Unraveling the Tapestry of Germanic Tribes: A Map of Migration and Cultural Development
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Germanic Tribes: A Map of Migration and Cultural Development
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Germanic Tribes: A Map of Migration and Cultural Development. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Germanic Tribes: A Map of Migration and Cultural Development

The Germanic tribes, a diverse collection of peoples who emerged in northern Europe, played a pivotal role in shaping the history and culture of the continent. Their migrations, conquests, and interactions with other cultures left an indelible mark on the political landscape, linguistic diversity, and societal structures of Europe. A map of Germanic tribes, while not a static representation, provides a valuable tool for understanding the complex movements and interactions of these groups.
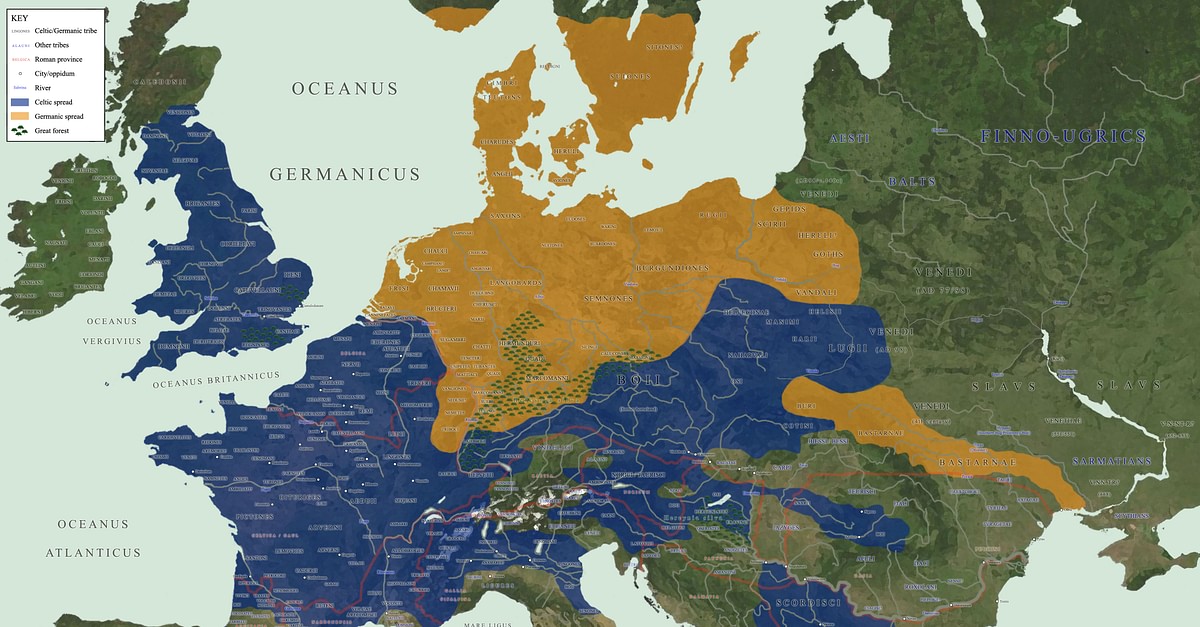
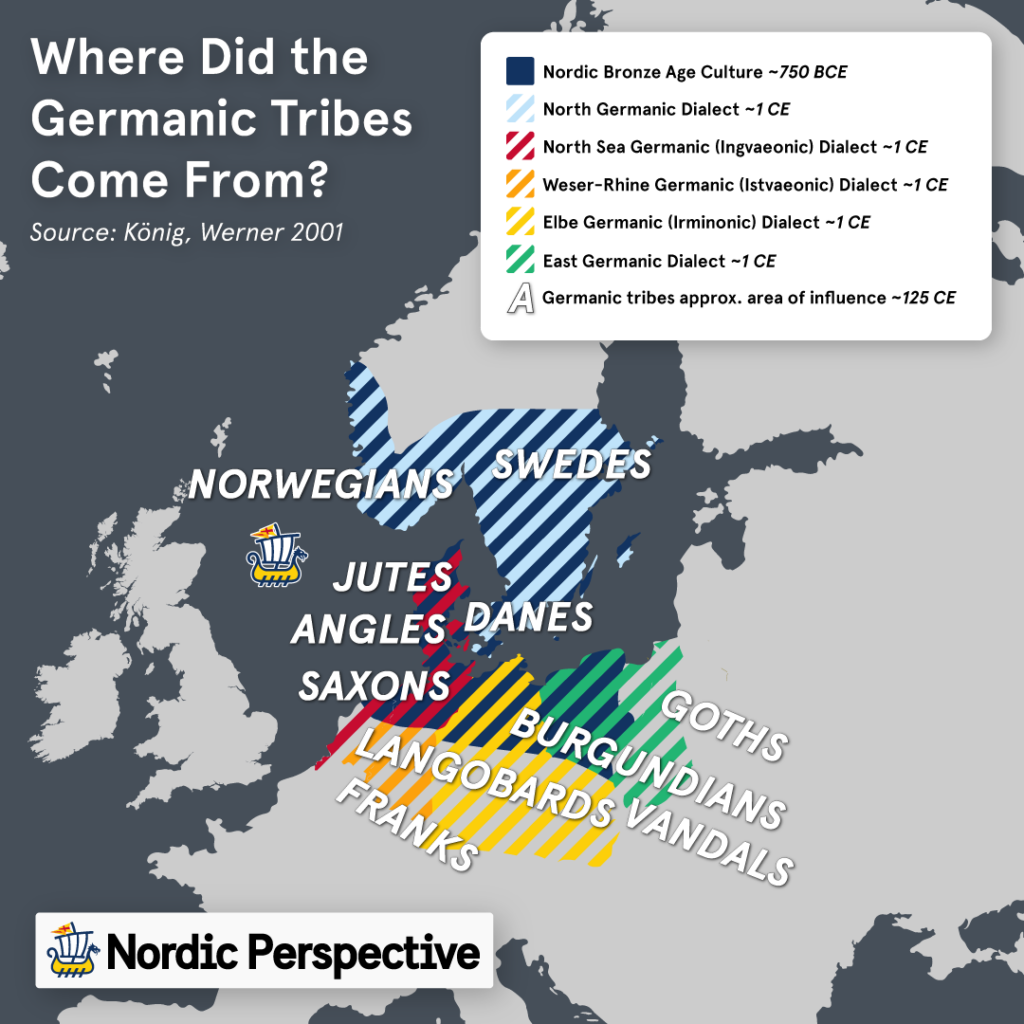
Tracing the Roots: The Germanic Homeland
The origins of the Germanic tribes are often traced back to the early Iron Age, around 500 BCE, in the region encompassing present-day Denmark, southern Sweden, northern Germany, and the Netherlands. This area, often referred to as the "Germanic homeland," witnessed the development of distinct cultural and linguistic traits that would define the Germanic tribes.
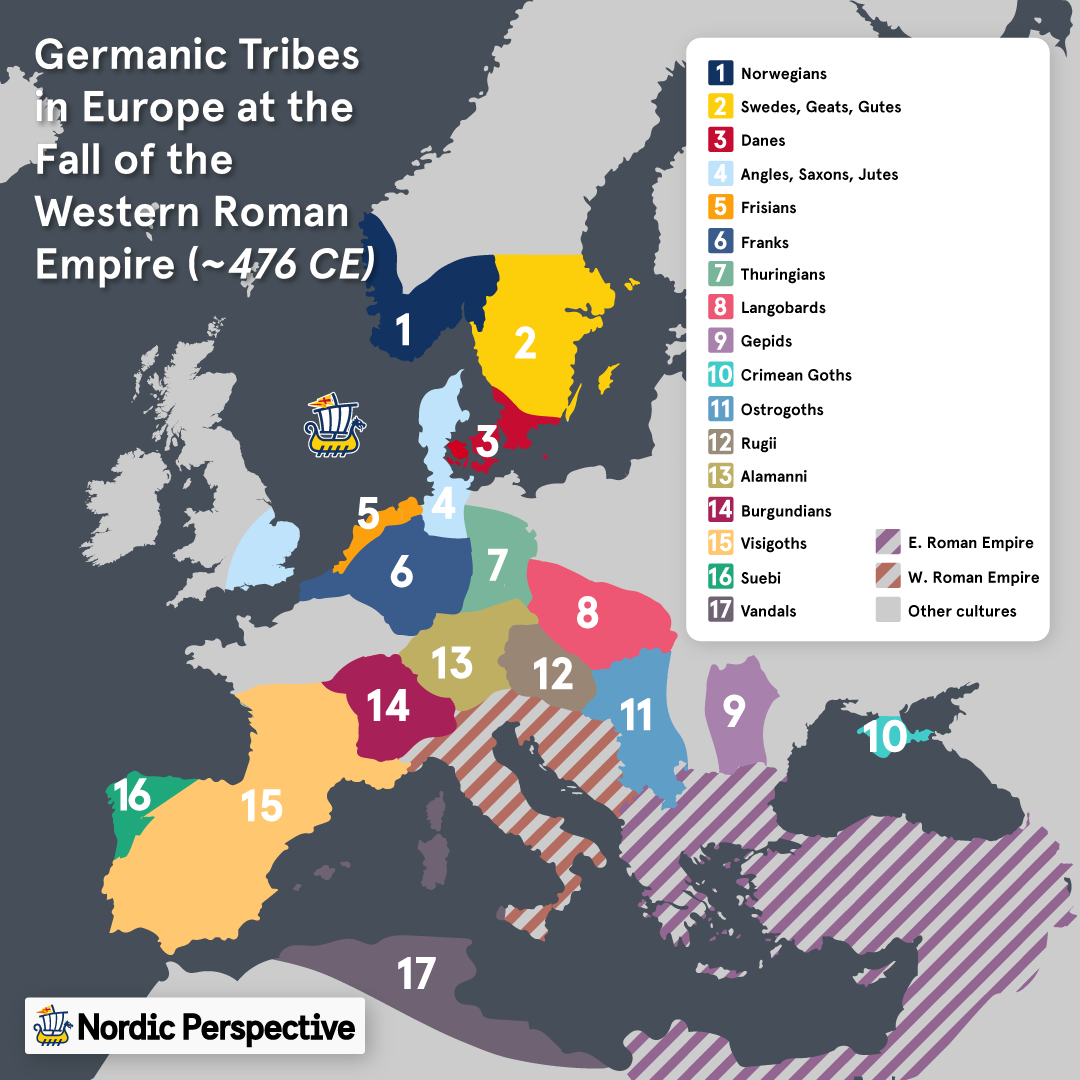
A Mosaic of Tribes: The Germanic World
The Germanic tribes were not a monolithic entity but a collection of distinct groups, each with its own cultural identity, language, and social structure. Some of the most prominent tribes included:
- Angles: Originating in the region of Angeln in northern Germany, the Angles migrated to Britain in the 5th century CE, contributing to the formation of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
- Saxons: Residing in northern Germany and the Netherlands, the Saxons were known for their seafaring skills and military prowess. They played a crucial role in the conquest of Britain and the formation of the Saxon kingdoms.
- Jutes: A tribe from the Jutland peninsula in Denmark, the Jutes also participated in the Anglo-Saxon conquest of Britain.
- Franks: A powerful tribe that emerged in the region of present-day Belgium and northern France, the Franks eventually established a vast empire encompassing much of Western Europe.
- Visigoths: One of the largest Germanic tribes, the Visigoths migrated from Scandinavia to the Black Sea region and eventually established a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula.
- Ostrogoths: Closely related to the Visigoths, the Ostrogoths migrated to Italy in the 5th century CE and established a kingdom there.
- Lombards: Originating in Scandinavia, the Lombards migrated to Italy in the 6th century CE and established a kingdom in northern Italy.
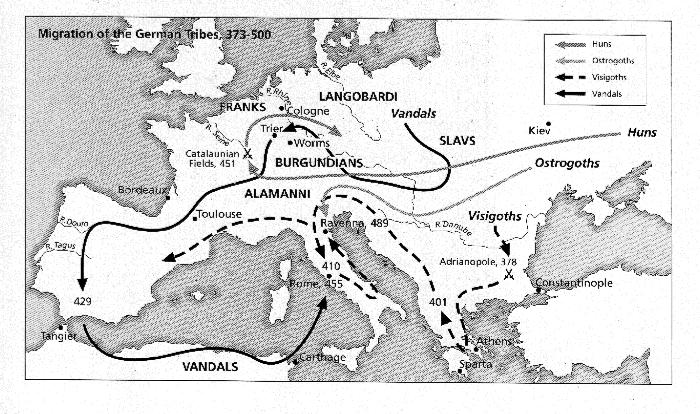
The Migrations: A Tapestry of Movement
The Germanic tribes were known for their expansive migrations, driven by factors such as population pressure, climatic changes, and the pursuit of new lands and resources. These movements had a profound impact on the political and cultural landscape of Europe.
- The Great Germanic Migrations: From the 3rd to the 6th centuries CE, a wave of Germanic tribes migrated south and west, leading to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of new Germanic kingdoms.
- The Anglo-Saxon Conquest: The migration of Angles, Saxons, and Jutes to Britain in the 5th century CE led to the displacement of the native Britons and the formation of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
- The Frankish Expansion: The Franks, under the leadership of Clovis I, conquered much of Gaul (present-day France) and established a powerful empire that extended across Western Europe.
- The Visigothic Kingdom: The Visigoths established a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula in the 5th century CE, which eventually encompassed most of Spain and Portugal.
Beyond Conquest: The Impact of Germanic Culture
The Germanic tribes left a lasting legacy on European culture, contributing to the development of language, law, and social structures.
- Language: The Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Swedish, and Norwegian, are spoken by hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
- Law: The Germanic tribes had a strong tradition of legal codes, which influenced the development of legal systems in Europe.
- Social Structure: The Germanic tribes had a complex social structure based on kinship and loyalty, which contributed to the development of feudalism in medieval Europe.
Interpreting the Map: A Window into the Past
A map of Germanic tribes provides a valuable tool for understanding the complex movements, interactions, and cultural influences of these peoples. It allows us to:
- Visualize the geographical spread of Germanic tribes: The map helps us understand the areas inhabited by different Germanic groups and their proximity to other cultures.
- Trace the routes of migration: The map highlights the paths taken by different Germanic tribes during their migrations, revealing the extent of their movements.
- Analyze the interactions between tribes: The map shows the areas where different Germanic tribes came into contact, providing insights into their relationships, alliances, and conflicts.
- Gain a deeper understanding of the formation of European nations: The map helps us understand how the migrations and conquests of Germanic tribes shaped the political and cultural landscape of Europe, contributing to the formation of nations such as England, France, and Germany.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of Germanic Tribes
1. What is the most accurate way to represent the location of Germanic tribes on a map?
The most accurate way to represent the location of Germanic tribes on a map is to use a dynamic representation that reflects the fluid nature of their movements and the changing political landscape. A map should not only show the approximate areas where tribes resided at a particular point in time but also illustrate the paths of their migrations.
2. How can we reconcile the different accounts of Germanic tribes found in historical sources?
Reconciling different accounts of Germanic tribes requires a careful examination of the sources and an understanding of their biases. It is essential to consider the perspective of the author, the historical context, and the potential for exaggeration or distortion. Cross-referencing different accounts and analyzing archaeological evidence can help to provide a more complete and nuanced picture.
3. What is the significance of the Germanic tribal system in shaping European history?
The Germanic tribal system played a crucial role in shaping European history by influencing the political, social, and cultural landscape of the continent. The migrations and conquests of Germanic tribes led to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of new Germanic kingdoms. Their legal systems and social structures had a profound impact on the development of medieval Europe.
4. How did the Germanic tribes interact with other cultures?
The Germanic tribes engaged in a variety of interactions with other cultures, ranging from peaceful trade to violent conflict. They often adopted aspects of other cultures, such as Roman law and Christianity, while also influencing the cultures they encountered.
5. What are the challenges in mapping the movements of Germanic tribes?
Mapping the movements of Germanic tribes presents several challenges:
- Limited historical sources: The historical record of Germanic tribes is often fragmented and incomplete, making it difficult to trace their precise movements.
- Fluid boundaries: The boundaries between different Germanic tribes were often fluid and subject to change, making it difficult to define their exact territories.
- Multiple interpretations: Different scholars may have varying interpretations of the available historical evidence, leading to different representations of tribal movements on maps.
Tips for Understanding Germanic Tribes
- Study the historical context: It is essential to understand the historical context in which the Germanic tribes lived, including the Roman Empire, the migrations of other peoples, and the development of new political and social structures.
- Analyze archaeological evidence: Archaeological evidence, such as burial mounds, settlements, and artifacts, can provide valuable insights into the lives and cultures of Germanic tribes.
- Examine linguistic connections: The study of Germanic languages can reveal connections between different tribes and their origins.
- Consider multiple perspectives: It is important to consider the perspectives of different cultures and groups involved in interactions with Germanic tribes, including those of the Romans, the Celts, and other Germanic tribes.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Influence
The Germanic tribes left an enduring legacy on the history and culture of Europe. Their migrations, conquests, and interactions with other cultures shaped the political landscape, linguistic diversity, and societal structures of the continent. A map of Germanic tribes serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex movements and interactions of these groups, providing insights into their origins, migrations, and lasting influence on European history and culture. While the map itself cannot fully capture the dynamism and complexity of these ancient peoples, it offers a framework for understanding the intricate tapestry of their lives and their lasting impact on the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Germanic Tribes: A Map of Migration and Cultural Development. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!