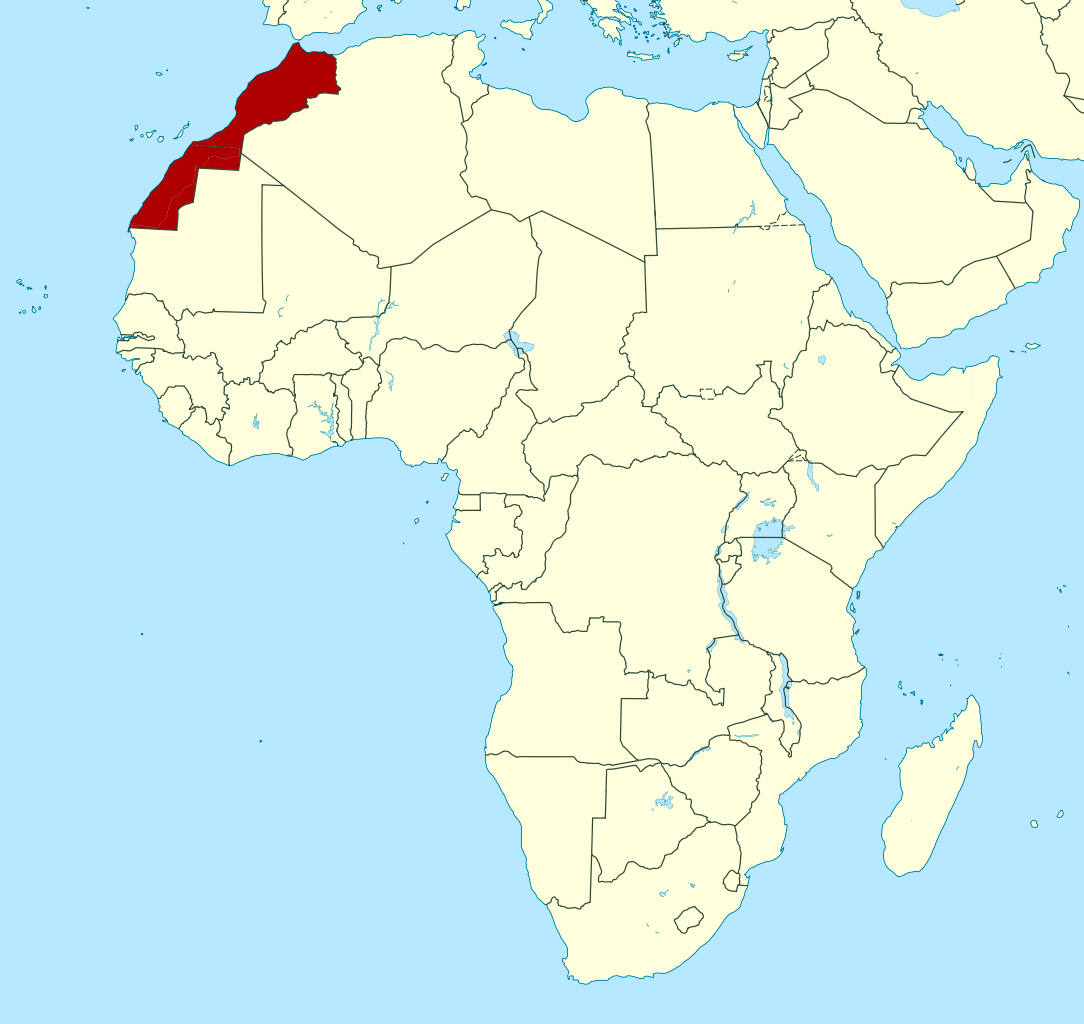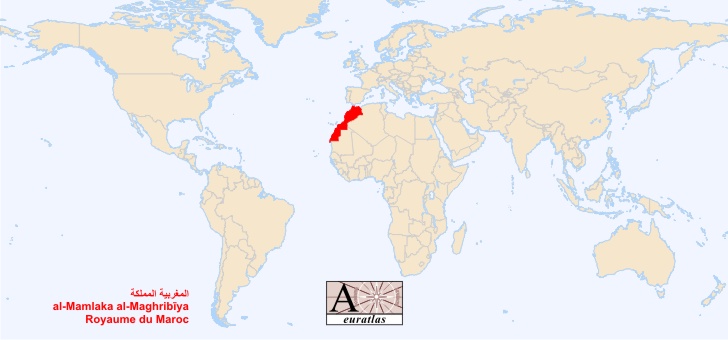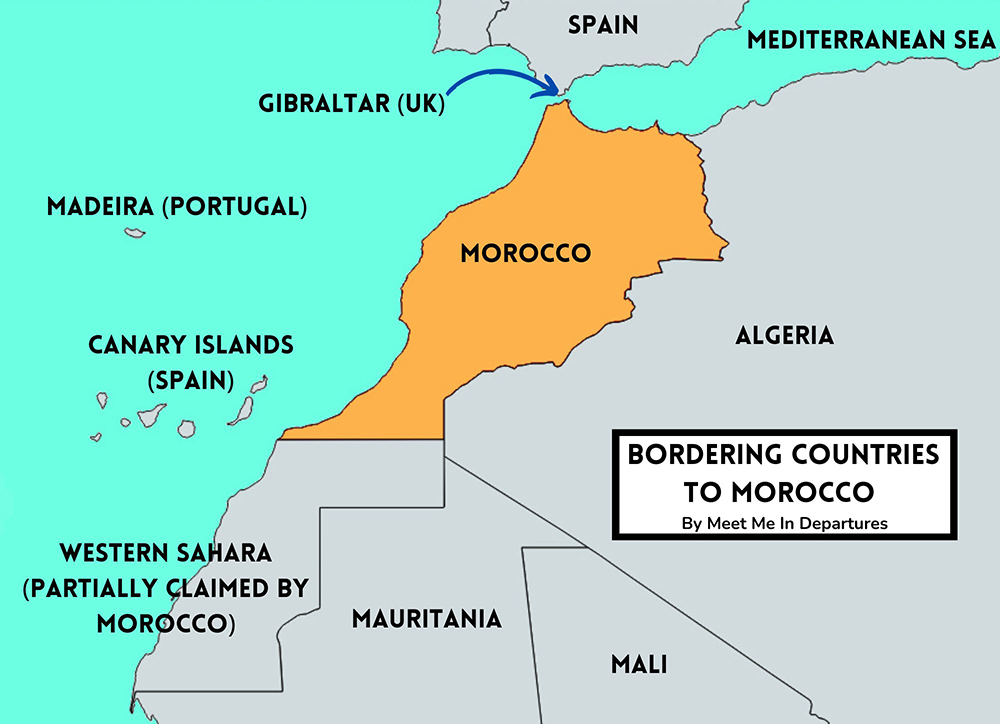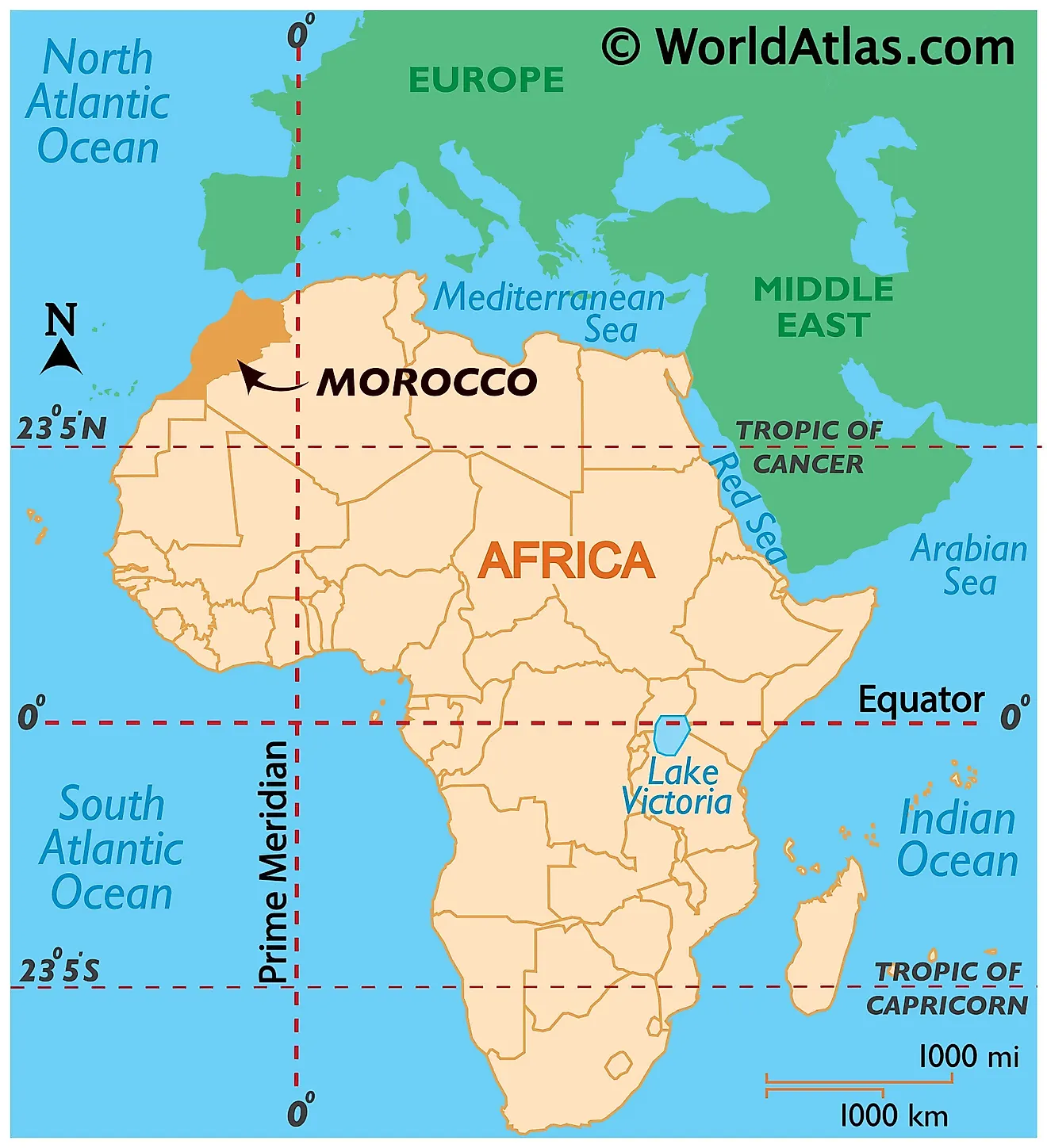
Morocco is situated in the northwestern corner of Africa. Its strategic location makes it a gateway between Africa and Europe. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Algeria to the east and southeast, and Mauritania to the south. This unique position has shaped Morocco’s history, culture, and economy for centuries.
To pinpoint Morocco’s location more precisely, consider these coordinates: approximately 32° North latitude and 5° West longitude. This places it squarely within the Northern Hemisphere and along the western edge of the African continent. The country’s proximity to Europe, with the Strait of Gibraltar separating it from Spain by a mere 13 kilometers (8 miles), has fostered significant cultural and economic exchange.
Strategically Important: Its location at the Strait of Gibraltar controls access between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, making it a vital point for international trade and naval activity.
Climate Diversity: The country’s location results in diverse climates, ranging from Mediterranean along the coast to arid in the Sahara Desert.
Cultural Crossroads: Being at the intersection of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, Morocco’s culture is a rich blend of Berber, Arab, and European influences.
The Kingdom of Morocco shares borders with Algeria to the east and southeast, and Mauritania to the south. The borders are mostly defined by the Sahara Desert, which creates natural barriers. The maritime borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north. These geographical boundaries have played a significant role in shaping Morocco’s relationships with its neighbors and its overall geopolitical strategy.
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow waterway that separates Morocco from Europe, specifically Spain. This strait is one of the world’s most important shipping lanes, connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea. Morocco’s proximity to this strait gives it significant strategic and economic importance.
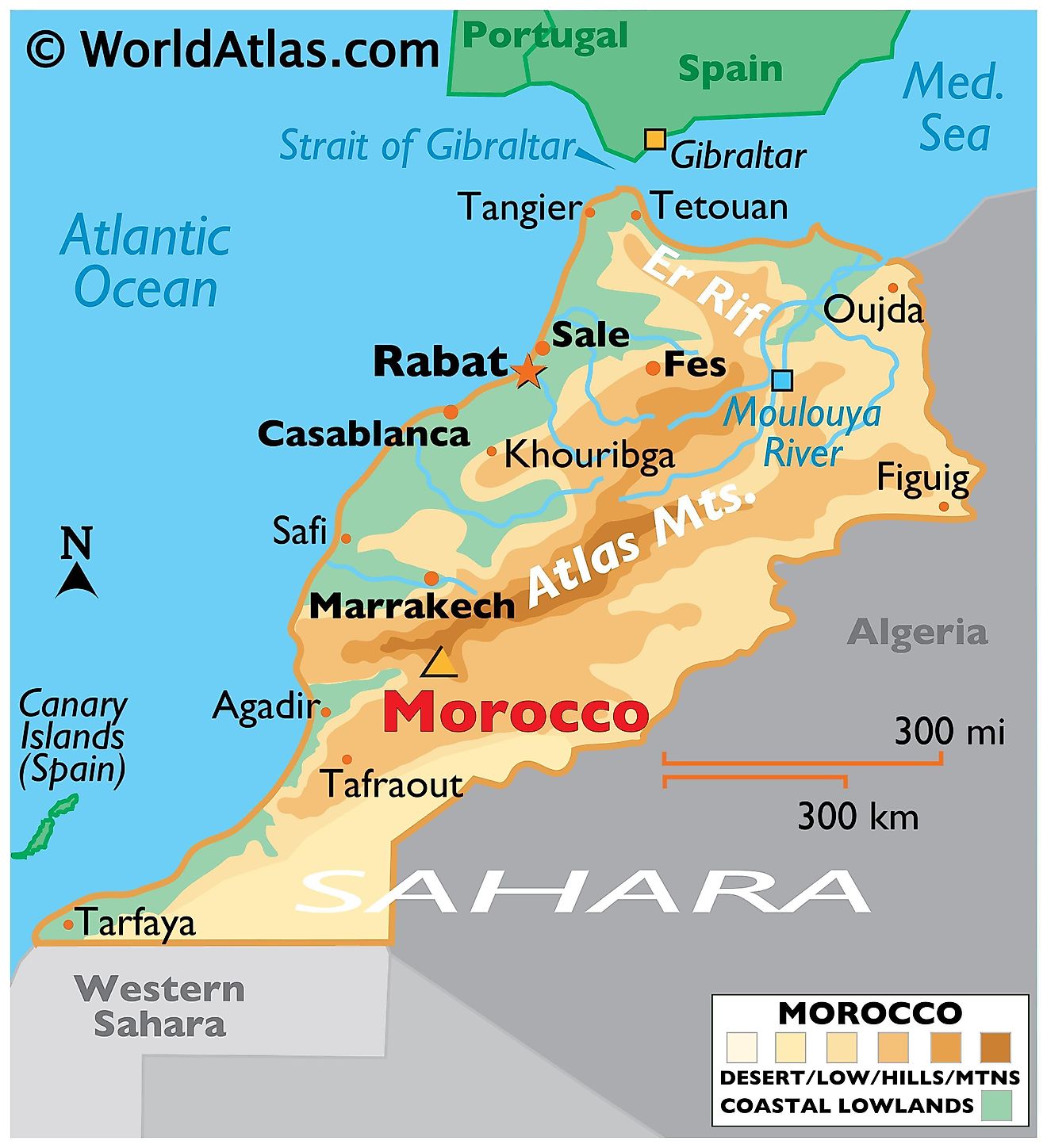
The Atlas Mountains: A mountain range that runs through the center of the country, providing water resources and creating microclimates.
The Sahara Desert: Covering the southern and eastern parts of Morocco, offering stunning desert landscapes and unique ecosystems.
Coastal Plains: Fertile plains along the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts, supporting agriculture and population centers.
Rivers and Waterways: Important rivers like the Draa, Sebou, and Moulouya, which provide water for irrigation and domestic use.
Morocco experiences a variety of climates due to its diverse geography. The coastal regions have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The interior experiences a more continental climate, with greater temperature extremes. The Sahara Desert region has a hot, arid climate with very little rainfall. The Atlas Mountains have an alpine climate with cold winters and milder summers.
Morocco’s climate significantly impacts its agriculture, tourism, and overall way of life. The fertile coastal plains support a variety of crops, including citrus fruits, vegetables, and grains. The tourism industry thrives on the sunny beaches and the unique desert landscapes. However, the country also faces challenges such as water scarcity and desertification due to its arid climate.
Morocco’s location has been a major factor in shaping its rich cultural heritage. The country has been influenced by Berber, Arab, European, and African cultures. This blend of influences is reflected in Morocco’s architecture, cuisine, music, and traditions. The major cities such as Marrakech, Fes, and Casablanca showcase this cultural diversity, attracting visitors from around the world.
Morocco’s economy benefits significantly from its strategic location. The country is a major exporter of phosphates, agricultural products, and manufactured goods. Its proximity to Europe makes it an attractive destination for foreign investment. The tourism industry is also a major contributor to the economy, drawing visitors with its rich history, diverse landscapes, and vibrant culture.
Is Morocco in Africa or Europe?
Morocco is geographically located in Africa, specifically in the northwestern part of the continent. However, it’s very close to Europe, with the Strait of Gibraltar separating it from Spain.
What are Morocco’s neighboring countries?
Morocco is bordered by Algeria to the east and southeast, and Mauritania to the south. It also has maritime borders with Spain and Portugal.
What ocean is near Morocco?
Morocco is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north.
Is Morocco a safe country to visit?
Generally, Morocco is considered a safe country for tourists. However, like any travel destination, it’s important to be aware of your surroundings and take precautions against petty theft.
What is the climate like in Morocco?
Morocco has a diverse climate ranging from Mediterranean along the coast to arid in the Sahara Desert. The Atlas Mountains have an alpine climate.
What languages are spoken in Morocco?
The official languages of Morocco are Arabic and Berber (Tamazight). French is also widely spoken, especially in business and government. English is becoming increasingly common in tourist areas.
What is Morocco known for?
Morocco is known for its vibrant culture, stunning landscapes, rich history, and delicious cuisine. Popular attractions include the ancient cities of Marrakech and Fes, the Sahara Desert, and the Atlas Mountains.
In conclusion, Morocco’s location in the northwestern corner of Africa is not just a matter of geography; it’s a defining factor in its history, culture, and economy. Its strategic position at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East has shaped its identity and made it a fascinating destination for travelers and a key player in global affairs. Understanding where Morocco is on the world map provides a deeper appreciation for this vibrant and diverse country. From its strategic importance to its diverse climate and rich cultural heritage, Morocco’s location is central to its unique character.
Whether you are planning a visit, studying its history, or simply curious about the world, knowing Morocco’s geographical context is essential. So, next time you look at a world map, take a moment to appreciate the significance of Morocco’s place on it – a land of contrasts, cultures, and captivating stories.