The Web of Entanglement: Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I
Related Articles: The Web of Entanglement: Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Web of Entanglement: Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Web of Entanglement: Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I

The outbreak of World War I in 1914 was not a sudden eruption of violence, but rather the culmination of a complex web of alliances that had been woven across Europe for decades. Understanding these alliances is crucial to comprehending the causes and dynamics of the conflict. The alliances map, a visual representation of these intricate relationships, reveals a system of interconnected commitments that ultimately propelled the continent into a devastating war.
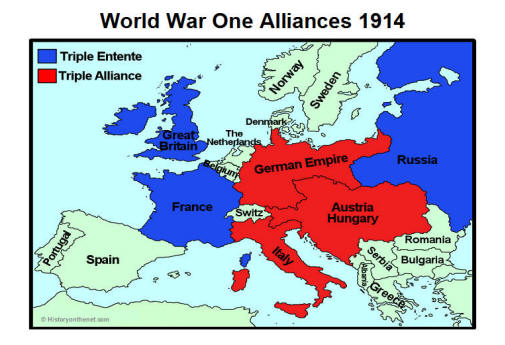
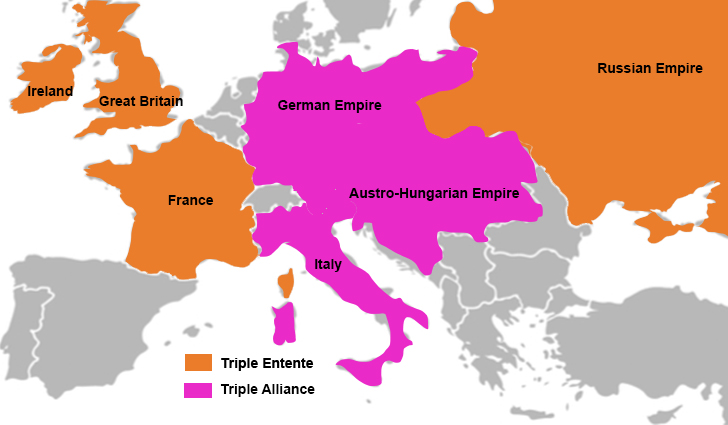
The Triple Alliance:
At the heart of the alliances map lay the Triple Alliance, formed in 1882 between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. This alliance was initially driven by Germany’s desire to counter the growing influence of France, which had been defeated in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71. Austria-Hungary, seeking to maintain its dominance in the Balkans, also saw the alliance as a way to bolster its position. Italy, initially motivated by a desire to gain territory in the Mediterranean, later found itself caught in a complex web of conflicting interests.
The Triple Entente:
The Triple Alliance was countered by the Triple Entente, a loose alliance between France, Russia, and Great Britain. This alliance, though less formal than the Triple Alliance, grew out of shared concerns about German expansionism and the growing power of the Central Powers. France, seeking revenge for its defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, saw an opportunity to regain lost territory. Russia, with ambitions in the Balkans, saw an alliance with France as a way to counter Austria-Hungary’s influence. Great Britain, initially hesitant to commit, eventually joined the Entente due to its concerns about German naval expansion and its desire to protect its colonial interests.
The Balkan Powder Keg:
The Balkans, known as the "powder keg of Europe," played a crucial role in the escalation of the alliances into a full-scale war. Austria-Hungary, seeking to maintain its control over the region, saw Serbia as a threat to its imperial ambitions. Serbia, on the other hand, aspired to unite all South Slavs under its rule. This rivalry, fueled by nationalist tensions and competing interests, created a volatile situation that could easily ignite into conflict.
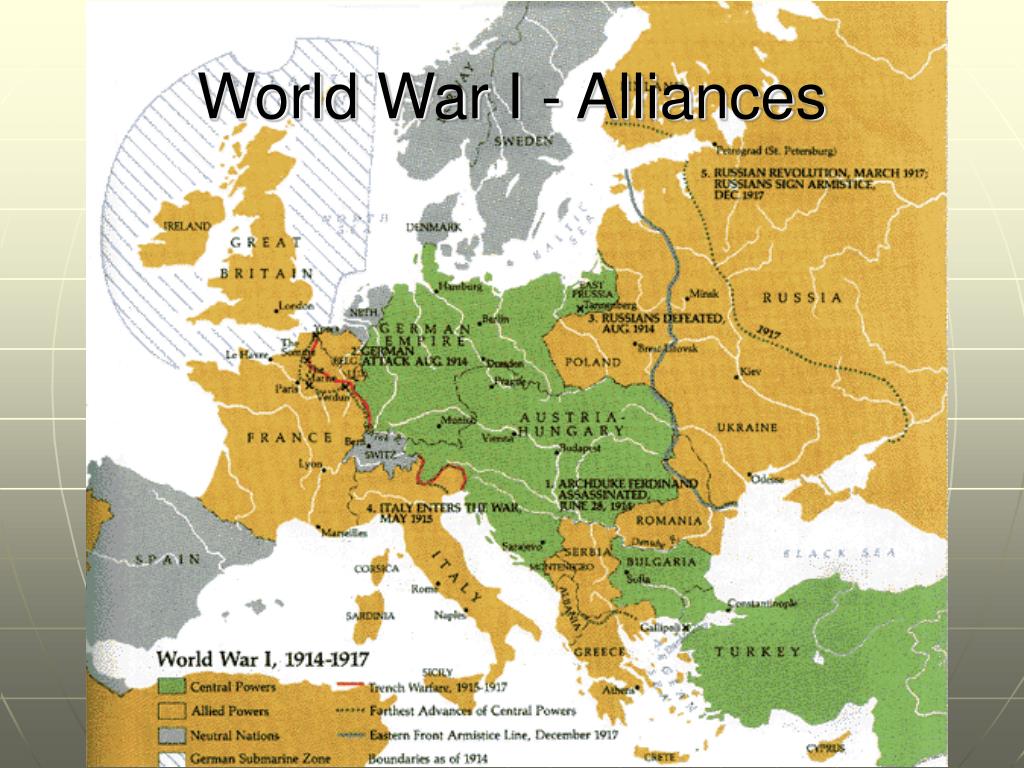
The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand:
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, in Sarajevo on June 28, 1914, by a Serbian nationalist, Gavrilo Princip, was the spark that ignited the powder keg. Austria-Hungary, seeing Serbia’s involvement in the assassination as a direct challenge to its authority, issued an ultimatum demanding Serbia’s cooperation in investigating the assassination. Serbia, unwilling to accept the ultimatum’s terms, triggered a chain reaction that ultimately led to war.
The Domino Effect:
The alliances map, with its intricate web of commitments, ensured that the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand would not be a localized conflict. Austria-Hungary’s declaration of war on Serbia triggered a domino effect, pulling other nations into the conflict. Russia, bound by its alliance with Serbia, mobilized its troops to protect its ally. Germany, allied with Austria-Hungary, declared war on Russia and France, which had mobilized its troops in support of Russia. Great Britain, bound by its alliance with France, declared war on Germany.
The Importance of the Alliances Map:
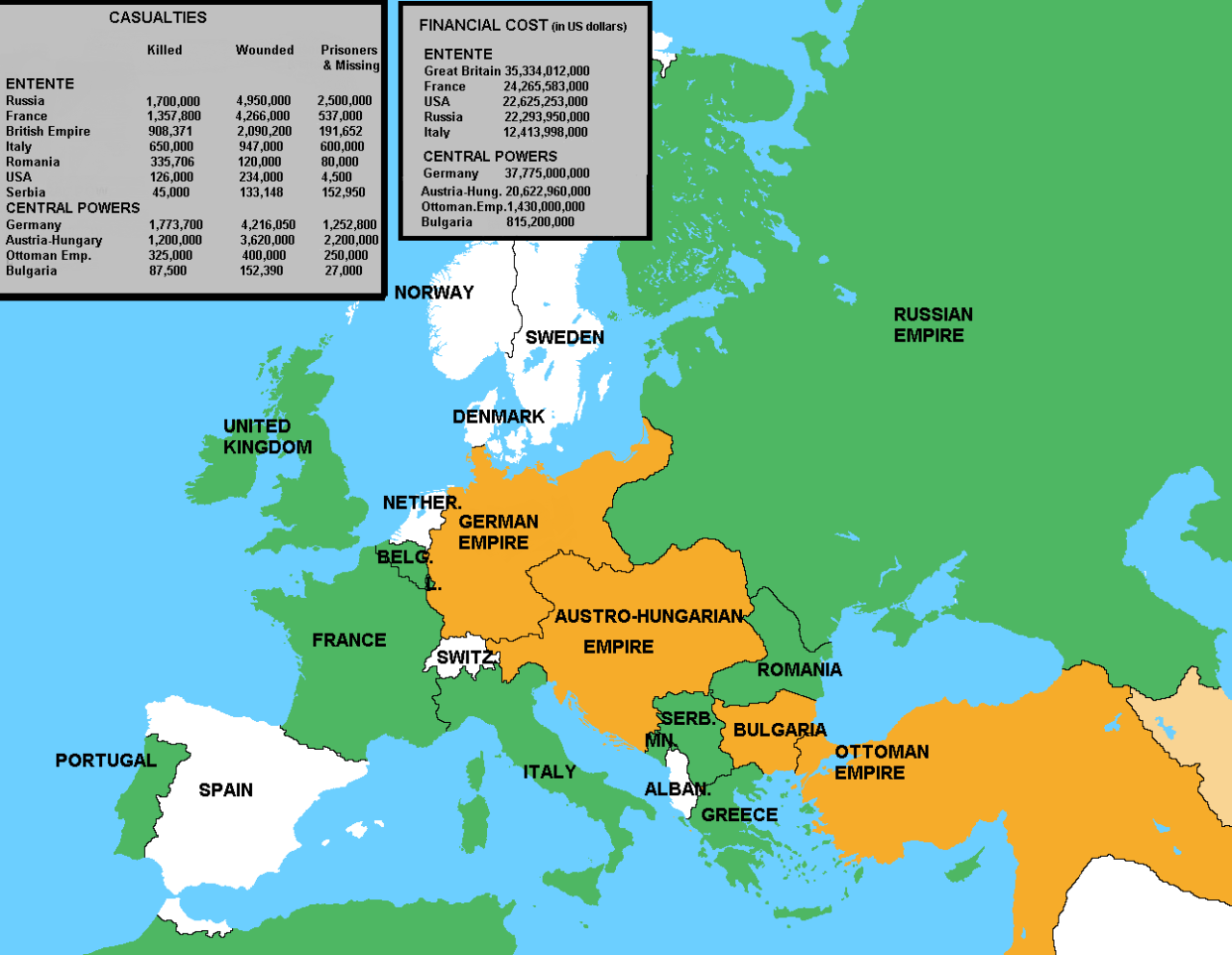
The alliances map played a pivotal role in the outbreak and escalation of World War I. The rigid system of alliances, based on mutual commitments and fears, ensured that a conflict in the Balkans would quickly escalate into a global war. The alliances, while intended to provide security and stability, ultimately led to the mobilization of vast armies and the unleashing of unprecedented violence.
The Legacy of the Alliances Map:
The alliances map serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism and the potential for seemingly localized conflicts to spiral out of control. The experience of World War I led to a reassessment of the role of alliances in international relations, with the League of Nations, established in 1920, attempting to create a system of collective security to prevent future conflicts.
FAQs about the Alliances Map of World War I:
-
What were the main alliances during World War I? The main alliances were the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy) and the Triple Entente (France, Russia, and Great Britain).
-
How did the alliances contribute to the outbreak of World War I? The alliances created a system of mutual commitments that made it difficult for nations to remain neutral in a conflict. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand triggered a chain reaction, as nations were obligated to support their allies.
-
What were the main goals of the alliances? The alliances were formed for various reasons, including maintaining power, protecting interests, and preventing the expansion of other nations.
-
Did the alliances change during the war? Yes, the alliances shifted during the war, with Italy switching sides from the Triple Alliance to the Triple Entente in 1915.
-
What was the impact of the alliances on the course of the war? The alliances significantly influenced the course of the war, dictating the alliances and military strategies of the participating nations.
Tips for Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I:
-
Visualize the alliances: Use maps and diagrams to understand the relationships between the nations.
-
Identify the key players: Focus on the main powers involved in the alliances and their motivations.
-
Trace the chain of events: Understand how the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand triggered a chain reaction that led to war.
-
Consider the impact of the alliances: Analyze how the alliances influenced the course of the war and its consequences.
Conclusion:
The alliances map of World War I is a complex and fascinating study of the interconnectedness of nations and the potential for alliances to both provide security and create instability. Understanding the alliances is crucial to comprehending the causes and dynamics of the conflict, and its legacy continues to shape our understanding of international relations and the importance of diplomacy in preventing future conflicts.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Web of Entanglement: Understanding the Alliances Map of World War I. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!