Understanding and Utilizing Flood Risk Information in the United States
Related Articles: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Risk Information in the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Utilizing Flood Risk Information in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Utilizing Flood Risk Information in the United States

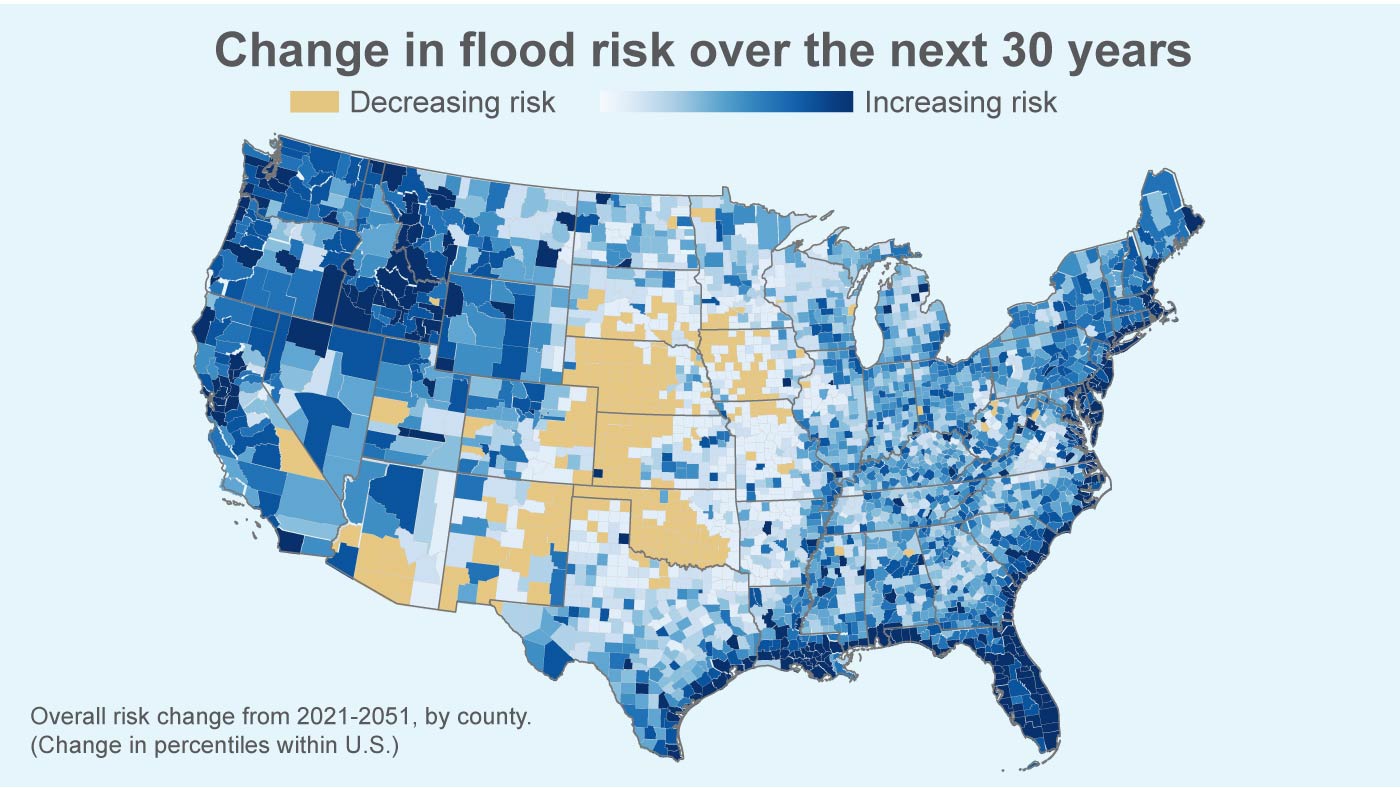
The United States faces significant challenges from flooding, a hazard impacting communities nationwide. Accurate and readily accessible flood risk information is crucial for effective mitigation, preparedness, and response. Various federal, state, and local agencies contribute to the development and dissemination of this crucial data, providing a comprehensive picture of flood vulnerability across the country. These resources empower individuals, businesses, and government entities to make informed decisions regarding land use, infrastructure development, and emergency planning.
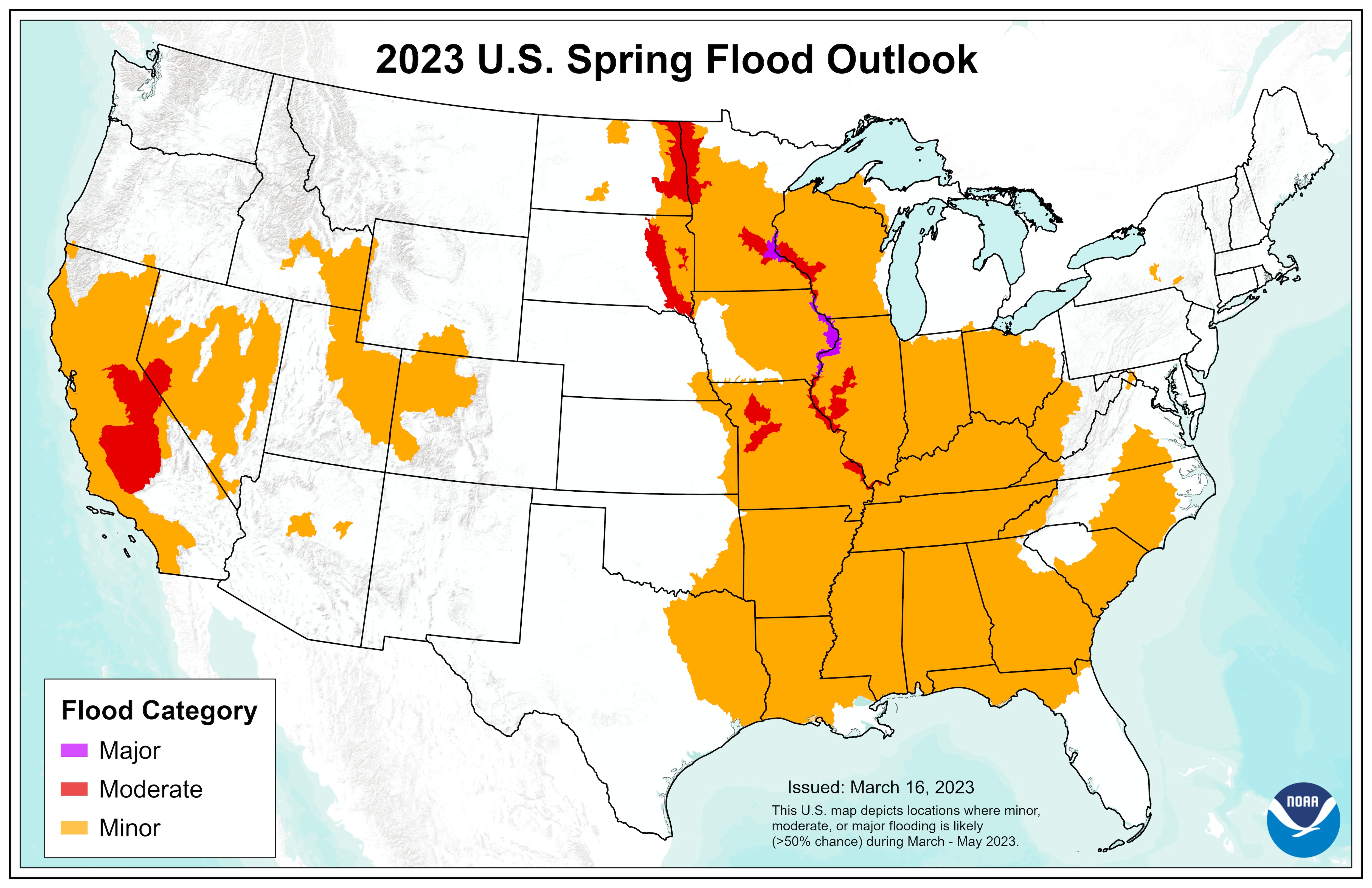
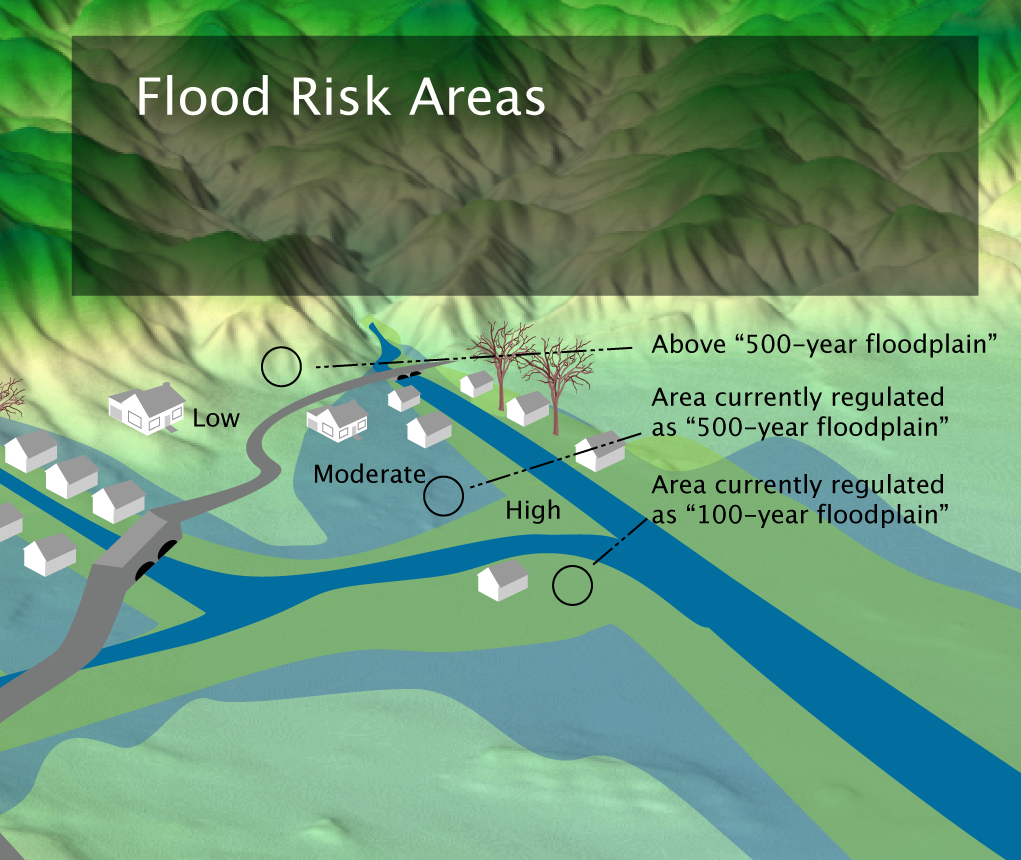
The primary source of national-level flood risk information is the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). FEMA’s Risk Mapping, Assessment, and Planning (Risk MAP) program produces flood hazard maps, often referred to as Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs). These maps depict areas with varying levels of flood risk based on factors such as historical flood data, hydrological modeling, and topographic information. FIRMs are essential for the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), providing the basis for determining flood insurance rates and eligibility. The higher the flood risk in a specific area, as indicated on the map, the higher the associated insurance premium.
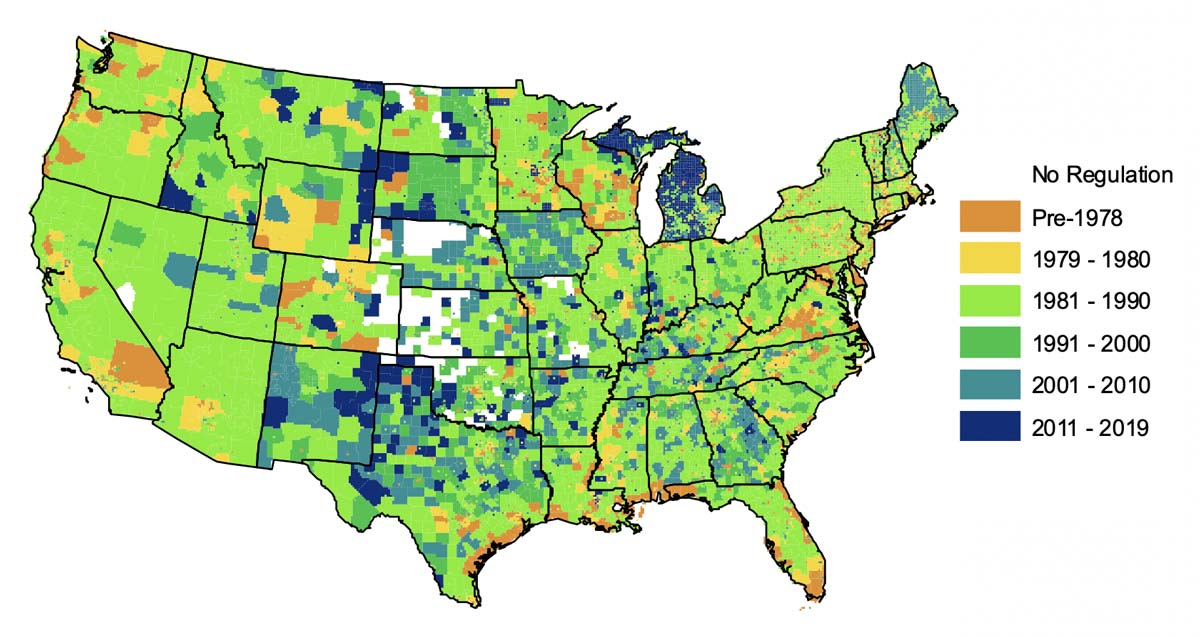
Beyond FEMA’s national efforts, numerous state and local agencies contribute to the refinement and enhancement of flood risk information. Many states maintain their own flood hazard mapping programs, often incorporating more localized data and higher-resolution modeling than the national maps. This localized information can be particularly valuable in identifying areas with specific vulnerabilities, such as those prone to flash flooding or riverine flooding. Local governments frequently utilize this data to guide zoning regulations, building codes, and infrastructure projects, minimizing potential flood damage and promoting community resilience.
The data utilized in creating these maps is multifaceted. Historical flood records are paramount, providing empirical evidence of past flood events and their impacts. Hydrological models simulate the movement of water through various landscapes, accounting for rainfall intensity, soil saturation, and river channel characteristics. Topographic data, often derived from LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) surveys, provides high-resolution elevation information, crucial for delineating floodplains and identifying areas particularly susceptible to inundation. Advanced computational techniques are employed to integrate these datasets and generate probabilistic flood risk assessments, quantifying the likelihood of flooding over various time horizons.
The benefits of utilizing this information are substantial. For homeowners, understanding the flood risk associated with a property allows for informed decisions regarding purchasing, insuring, and mitigating flood hazards. Insurance premiums are directly influenced by the flood risk zone designation, emphasizing the importance of accurate mapping. Property owners in high-risk areas may need to implement mitigation measures, such as elevating structures or installing flood barriers, to reduce potential damage.
For businesses, access to flood risk information informs strategic planning and investment decisions. Businesses operating in high-risk areas need to consider the potential for business interruption and property damage, incorporating flood resilience into their operational strategies. This might involve relocating critical infrastructure, developing robust backup systems, or securing adequate flood insurance coverage.
For government agencies, accurate flood risk data is fundamental for effective emergency management and infrastructure planning. Understanding flood vulnerability allows for targeted investments in flood control infrastructure, such as levees and drainage systems. It also supports the development of comprehensive emergency response plans, ensuring the efficient allocation of resources during flood events. Zoning regulations and building codes are informed by these maps, promoting safer and more resilient community development.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: How accurate are these maps? A: The accuracy of flood hazard maps varies depending on the data used and the methodologies employed. While continuous improvement efforts enhance accuracy, maps represent probabilistic assessments, not guarantees of future flood events.
-
Q: What if my property is not shown on the map? A: The absence of a property on a map does not necessarily indicate a lack of flood risk. Factors such as local topography and drainage patterns can influence flood risk independently of the mapped areas.
-
Q: How often are these maps updated? A: Maps are updated periodically, often reflecting new data or improved modeling techniques. However, the frequency of updates can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the availability of resources. Regularly checking for updates is advisable.
-
Q: What is the role of the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP)? A: The NFIP provides federally backed flood insurance, making it accessible to property owners in flood-prone areas. Flood insurance rates are directly tied to the flood risk zone designation on the FIRMs.
-
Q: Where can I access these maps? A: Flood hazard maps are typically accessible online through FEMA’s website and the websites of state and local agencies.
Tips for Utilizing Flood Risk Information:
-
Consult multiple sources: Compare information from FEMA, state, and local sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of flood risk.
-
Understand the limitations: Recognize that flood maps represent probabilistic assessments, and actual flood events may vary.
-
Incorporate risk into planning: Consider flood risk when making decisions regarding property purchase, development, and insurance.
-
Implement mitigation measures: Take proactive steps to reduce vulnerability to flooding, such as elevating structures or installing flood barriers.
-
Stay informed: Regularly check for updates to flood hazard maps and be aware of potential flood warnings.
Conclusion:
Access to accurate and up-to-date flood risk information is essential for mitigating the impacts of flooding in the United States. The collaborative efforts of federal, state, and local agencies provide a comprehensive framework for assessing and managing flood risk. Effective utilization of this information empowers individuals, businesses, and government entities to make informed decisions, reducing vulnerability and promoting community resilience in the face of this significant natural hazard. Continued investment in data collection, modeling techniques, and public education is crucial for enhancing the effectiveness of these vital resources and minimizing the devastating consequences of flooding.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Utilizing Flood Risk Information in the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!