Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps
- 3.1 The Science Behind the Maps
- 3.2 Benefits of Global Earthquake Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Global Earthquake Map: A User’s Guide
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Global Earthquake Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps
/worldseismap-56a368c65f9b58b7d0d1d07a.png)
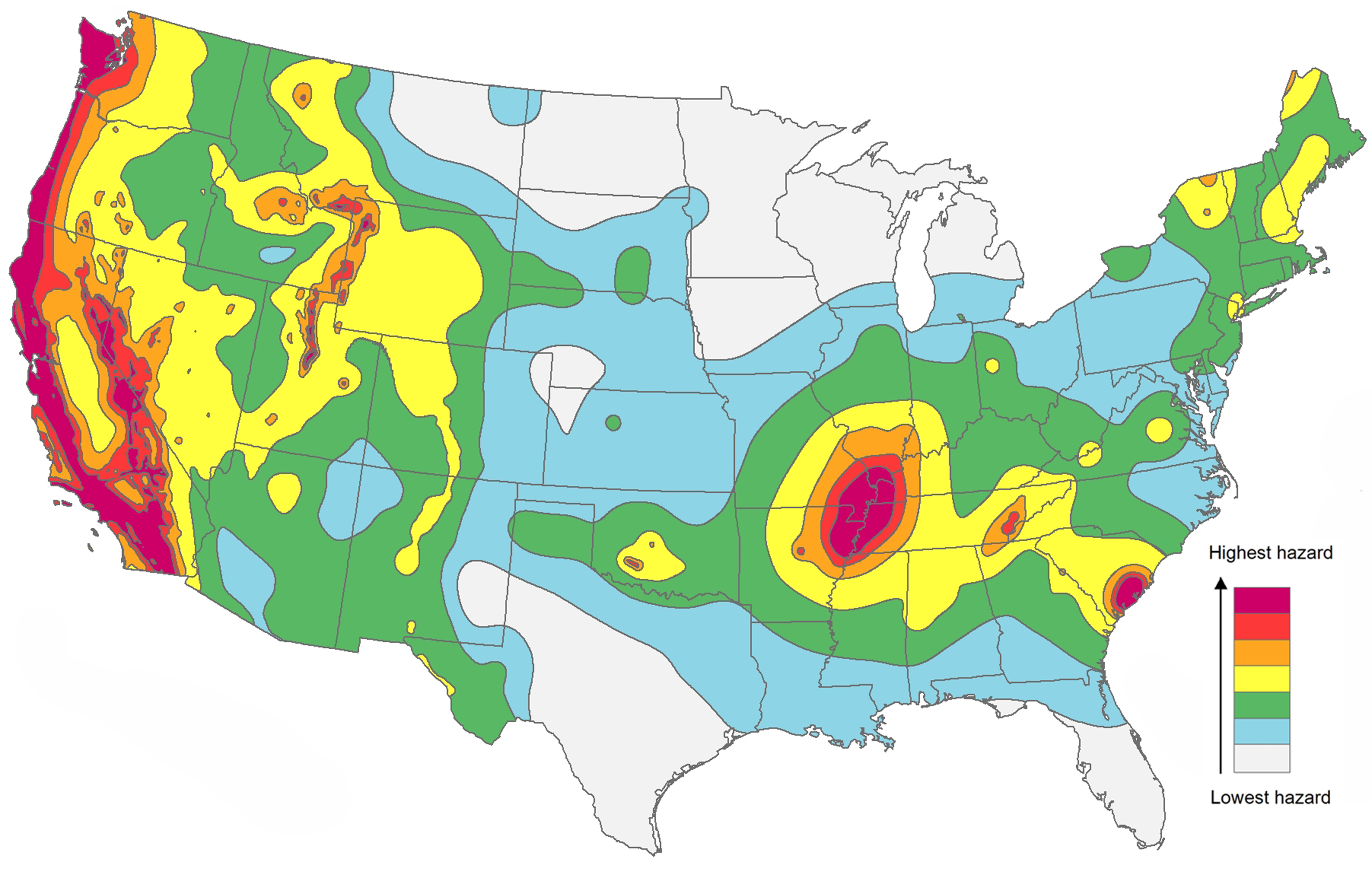
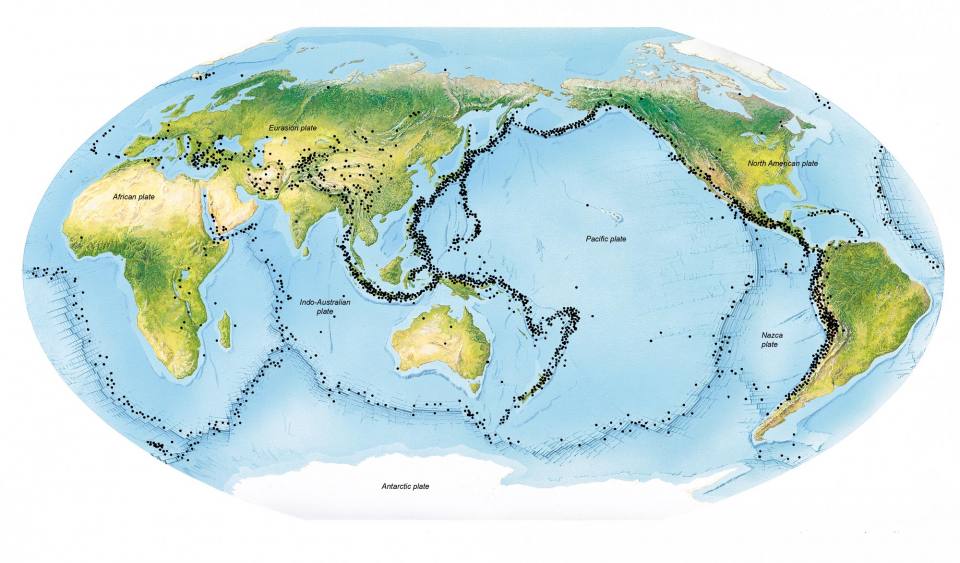
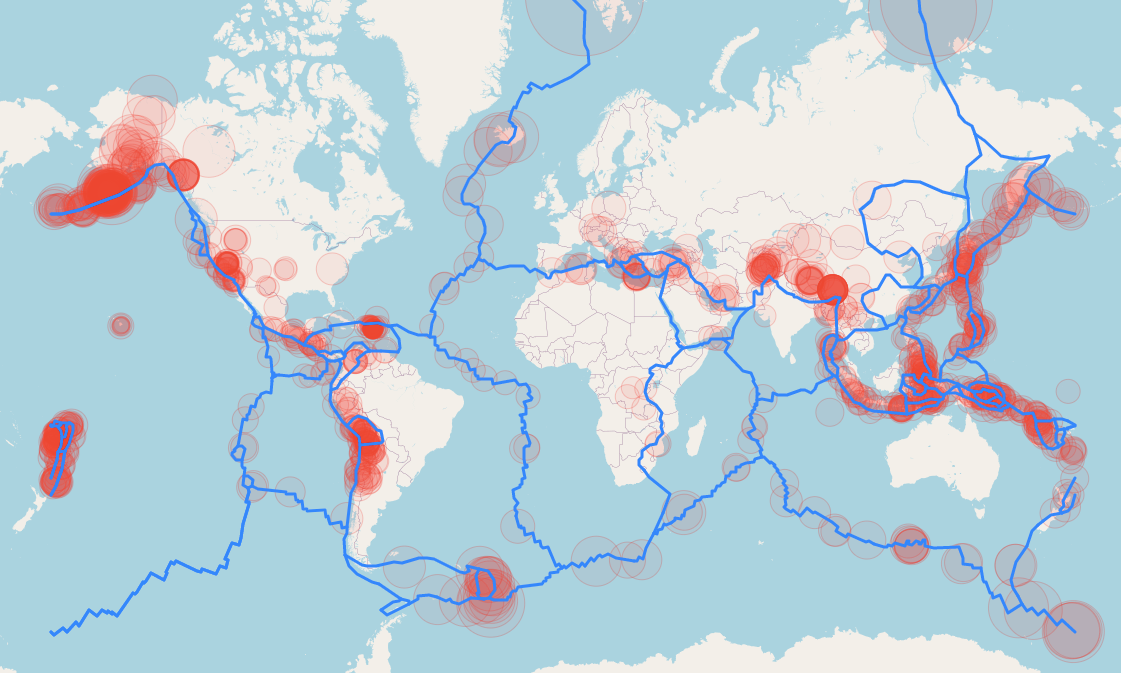
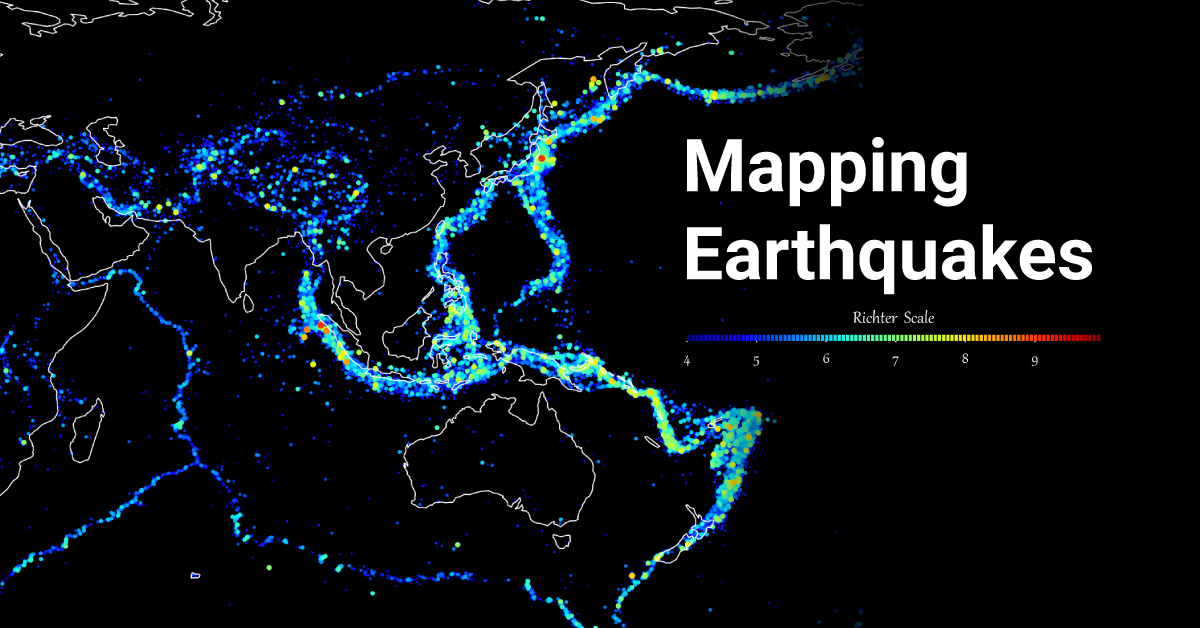
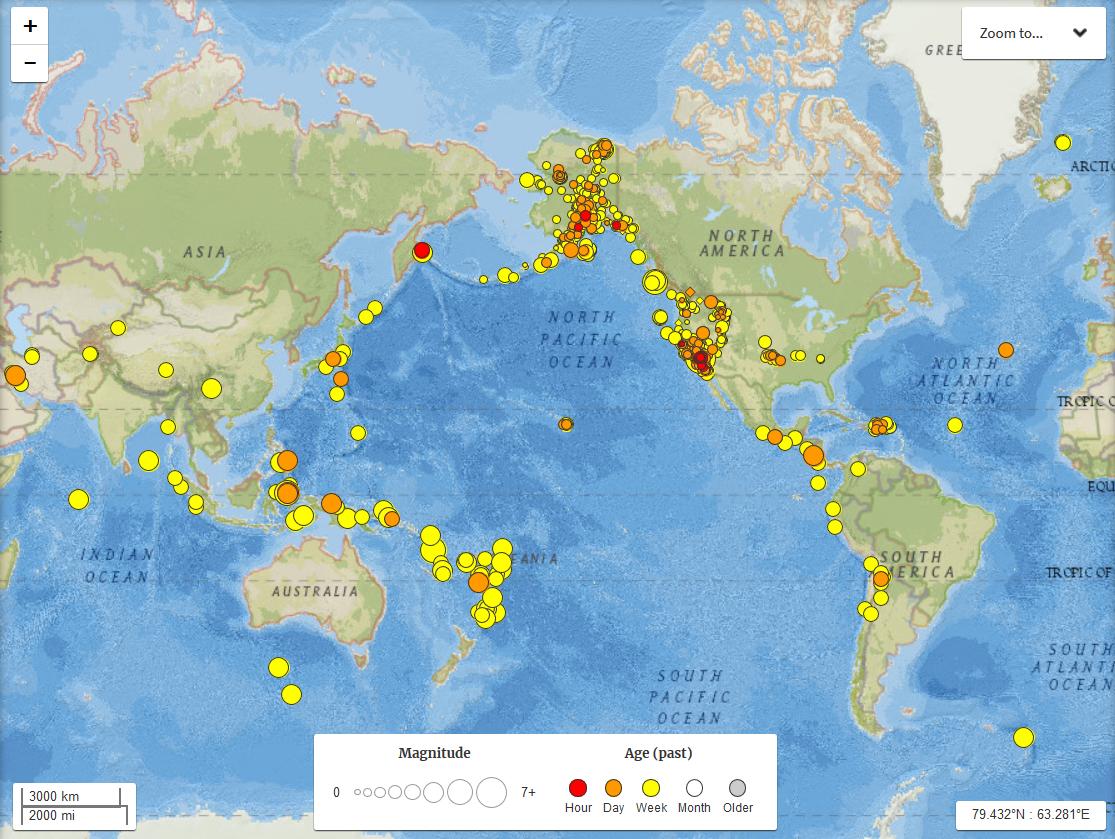
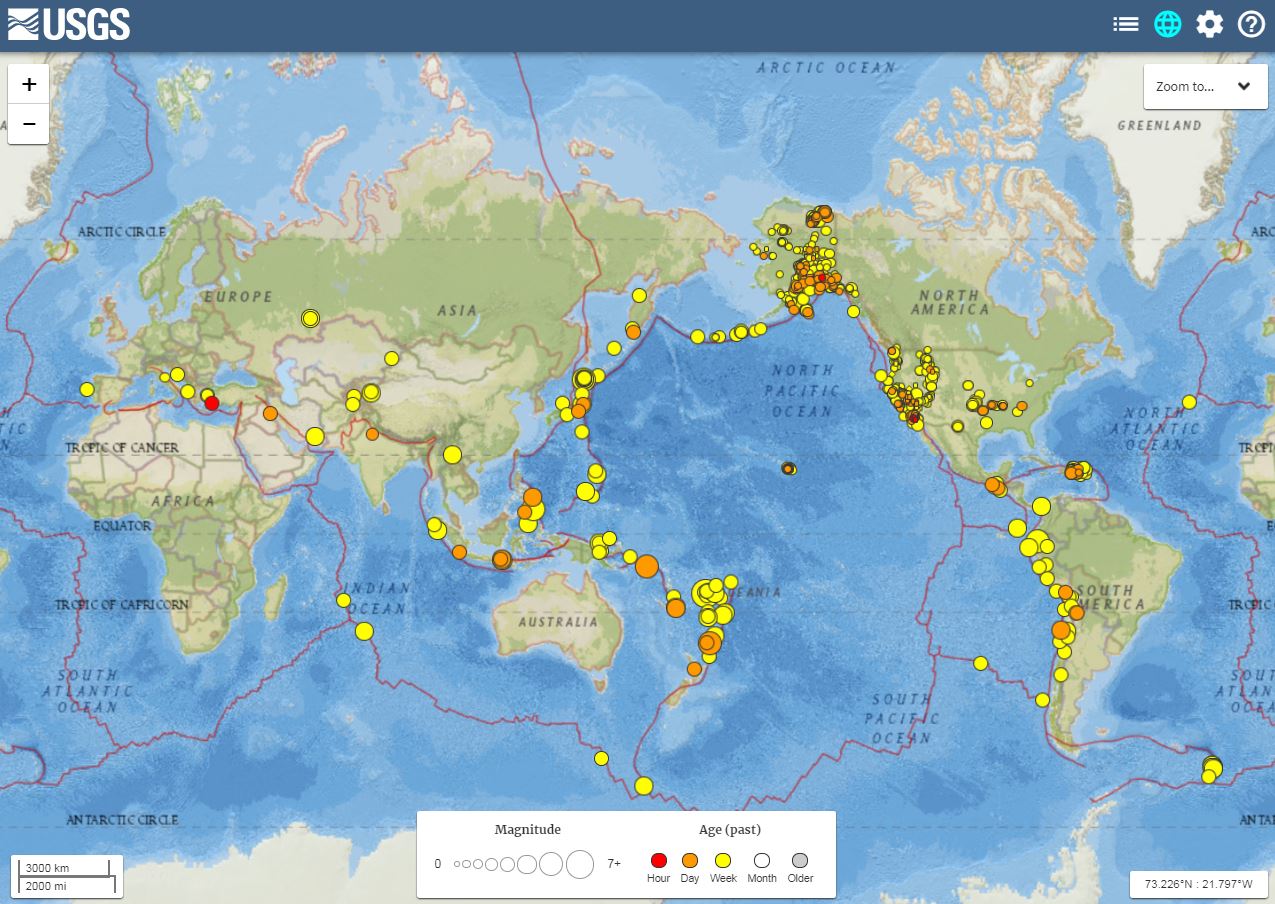
The Earth, a dynamic and ever-shifting sphere, is constantly in motion. This dynamism manifests itself in various ways, with earthquakes being one of the most dramatic and impactful. These seismic events, often unpredictable and powerful, can reshape landscapes, devastate communities, and even alter the course of history. To better understand and prepare for these geological forces, scientists and organizations have developed global earthquake maps – invaluable tools that visualize and analyze seismic activity across the planet.
The Science Behind the Maps
Global earthquake maps are not simply static representations of past events; they are dynamic visualizations that integrate data from various sources, including:
- Seismometers: These sensitive instruments, deployed across the globe, detect and record ground vibrations caused by earthquakes.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): By monitoring the subtle shifts in the Earth’s crust, GPS data provides insights into tectonic plate movement and potential earthquake zones.
- Historical Records: Studying historical accounts of earthquakes, including written records, archaeological evidence, and folklore, provides valuable context for understanding long-term seismic trends.
This data is then processed and analyzed using sophisticated algorithms and statistical models to generate maps that highlight:
- Earthquake Epicenters: The exact location where an earthquake originates.
- Magnitude: The strength of an earthquake, measured on the Richter scale or other magnitude scales.
- Depth: The distance below the Earth’s surface where the earthquake originates.
- Frequency: The number of earthquakes occurring in a specific region over a given period.
- Fault Lines: The boundaries between tectonic plates where earthquakes are most likely to occur.
Benefits of Global Earthquake Maps
The creation and utilization of global earthquake maps offer numerous benefits, contributing to a safer and more informed world:
1. Enhanced Understanding of Seismic Activity: Maps provide a visual representation of the Earth’s seismic activity, enabling scientists to identify patterns, trends, and potential risks. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the underlying tectonic processes driving earthquakes.
2. Improved Earthquake Prediction and Early Warning Systems: While predicting the exact time and location of an earthquake remains a challenge, global earthquake maps help pinpoint regions at higher risk. This information aids in developing early warning systems, giving communities precious time to prepare and evacuate.
3. Effective Disaster Management and Mitigation: Maps help authorities prioritize resources, plan evacuation routes, and implement building codes in earthquake-prone areas. This proactive approach significantly reduces the potential impact of earthquakes on communities and infrastructure.
4. Research and Development: Global earthquake maps serve as a valuable resource for researchers studying earthquake dynamics, fault behavior, and the relationship between seismic activity and other geological phenomena.
5. Public Awareness and Education: Accessible and user-friendly maps can educate the public about earthquake risks, promoting preparedness and responsible behavior in earthquake-prone regions.
Navigating the Global Earthquake Map: A User’s Guide
Global earthquake maps are available through various online platforms, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS maintains an extensive earthquake catalog and provides interactive maps showcasing global seismic activity.
- European-Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC): The EMSC offers a comprehensive earthquake map for Europe and the Mediterranean region, providing real-time updates and historical data.
- International Seismological Centre (ISC): The ISC compiles earthquake data from around the world, offering a global perspective on seismic activity.
These platforms often feature:
- Interactive Maps: Users can zoom in and out, explore different regions, and filter data based on magnitude, time, and other criteria.
- Earthquake Catalogs: Detailed information on past earthquakes, including location, magnitude, depth, and date.
- Real-Time Data: Updates on ongoing seismic activity, providing near-instantaneous information on earthquakes as they occur.
- Educational Resources: Explanations of earthquake science, terminology, and safety guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How are earthquake magnitudes measured?
Earthquake magnitudes are measured using the Richter scale, a logarithmic scale where each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of seismic waves and a 31.6-fold increase in the energy released.
2. What is the difference between an earthquake’s epicenter and its focus?
The epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s focus, which is the point of origin beneath the surface where the rupture occurs.
3. How often do earthquakes occur?
Earthquakes occur constantly, with thousands happening every day, but most are too small to be felt. Major earthquakes, those with magnitudes greater than 7.0, occur less frequently, typically a few times a year.
4. Can earthquakes be predicted?
While scientists can identify areas at higher risk for earthquakes and develop early warning systems, predicting the exact time and location of an earthquake remains a significant challenge.
5. What should I do during an earthquake?
During an earthquake, it’s crucial to drop, cover, and hold on. Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy object, and hold on until the shaking stops.
Tips for Utilizing Global Earthquake Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the platform: Explore the features, options, and data available on the chosen platform.
- Focus on your region: Pay particular attention to the seismic activity in your area, understanding the potential risks and preparedness measures.
- Use the maps for planning: Utilize the maps to identify evacuation routes, locate safe zones, and plan for earthquake scenarios.
- Stay informed: Regularly check for updates on earthquake activity and subscribe to alerts from relevant organizations.
- Share knowledge: Educate your family, friends, and community about earthquake preparedness and the resources available on global earthquake maps.
Conclusion
Global earthquake maps are not just scientific tools; they are vital resources for promoting safety, resilience, and informed decision-making in a world constantly shaped by the Earth’s dynamism. By providing a visual understanding of seismic activity, these maps empower communities to prepare for earthquakes, mitigate their impact, and ultimately build a more resilient future. As technology advances and scientific understanding deepens, global earthquake maps will continue to evolve, offering even more comprehensive insights into the Earth’s pulse and helping us navigate the challenges of living on a dynamic planet.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Pulse: A Comprehensive Look at Global Earthquake Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!