The Power of Four: Understanding the Map of 4 Train
Related Articles: The Power of Four: Understanding the Map of 4 Train
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Four: Understanding the Map of 4 Train. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Four: Understanding the Map of 4 Train
The "Map of 4 Train" is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating complex systems, particularly those involving multiple interconnected elements. It is a visual representation that simplifies intricate relationships, revealing patterns and potential areas for improvement. This map, also known as a "4-Square Matrix," "Four-Quadrant Model," or simply "Four-Box Model," is a versatile framework applicable across diverse fields, including business strategy, project management, problem-solving, and personal development.
The Structure of the Map
The Map of 4 Train is characterized by its simplicity. It consists of a square divided into four equal quadrants, each representing a distinct aspect of the system under analysis. The quadrants are typically labelled with descriptive terms, such as:
- Strengths: Positive attributes, inherent advantages, and areas of excellence.
- Weaknesses: Areas requiring improvement, limitations, and vulnerabilities.
- Opportunities: External factors that can be leveraged for growth and advancement.
- Threats: External factors that pose potential risks and challenges.
This framework allows for a comprehensive analysis of the system by systematically examining each quadrant and its interactions with the others.
Applications of the Map of 4 Train
The Map of 4 Train finds extensive application in various domains. Some notable examples include:
1. Business Strategy:
- SWOT Analysis: The most common application, where the map helps identify a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to inform strategic decision-making.
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding the competitive landscape by analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of competitors and identifying potential opportunities for differentiation.
- Market Research: Identifying emerging trends, market gaps, and potential threats to guide product development and marketing strategies.
2. Project Management:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies for a project’s success.
- Resource Allocation: Determining the most effective allocation of resources based on project strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
- Project Planning: Defining clear objectives, milestones, and timelines based on the project’s strengths and weaknesses.
3. Problem-Solving:
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of a problem by examining its contributing factors, both internal and external.
- Brainstorming Solutions: Generating creative solutions by exploring different perspectives and considering both strengths and weaknesses.
- Decision-Making: Evaluating potential solutions based on their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
4. Personal Development:
- Self-Assessment: Identifying personal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities for growth, and potential threats to personal goals.
- Career Planning: Defining career aspirations, identifying skill gaps, and exploring potential opportunities.
- Goal Setting: Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals based on personal strengths and opportunities.
Benefits of Using the Map of 4 Train
The Map of 4 Train offers numerous benefits, including:
- Structured Thinking: Provides a clear and structured framework for analysis and decision-making.
- Comprehensive Perspective: Encourages a holistic view of the system by considering all relevant aspects.
- Identifying Opportunities: Reveals potential opportunities for growth and improvement.
- Prioritizing Actions: Helps prioritize actions based on the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Collaboration and Communication: Facilitates effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
FAQs
Q: What are the limitations of the Map of 4 Train?
A: While powerful, the Map of 4 Train has limitations. It can be overly simplistic, potentially overlooking complex interdependencies within the system. Additionally, it requires careful data collection and analysis to ensure accurate and relevant insights.
Q: How can I effectively use the Map of 4 Train?
A:
- Define the System: Clearly define the system being analyzed.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant data on the system’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Analyze the Data: Identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
- Prioritize Actions: Develop actionable strategies based on the analysis.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and make necessary adjustments.
Tips for Using the Map of 4 Train
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage relevant stakeholders in the data gathering and analysis process.
- Use Visual Aids: Utilize charts, graphs, and diagrams to present the data effectively.
- Focus on Actionable Insights: Ensure the analysis leads to actionable strategies and solutions.
- Be Objective: Strive for objectivity in the analysis, avoiding personal biases and assumptions.
- Embrace Iteration: The Map of 4 Train is a dynamic tool that should be revisited and updated regularly.
Conclusion
The Map of 4 Train is a versatile and powerful tool for understanding and navigating complex systems. Its simplicity and comprehensiveness make it a valuable framework for strategic planning, problem-solving, and personal development. By systematically examining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within a system, the Map of 4 Train provides a clear roadmap for informed decision-making and effective action. However, it is important to remember that it is a tool, not a solution in itself. Effective utilization requires careful data collection, objective analysis, and a focus on actionable insights.

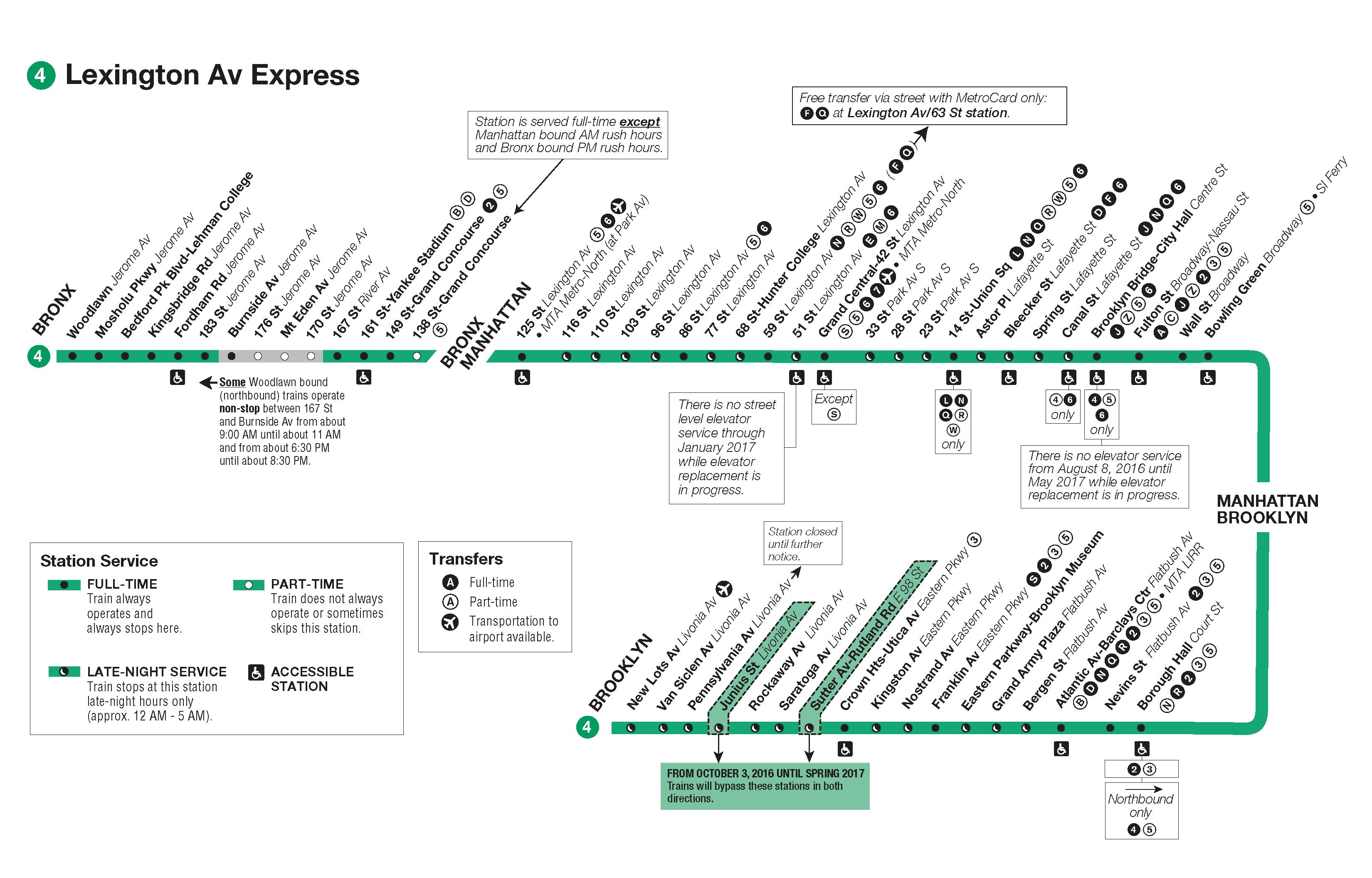

:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23673699/whole_map.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Four: Understanding the Map of 4 Train. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!