Navigating the World with Precision: Understanding UTM Map Zones
In a world more and more reliant on exact location information, understanding how we map and symbolize the Earth’s floor is essential. The Common Transverse Mercator (UTM) system is a globally acknowledged coordinate system used extensively in mapping, surveying, and geographic data techniques (GIS). On the coronary heart of the UTM system lies the idea of UTM map zones, which divide the Earth into manageable segments to reduce distortion inherent in projecting a curved floor onto a flat aircraft. This text will delve into the intricacies of UTM map zones, exploring their construction, goal, advantages, and limitations.
The Problem of Mapping a Sphere:
The basic problem in cartography is representing the three-dimensional floor of the Earth on a two-dimensional map. Any methodology of doing so inevitably introduces distortion, affecting properties like form, space, distance, and course. Completely different map projections prioritize minimizing distortion in sure areas whereas accepting better distortion in others.
The Mercator projection, a cylindrical projection developed by Gerardus Mercator within the sixteenth century, is a first-rate instance. Whereas preserving shapes and angles domestically, it severely distorts areas, particularly at greater latitudes. Greenland, for example, seems a lot bigger than it truly is in comparison with nations close to the equator.
The UTM Answer: Minimizing Distortion By way of Zoning
The UTM system addresses the distortion downside by dividing the Earth right into a grid of zones, every projected onto a flat floor utilizing a transverse Mercator projection. This projection is much like the Mercator projection however with the cylinder oriented sideways, touching the Earth alongside a meridian of longitude slightly than the equator. This orientation minimizes distortion alongside that central meridian.
As a substitute of projecting your entire Earth without delay, the UTM system focuses on projecting slim strips of the Earth’s floor, considerably lowering the general distortion inside every zone. This zonal method is the important thing to the UTM system’s accuracy and practicality.
Construction of UTM Zones:
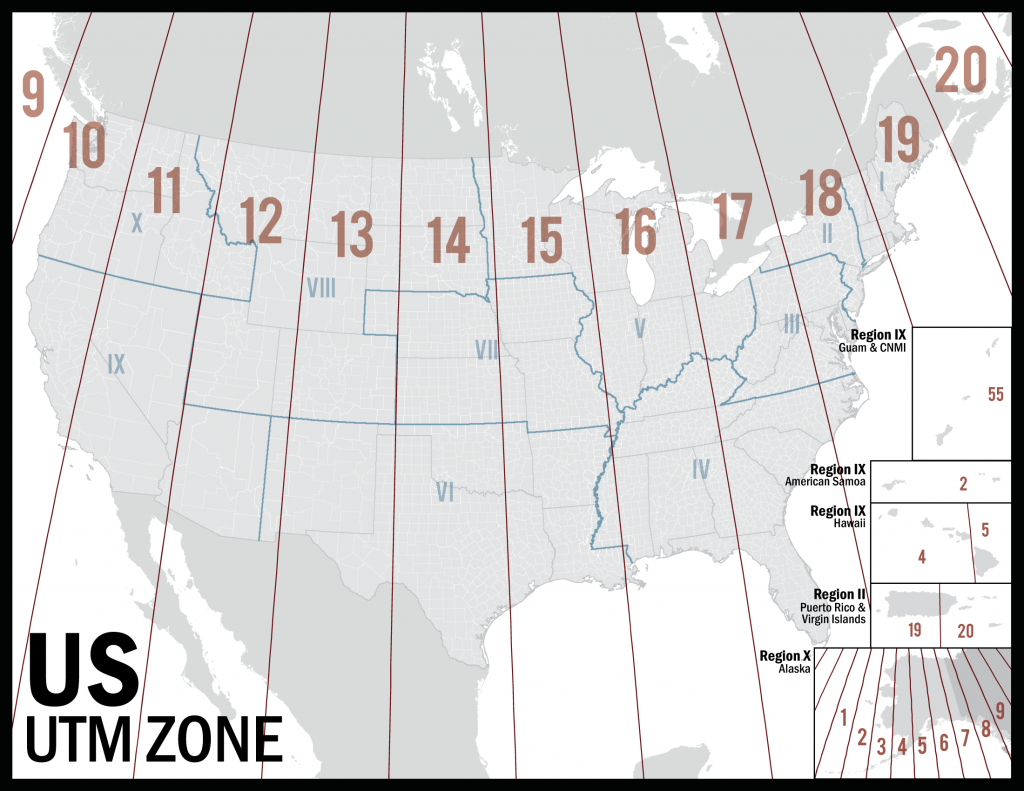
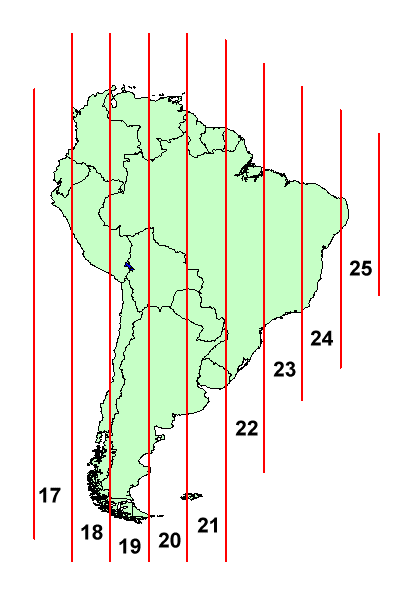
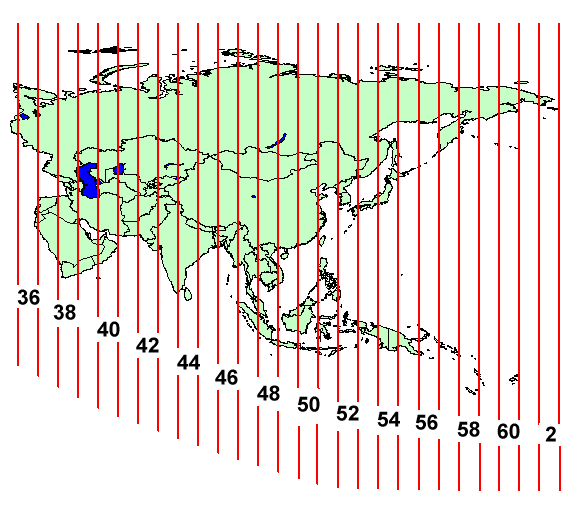
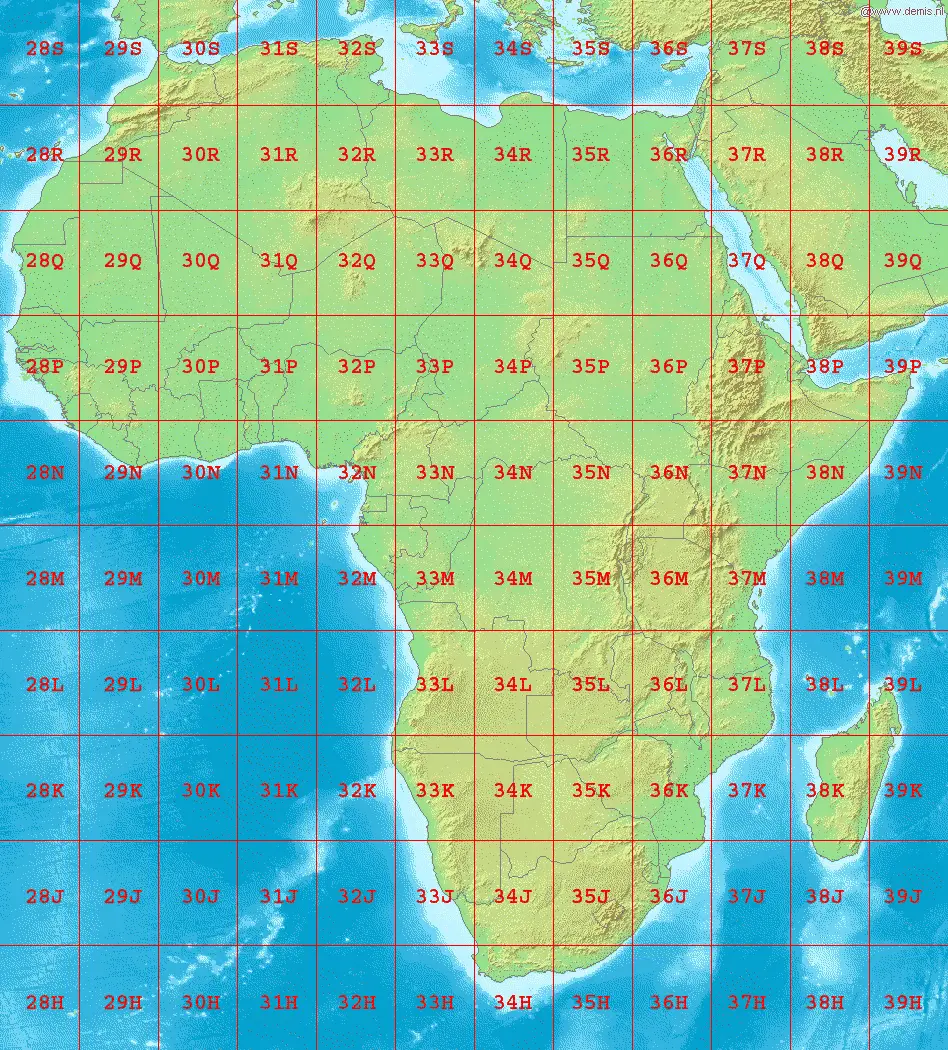
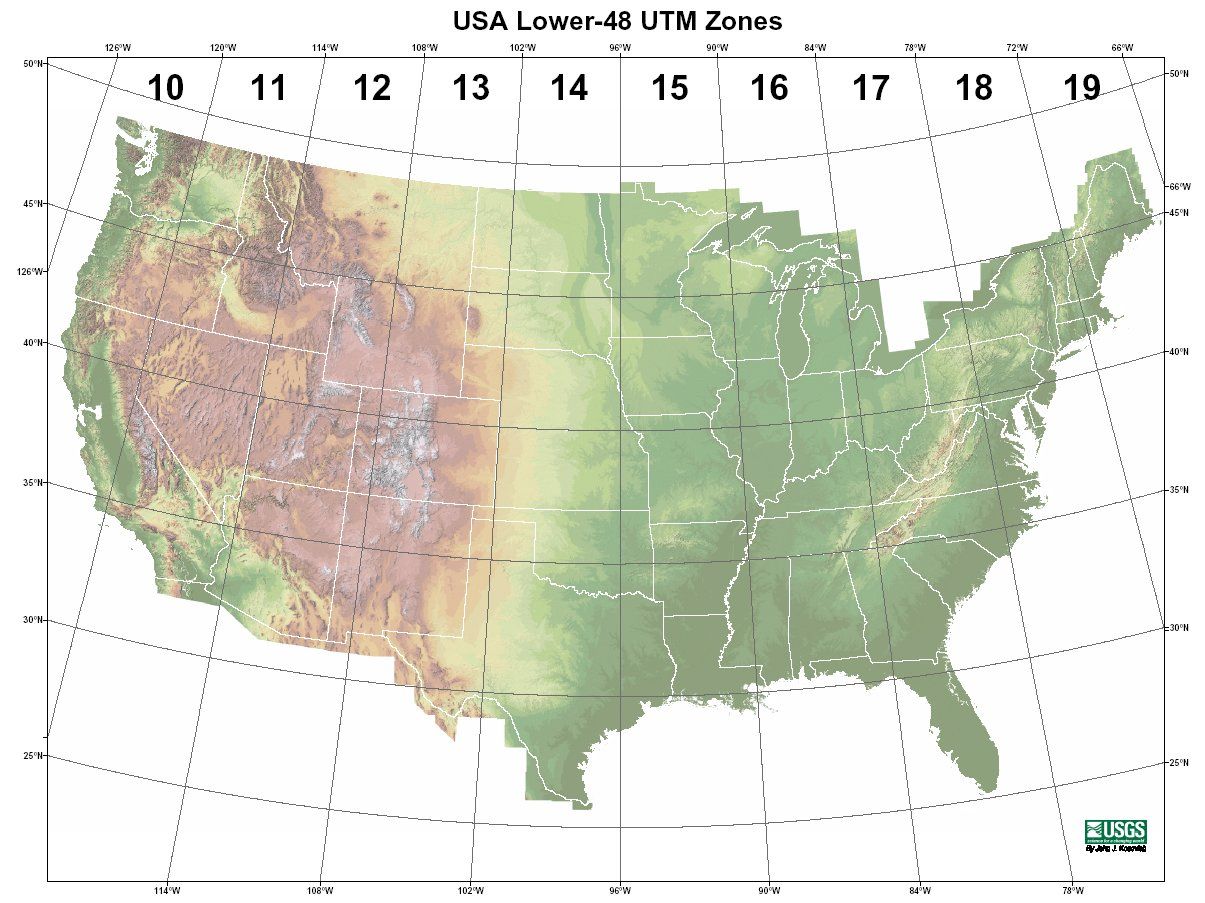
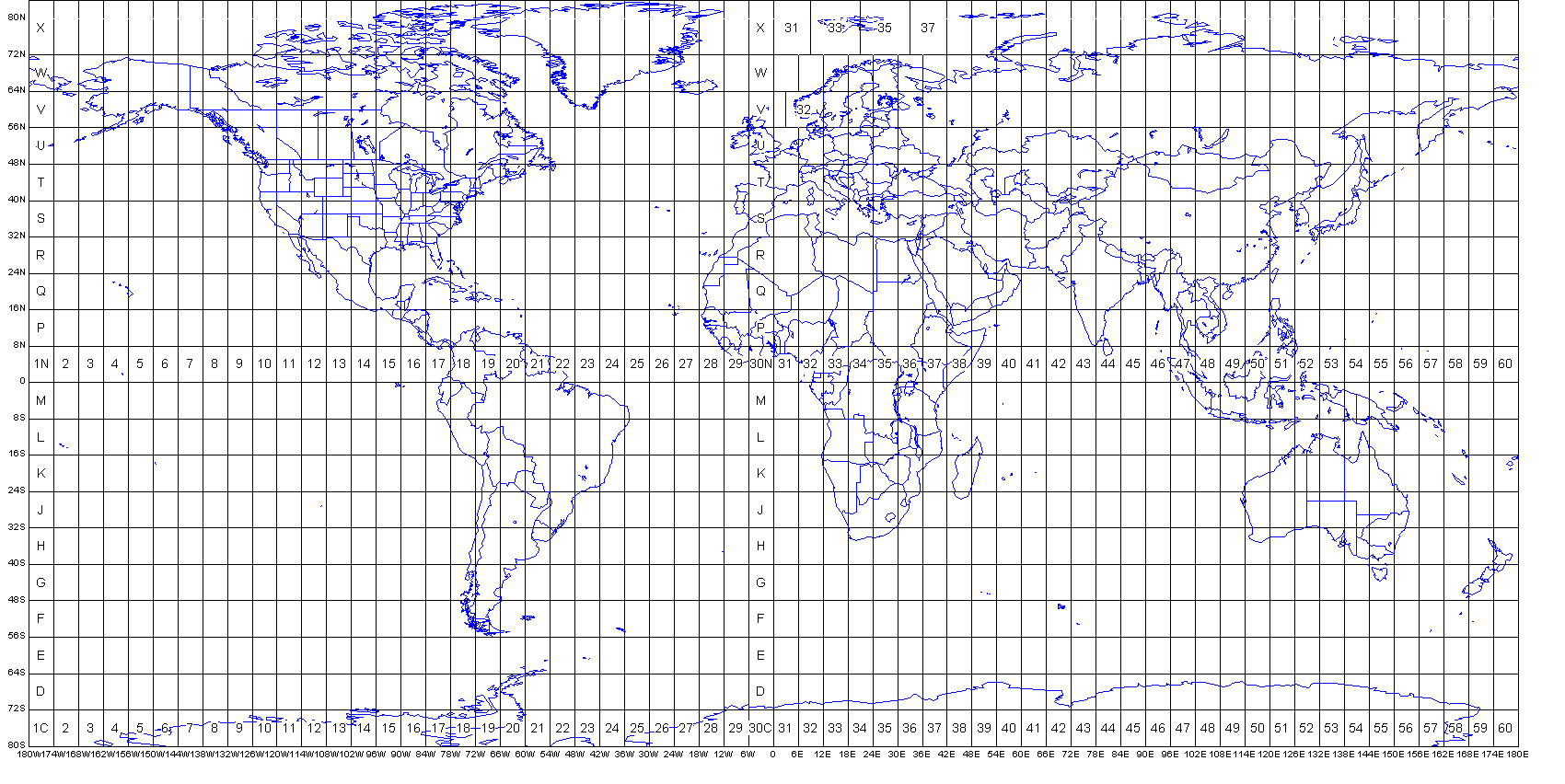
The UTM system divides the Earth into 60 longitudinal zones, every spanning 6 levels of longitude. These zones are numbered from 1 to 60, progressing eastward from the one hundred and eightieth meridian (close to the Worldwide Date Line). Zone 1 covers the realm between 180°W and 174°W longitude, Zone 2 covers the realm between 174°W and 168°W longitude, and so forth.
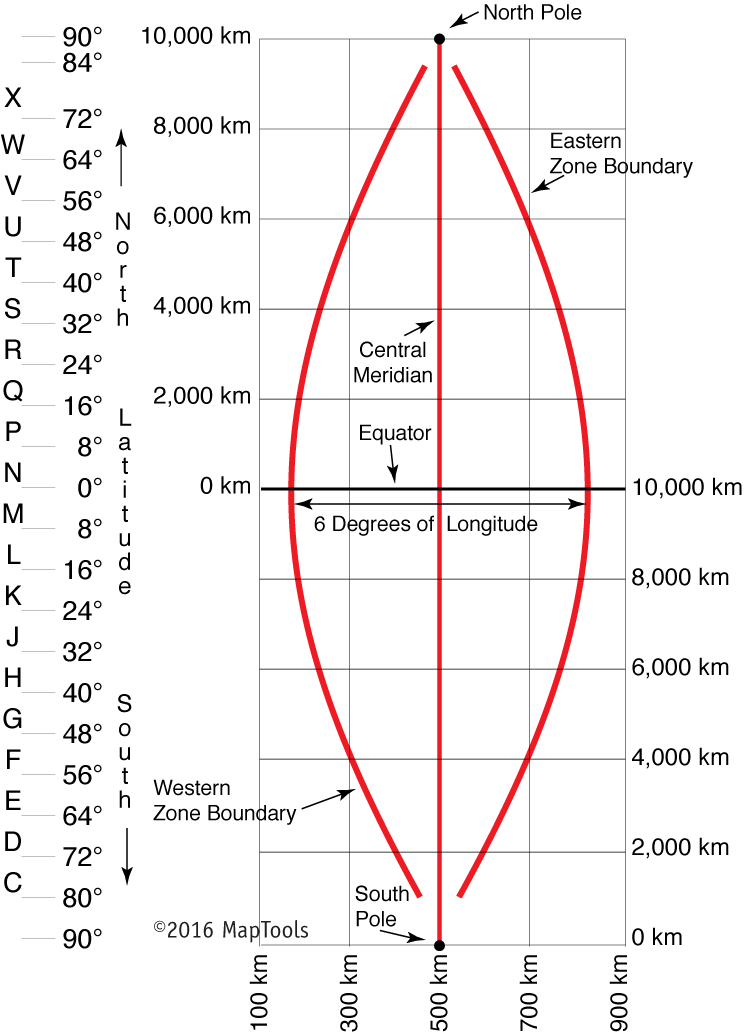
Along with the longitudinal zones, the UTM system additionally divides the Earth into latitudinal bands, every spanning 8 levels of latitude. These bands are lettered from C to X, excluding I and O to keep away from confusion. The bands progress northward from 80°S latitude to 84°N latitude. The letters A and B are reserved for areas south of 80°S, and Y and Z are reserved for areas north of 84°N, however these should not a part of the usual UTM grid.
Subsequently, every UTM zone is uniquely recognized by its zone quantity and latitudinal band letter. For instance, UTM Zone 17T refers back to the space between 84°W and 78°W longitude and 40°N and 48°N latitude.
Coordinate System inside a UTM Zone:
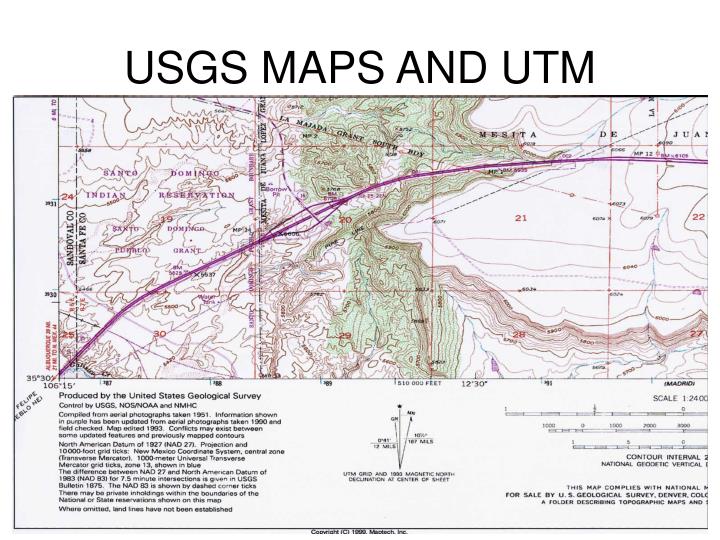
Inside every UTM zone, a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system is established. This method makes use of meters because the unit of measurement, offering excessive precision for location dedication.
-
Easting: The easting coordinate represents the gap east of a central meridian throughout the zone. To keep away from detrimental numbers, the central meridian is assigned a false easting worth of 500,000 meters. Which means that a location on the central meridian has an easting of 500,000 meters, and places to the east have eastings better than 500,000 meters, whereas places to the west have eastings lower than 500,000 meters.
-
Northing: The northing coordinate represents the gap north of the equator. Within the Northern Hemisphere, the equator is assigned a northing worth of 0 meters. Within the Southern Hemisphere, the equator is assigned a false northing worth of 10,000,000 meters to keep away from detrimental numbers.
Subsequently, a UTM coordinate is usually expressed as: Zone Quantity + Zone Letter, Easting, Northing. For instance, 17T 450000E 5400000N represents a location in UTM Zone 17T, 50,000 meters west of the central meridian and 5,400,000 meters north of the equator.
Benefits of Utilizing UTM Zones:
The UTM system gives a number of key benefits:
-
Minimized Distortion: By dividing the Earth into smaller zones, the UTM system considerably reduces distortion in comparison with projections that cowl your entire Earth. This makes it appropriate for purposes requiring correct measurements of distance, space, and form.
-
World Protection: The UTM system covers virtually your entire Earth, making it a universally relevant coordinate system.
-
Metric System: The usage of meters because the unit of measurement simplifies calculations and promotes consistency.
-
Straightforward Calculation of Distances and Areas: The Cartesian coordinate system inside every zone permits for simple calculations of distances and areas utilizing easy geometric formulation.
-
Compatibility with GIS Software program: Most GIS software program packages help the UTM system, making it straightforward to combine UTM coordinates into geographic analyses.
Limitations of UTM Zones:
Regardless of its many benefits, the UTM system additionally has some limitations:
-
Zone Boundaries: Crossing UTM zone boundaries can complicate calculations and require coordinate transformations. Areas close to zone boundaries can expertise barely greater distortion than these nearer to the central meridian.
-
Polar Areas: The UTM system is just not used within the polar areas (above 84°N and beneath 80°S) on account of extreme distortion. The Common Polar Stereographic (UPS) coordinate system is utilized in these areas as an alternative.
-
A number of Zones in a Single Space: Bigger areas can span a number of UTM zones, requiring cautious consideration when performing spatial evaluation or creating maps.
-
Flat Earth Assumption: Whereas the UTM system minimizes distortion, it nonetheless depends on projecting a curved floor onto a flat aircraft. For very exact measurements over lengthy distances, the curvature of the Earth should be thought of.
Sensible Purposes of UTM Zones:
The UTM system is extensively utilized in a wide range of purposes, together with:
-
Mapping and Surveying: Surveyors and cartographers depend on UTM coordinates to precisely map and measure the Earth’s floor.
-
Navigation: GPS gadgets and different navigation techniques typically use UTM coordinates to offer exact location data.
-
Geographic Data Programs (GIS): GIS professionals use UTM coordinates to research spatial information, create maps, and carry out varied geographic analyses.
-
Army Purposes: The UTM system is extensively utilized by the navy for navigation, concentrating on, and different operational functions.
-
Useful resource Administration: Pure useful resource managers use UTM coordinates to trace and handle forests, water assets, and different pure assets.
-
City Planning: City planners use UTM coordinates to plan and handle city improvement, transportation networks, and infrastructure.
Reworking Between UTM Zones:
When working with information that spans a number of UTM zones, it is typically needed to remodel coordinates from one zone to a different. This course of includes changing the UTM coordinates to geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) after which projecting them into the specified UTM zone.
A number of software program instruments and on-line calculators can be found to carry out UTM coordinate transformations. It is essential to make use of dependable and correct transformation strategies to reduce errors.
Conclusion:
UTM map zones are a elementary part of the Common Transverse Mercator coordinate system, offering a globally constant and correct methodology for representing the Earth’s floor. By dividing the Earth into smaller zones, the UTM system minimizes distortion and permits for exact measurements of distance, space, and form. Whereas it has some limitations, the UTM system stays a extensively used and priceless instrument for mapping, surveying, navigation, and a variety of different purposes. Understanding the construction, goal, and limitations of UTM map zones is important for anybody working with geospatial information and searching for to precisely symbolize and analyze the world round us. As expertise continues to advance, the UTM system will possible stay a cornerstone of geospatial data administration for years to return.