The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map: A Complex Landscape of Representation
Related Articles: The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map: A Complex Landscape of Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map: A Complex Landscape of Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map: A Complex Landscape of Representation

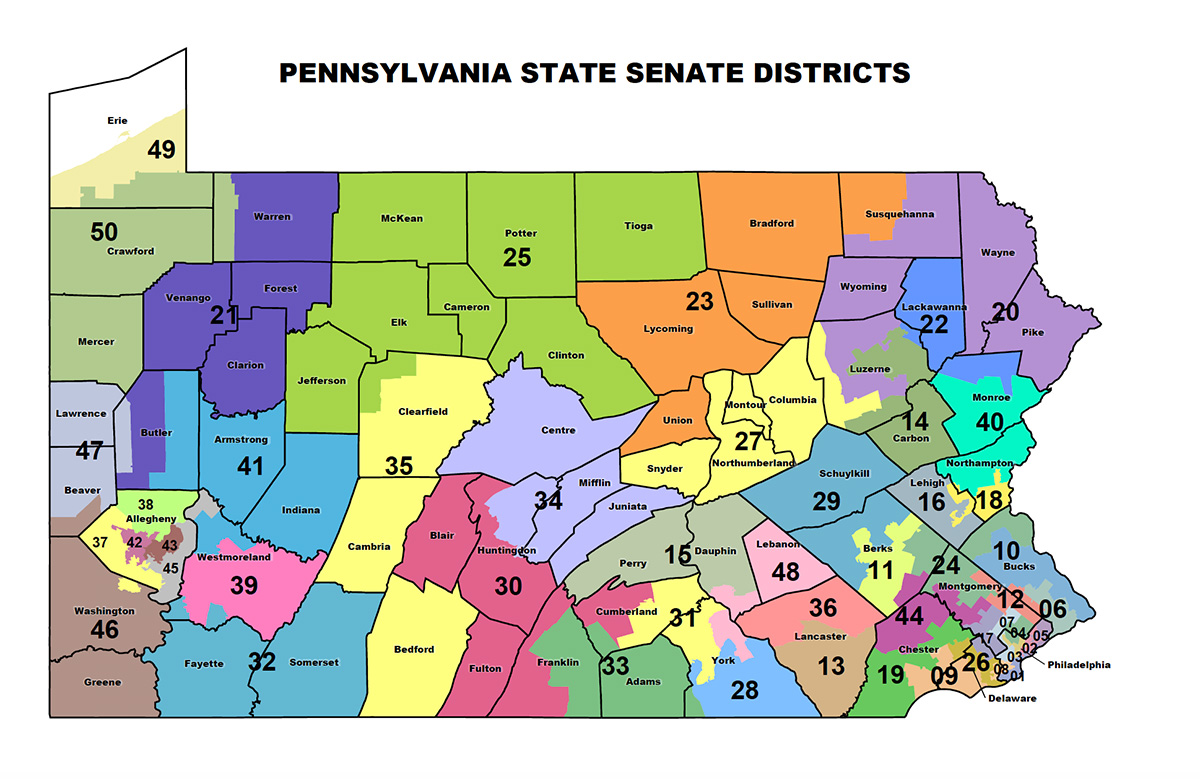
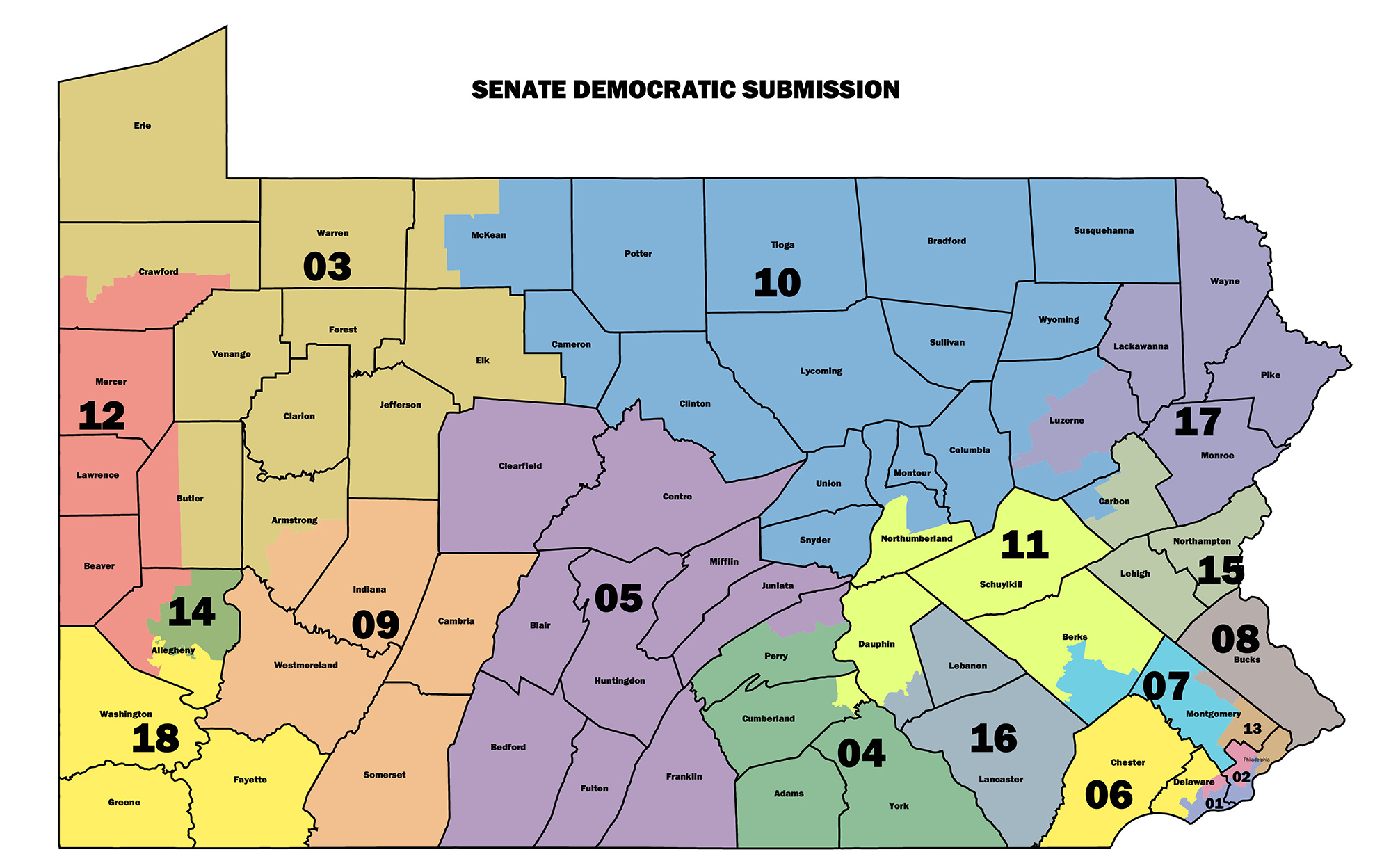
The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map is a critical component of the state’s political landscape, shaping the representation of its citizens in the state legislature. This map, which divides the Commonwealth into 50 districts, each electing one senator to serve a four-year term, plays a significant role in determining the political balance of power and the voice of different communities within the state.
Understanding the map’s intricacies requires delving into its historical evolution, the principles guiding its creation, and the ongoing debates surrounding its fairness and effectiveness.
A History of Redistricting and Controversy
The process of drawing electoral district boundaries, known as redistricting, is a complex and often contentious one. In Pennsylvania, the responsibility for redrawing Senate districts lies with the state legislature. This process occurs every ten years following the decennial census, aiming to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation across the state.
However, the redistricting process has historically been fraught with partisan maneuvering and accusations of gerrymandering. Gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group, can lead to unrepresentative outcomes, where districts are drawn to concentrate voters of a specific ideology, effectively silencing the voices of opposing viewpoints.
The history of Pennsylvania’s Senate district map reflects this dynamic. In the past, redistricting efforts have been criticized for favoring one party over another, leading to accusations of unfair representation and undermining the principles of fair elections.
Principles Guiding District Creation
Despite the potential for manipulation, the redistricting process is guided by certain fundamental principles aimed at ensuring fair and equitable representation. These principles include:
- Equal Population: Districts should be drawn with roughly equal populations to ensure that each voter has an equal voice in the electoral process.
- Contiguity: Districts must be contiguous, meaning that all parts of a district must be connected and not separated by another district.
- Compactness: Districts should be as compact as possible, minimizing unnecessary sprawl and maximizing the sense of community within each district.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: Districts should be drawn to respect existing communities of interest, such as shared cultural, economic, or social characteristics.
While these principles provide a framework for redistricting, their application in practice can be subjective and subject to interpretation, leading to ongoing debates about the fairness and effectiveness of the resulting map.
The Current Map and its Impact
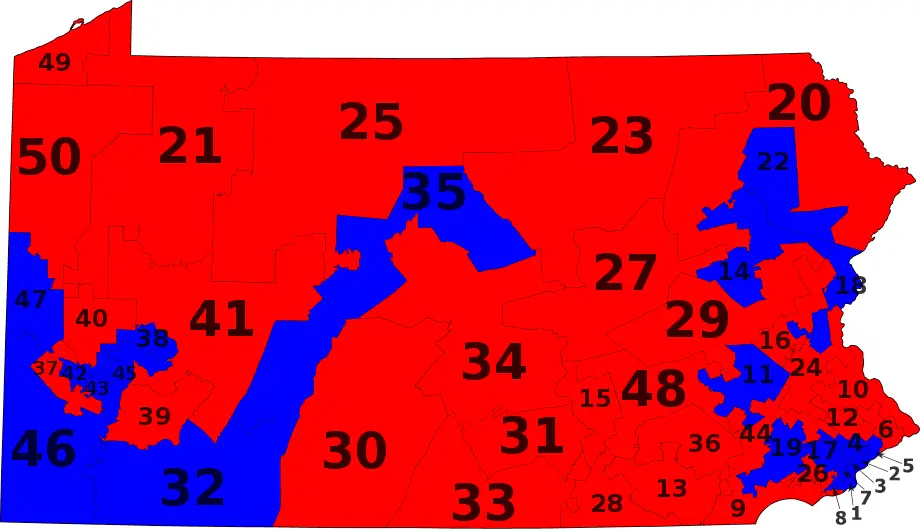
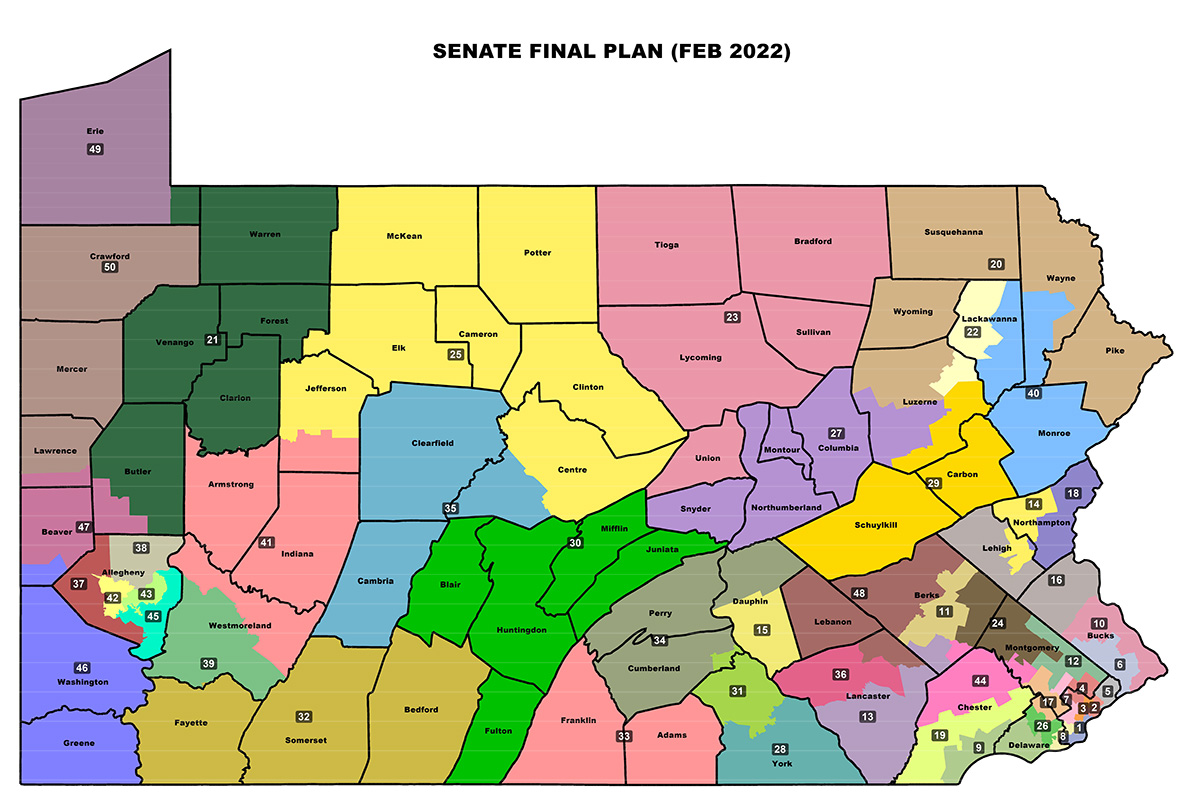
The current Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map, adopted in 2011, has been a subject of significant controversy. Critics argue that it was gerrymandered to favor the Republican Party, resulting in an uneven distribution of political power and a lack of competitive elections in many districts.
The map’s impact extends beyond electoral outcomes, influencing the representation of diverse communities and the ability of voters to hold their elected officials accountable. For instance, concerns have been raised about the map’s impact on minority representation, as some districts are drawn to dilute the voting power of minority communities.
The Future of Redistricting in Pennsylvania
The ongoing debates surrounding the current map have led to calls for reform, aiming to create a more fair and transparent redistricting process. Proposals include:
- Independent Redistricting Commissions: Establishing independent commissions, composed of non-partisan experts, to take over the redistricting process, removing it from the control of the legislature.
- Public Participation: Increasing public participation in the redistricting process, ensuring that communities have a voice in shaping the map.
- Transparency and Accountability: Implementing measures to increase transparency and accountability in the redistricting process, such as public hearings and independent review of proposed maps.
These reforms aim to address the concerns surrounding the current map and create a system that prioritizes fairness, representation, and the voice of the people.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map
Q: How often is the Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map redrawn?
A: The map is redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, aiming to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation across the state.
Q: What are the main principles guiding the creation of Senate districts?
A: The principles include equal population, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest.
Q: What is gerrymandering, and how does it impact the Senate districts map?
A: Gerrymandering is the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group. It can lead to unrepresentative outcomes, where districts are drawn to concentrate voters of a specific ideology, effectively silencing the voices of opposing viewpoints.
Q: What are the criticisms of the current Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map?
A: Critics argue that the current map was gerrymandered to favor the Republican Party, resulting in an uneven distribution of political power and a lack of competitive elections in many districts.
Q: What are the proposed reforms to the redistricting process in Pennsylvania?
A: Proposed reforms include establishing independent redistricting commissions, increasing public participation, and implementing measures to increase transparency and accountability.
Tips for Understanding the Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map
- Consult official resources: Utilize resources provided by the Pennsylvania State Government, such as the Pennsylvania Department of State, to access official maps, data, and information about the redistricting process.
- Engage with local organizations: Connect with local organizations and advocacy groups working on redistricting reform to learn about their efforts and how to get involved.
- Follow news coverage: Stay informed about the latest developments in redistricting by following news coverage and engaging with reputable sources.
- Participate in public hearings: Attend public hearings and provide feedback on proposed maps to ensure your voice is heard.
Conclusion
The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map is a powerful tool that shapes the state’s political landscape and the representation of its citizens. Understanding its history, principles, and ongoing debates is crucial for ensuring fair and equitable representation in the state legislature. As the state grapples with the challenges of redistricting, ongoing efforts to reform the process and ensure a more democratic and representative system are essential.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Pennsylvania Senate Districts Map: A Complex Landscape of Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!