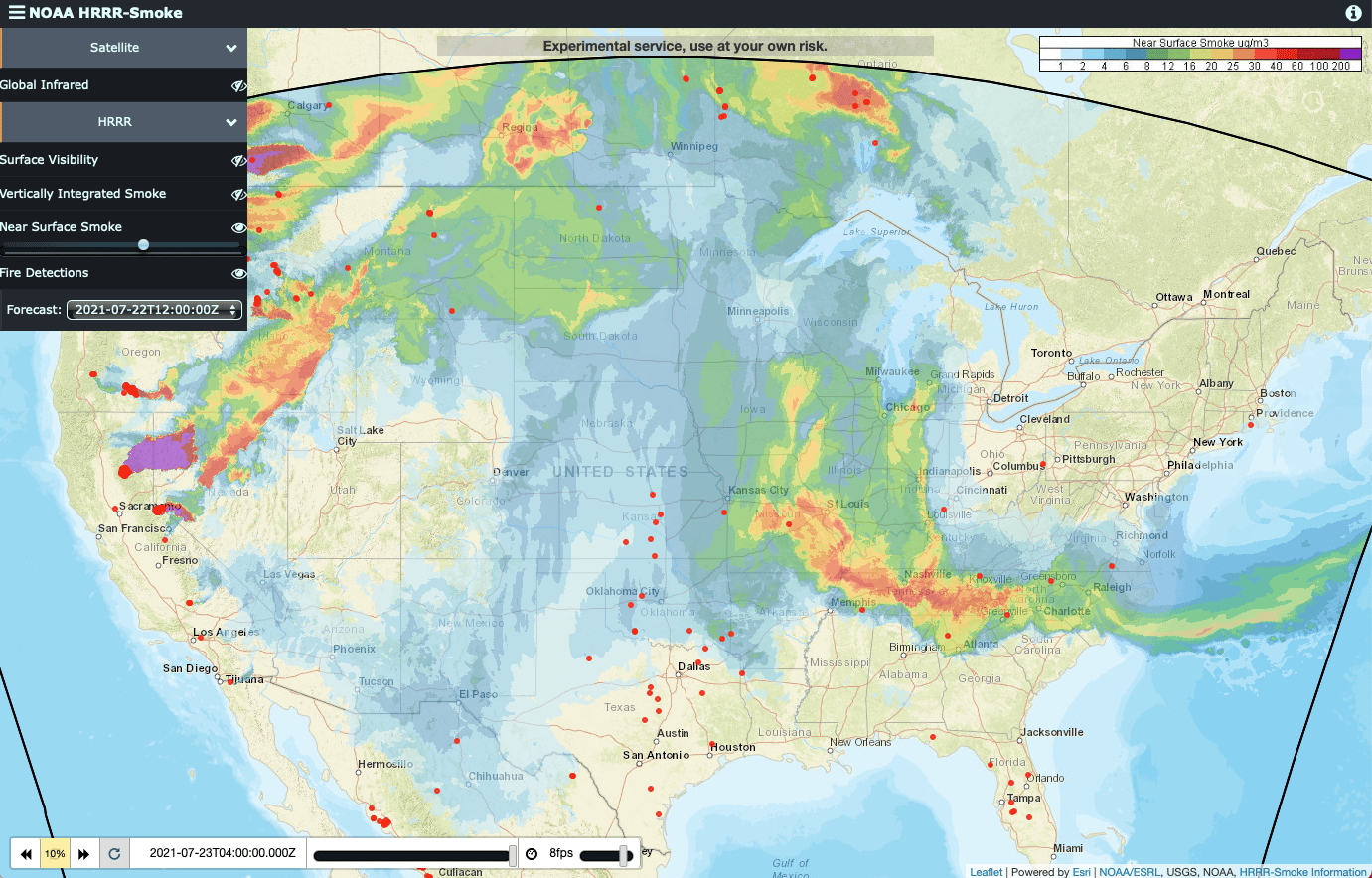
A wildfire smoke map is a visual representation that illustrates the current and forecasted dispersion of smoke plumes from active wildfires. These maps utilize complex atmospheric models, satellite imagery, and real-time data to predict where smoke is likely to travel and how concentrated it might be. They are designed to provide timely information to individuals, communities, and emergency responders.
The primary purpose of a wildfire smoke map is to inform the public about potential health risks associated with poor air quality. By displaying areas with elevated levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) – the primary component of smoke that is harmful to human health – these maps empower people to take necessary precautions.
These maps are not just about current conditions; many also offer forecasts. This forward-looking capability is vital for planning. Whether you’re organizing outdoor events, planning travel, or simply deciding whether to open your windows, a smoke forecast can help you make informed decisions days in advance.
Understanding the data presented on a wildfire smoke map is key to its effective use. Typically, you’ll see different colors or intensity levels representing varying concentrations of smoke or air quality index (AQI) values. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the legend or key provided on the specific map you are using.
One of the most critical metrics displayed is the Air Quality Index (AQI). The AQI is a standardized system used to report daily air quality. It breaks down how pollution will affect your health. When the AQI is high, it means pollution levels are high, and so are the health risks.
Fine particulate matter, or PM2.5, is the most concerning pollutant in wildfire smoke. These particles are microscopic and can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, leading to a range of health issues from respiratory irritation to cardiovascular problems.
The concentration of PM2.5 is often the underlying data that drives the AQI. Higher PM2.5 levels directly correlate to a higher AQI and a greater risk to health. Smoke maps often visualize these PM2.5 concentrations directly, allowing users to see the density of the smoke.
Different wildfire smoke maps exist, each with its unique strengths and data sources. Some are developed by government agencies like the EPA or NOAA, while others are provided by academic institutions or private weather companies. Each offers a slightly different perspective and forecasting model.
The BlueSky Smoke Forecasting System is a prominent example, often used by agencies to predict smoke dispersion. It’s a sophisticated model that takes into account weather patterns, fuel types, and fire intensity to generate its forecasts.
The EPA’s AirNow.gov website is another excellent resource. It provides real-time air quality data, including AQI, and often integrates information about wildfire smoke when it’s a significant factor. They often feature interactive maps.
Fire.airnow.gov specifically focuses on wildfire smoke and provides detailed information on current fire locations, smoke plumes, and air quality impacts. It’s a go-to for many dealing with active fire events.
Commercial weather services and apps also offer wildfire smoke tracking. While they may use similar data sources, their presentation and forecasting algorithms can vary. It’s worth exploring a few to find one that best suits your needs.
When using a smoke map, pay attention to the time stamps. Smoke plumes are dynamic; they move and dissipate. Ensure you are looking at the most current data and forecasts to get an accurate picture of the air quality situation.
Understanding the forecast is just as important as understanding current conditions. Smoke forecasts can extend from a few hours to several days. These forecasts are crucial for planning activities and protecting vulnerable populations.
Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, individuals with pre-existing respiratory or heart conditions, and pregnant women, are at a higher risk from exposure to wildfire smoke. Smoke maps help these individuals and their caregivers make informed decisions about staying indoors or seeking cleaner air.
What are the health effects of wildfire smoke? Exposure can cause symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, sore throat, and eye irritation. For those with chronic conditions, it can trigger asthma attacks, worsen COPD, and increase the risk of heart problems.
How can you protect yourself from wildfire smoke? The primary recommendation is to stay indoors in an air-conditioned environment with windows and doors closed. If you must go outside, wear a high-quality mask, such as an N95 respirator, which can filter out fine particles.
What about air purifiers? Using a portable air purifier with a HEPA filter can significantly improve indoor air quality by removing fine particulate matter from the smoke. Ensure the purifier is appropriately sized for the room.
What if I need to evacuate? If evacuation orders are in place, follow the guidance of local authorities. Your safety is paramount, and air quality should be a secondary concern to immediate danger. Once in a safer location, you can then focus on air quality.
Are there any long-term health effects? Research is ongoing, but prolonged or repeated exposure to wildfire smoke may have long-term consequences for respiratory and cardiovascular health. This underscores the importance of minimizing exposure whenever possible.
How do these maps predict smoke movement? They use atmospheric dispersion models that simulate how smoke particles travel through the atmosphere. These models consider wind speed and direction, atmospheric stability, humidity, and the amount of smoke released by the fire.
What is the difference between smoke maps and weather maps? While both use meteorological data, smoke maps specifically focus on the movement and concentration of airborne pollutants from fires, whereas weather maps focus on broader atmospheric conditions like temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns for general weather forecasting.
Can I rely on these maps completely? While highly valuable, smoke maps are predictions. Actual smoke concentrations can vary due to localized weather phenomena, the unpredictable nature of fires, and limitations in model accuracy. It’s always wise to cross-reference information and observe local conditions.
The role of technology in wildfire management and public safety is continually expanding. Advanced modeling and data visualization tools, like those used in smoke maps, are critical for mitigating the impact of these events.
Furthermore, understanding the types of fires (e.g., ground fires vs. crown fires) can sometimes provide clues about the intensity and type of smoke produced, though smoke maps abstract this to focus on dispersion.
Educating yourself and your community about wildfire smoke and how to use these maps is a proactive step towards better preparedness. Knowing when and how to protect yourself can make a significant difference during fire season.
In conclusion, wildfire smoke maps are essential tools for navigating the challenges posed by wildfire smoke. By understanding how to interpret these maps, recognizing the health risks, and taking appropriate protective measures, individuals can significantly improve their safety and well-being during periods of poor air quality.






