator’s influence on climate and ecosystems plays a significant role in the global distribution of resources. Tropical regions, influenced by the equator, are rich in biodiversity, mineral deposits, and agricultural potential. However, these regions also face challenges such as deforestation, climate change, and resource depletion.
The Equatorial Line and Its Impact on Human Life:
The equator’s influence extends beyond the physical environment, impacting human societies and cultures.
1. Population Distribution: Tropical regions, influenced by the equator, are home to a significant portion of the world’s population. The consistent warmth and abundant rainfall support agriculture and allow for dense population settlements.
2. Cultural Diversity: The equatorial regions are characterized by a wide range of cultures and traditions, influenced by the unique climate and environment. The diverse populations have developed distinct languages, religions, and cultural practices, creating a vibrant tapestry of human diversity.
3. Economic Activities: The equator’s influence on climate and resources fuels various economic activities, including agriculture, fishing, tourism, and mining. The abundance of natural resources and diverse ecosystems offer opportunities for economic development, but also require careful management to ensure sustainability.
4. Global Trade and Transportation: The equator’s location facilitates global trade and transportation. Major shipping routes traverse the equator, connecting continents and facilitating the exchange of goods and services. The equator’s influence on climate and resource availability also shapes global trade patterns.
FAQs About the Equator:
1. What is the exact length of the equator?
The circumference of the Earth at the equator is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
2. How does the equator affect the length of day and night?
The equator experiences almost equal day and night lengths throughout the year, with variations of only a few minutes. This is due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis, which causes seasonal variations in day length at other latitudes.
3. Is the equator always at 0 degrees latitude?
Yes, the equator is always at 0 degrees latitude. It serves as the reference point for measuring latitude, with all other latitudes measured north or south of the equator.
4. Can you walk across the equator?
Yes, it is possible to walk across the equator, as it is an imaginary line. Many countries and cities are situated on or near the equator, offering opportunities to experience its unique characteristics.
5. What is the significance of the International Date Line?
The International Date Line, located roughly along the 180th meridian, marks the boundary between two consecutive calendar days. It is an imaginary line that helps to synchronize time across the globe.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map helps to understand its position and significance.
- Explore equatorial regions: Traveling to countries situated on or near the equator provides firsthand experience of its unique climate, ecosystems, and cultural diversity.
- Read about equatorial cultures and history: Researching the history and cultural practices of equatorial communities provides insights into their adaptations to the unique environment.
- Engage in discussions about climate change and its impact on equatorial regions: Understanding the challenges faced by equatorial regions due to climate change and resource depletion fosters awareness and promotes responsible actions.
Conclusion:
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s physical characteristics and influencing life across the globe. From its impact on climate and ecosystems to its role in navigation and cultural diversity, the equator remains a fundamental concept in understanding our planet. By appreciating its significance, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of responsible stewardship of its resources.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equatorial Divide: Understanding the Earth’s Zero Degree Line. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!