The Unfolding World: Herodotus’ Map and Its Enduring Legacy
Related Articles: The Unfolding World: Herodotus’ Map and Its Enduring Legacy
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Unfolding World: Herodotus’ Map and Its Enduring Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unfolding World: Herodotus’ Map and Its Enduring Legacy

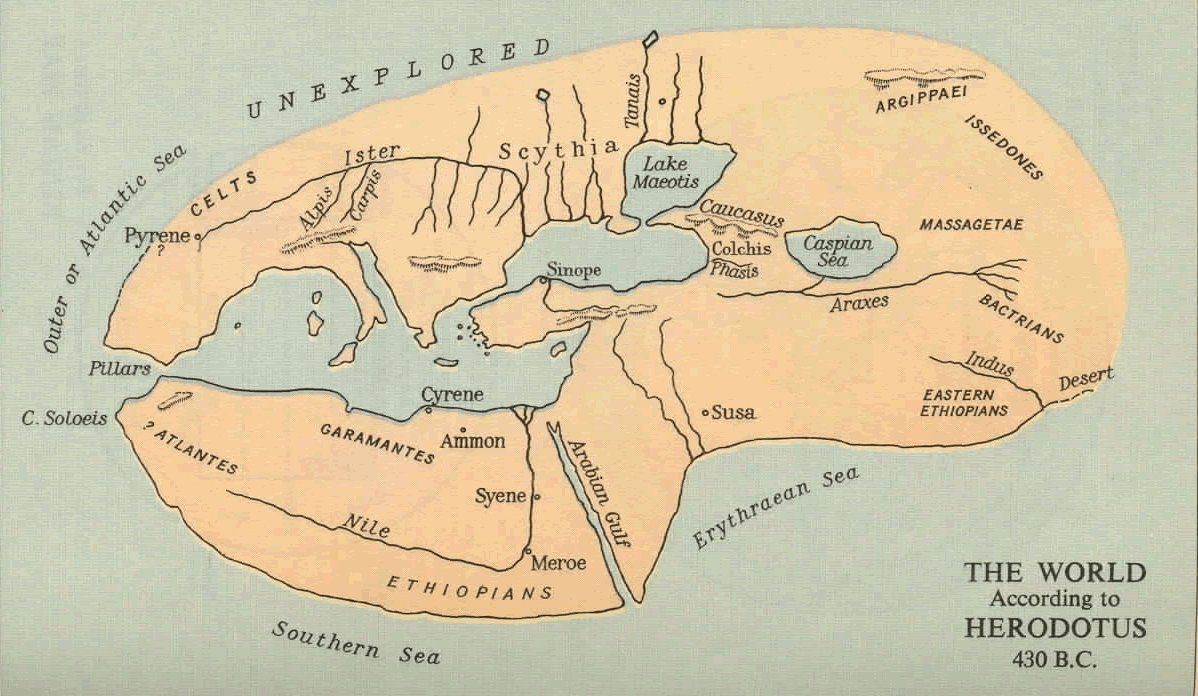
Herodotus, the "Father of History," is renowned for his meticulous account of the Persian Wars. However, his contributions extend beyond mere narrative. He was also a pioneering geographer, meticulously recording the vast world he encountered through his travels. While no physical map created by Herodotus has survived, his writings provide a detailed and invaluable blueprint of the known world in the 5th century BCE.
A Mosaic of Knowledge: Herodotus’ map is not a single, unified creation, but rather a tapestry woven from diverse sources and observations. He meticulously recorded the geographical information gleaned from his journeys, his interactions with travelers, and his study of historical texts. This mosaic approach resulted in a remarkably comprehensive representation of the world, stretching from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Indus Valley in the east.
The Known World Unveiled: Herodotus’ map, reconstructed from his writings, reveals a world vastly different from our modern cartographic understanding. It is a world of interconnected empires, diverse cultures, and vast stretches of unexplored territory. His detailed descriptions of rivers, mountains, and cities provide valuable insights into the geography and infrastructure of the ancient world.
Beyond the Physical Landscape: Herodotus’ map transcends mere physical locations. It is a tapestry of cultural and political realities. He meticulously describes the customs, beliefs, and political structures of the various peoples he encountered, providing a unique window into the diverse societies of his time. He chronicles the rise and fall of empires, the dynamics of trade, and the complexities of intercultural interaction.
A Foundation for Future Exploration: Herodotus’ map, while lacking the precision of modern cartography, laid the groundwork for future geographical understanding. It provided a foundation for subsequent explorers and geographers, offering a framework for their own investigations and expanding upon his initial observations. His meticulous documentation of geographical features and cultural nuances paved the way for the development of more refined and accurate maps in the centuries that followed.
Engaging with the Past: Herodotus’ map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the past. It allows us to visualize the world as it was perceived in the 5th century BCE, offering a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of ancient societies and the complexities of their interactions. By engaging with his descriptions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context of the ancient world and the challenges faced by those who lived within it.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of Herodotus’ Map
1. What were the primary sources of information for Herodotus’ map?
Herodotus relied on a combination of sources, including:
- Personal travel and observation: He traveled extensively, recording his firsthand observations of the landscapes and cultures he encountered.
- Interviews with travelers and locals: He actively sought information from people who had traveled to distant lands, gathering their accounts of geography and customs.
- Historical texts and records: He consulted existing written records, drawing upon the knowledge of previous historians and travelers.
2. How accurate was Herodotus’ map in terms of geographical representation?
While impressive for its time, Herodotus’ map exhibits inaccuracies, particularly concerning distances and proportions. His reliance on anecdotal information and the limitations of ancient navigation led to distortions in the map’s representation of the world. However, it is essential to recognize the map’s value not as a precise geographical representation, but as a reflection of the knowledge and understanding of the world at the time.
3. What are some of the key geographical features highlighted in Herodotus’ map?
Herodotus’ map showcases a range of significant geographical features, including:
- The Mediterranean Sea: He meticulously describes the coastline, islands, and major ports along the Mediterranean Sea, emphasizing its role in trade and communication.
- The Nile River: He details the course of the Nile, its tributaries, and its importance to Egyptian civilization, highlighting its role in agriculture and transportation.
- The Black Sea: He provides a detailed account of the Black Sea, its surrounding regions, and its significance as a trade route connecting the Mediterranean world with the East.
4. How did Herodotus’ map contribute to the development of cartography?
Herodotus’ map, while not a perfect representation of the world, played a crucial role in the development of cartography. His meticulous documentation of geographical features and cultural nuances provided a foundation for future explorers and geographers, offering a framework for their own investigations and expanding upon his initial observations.
Tips for Exploring Herodotus’ Map:
1. Engage with the text: Read Herodotus’ "Histories" with a focus on his geographical descriptions. Pay attention to his accounts of rivers, mountains, cities, and the cultural characteristics of the peoples he encountered.
2. Visualize the world: Use modern maps and resources to visualize the locations and regions described by Herodotus, allowing you to connect his textual descriptions with the actual geographical landscape.
3. Consider the historical context: Recognize the limitations of ancient knowledge and navigation. Understand that Herodotus’ map reflects the understanding of the world at his time, not a perfect representation of the world today.
4. Seek out reconstructions: Explore reconstructions of Herodotus’ map created by scholars and historians. These reconstructions offer a visual representation of his geographical understanding, aiding in your comprehension of his work.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Exploration and Understanding
Herodotus’ map, while lacking the precision of modern cartography, stands as a testament to his inquisitive spirit and his dedication to understanding the world around him. It is a testament to the power of observation, documentation, and the human desire to explore and connect with the vastness of the world. His map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the past, offering a glimpse into the world as it was perceived in the 5th century BCE and providing a foundation for the development of more refined cartographic representations in the centuries that followed. Through his meticulous descriptions, Herodotus left an enduring legacy, inspiring generations of explorers, historians, and cartographers to continue unraveling the mysteries of the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unfolding World: Herodotus’ Map and Its Enduring Legacy. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!